Observing the Sun Description
... Light from the Sun enters the telescope, where it is focussed by lenses onto the viewing screen. The farther the eyepiece of the telescope is from the viewing screen, the larger the image will appear. However, increasing the magnification in this way also magnifies any motion. Thus it become more di ...
... Light from the Sun enters the telescope, where it is focussed by lenses onto the viewing screen. The farther the eyepiece of the telescope is from the viewing screen, the larger the image will appear. However, increasing the magnification in this way also magnifies any motion. Thus it become more di ...
8_StarGalaxiesUniversePP
... Star Clusters larger groupings stars belong to All stars in a cluster formed from the SAME nebula at about the SAME time and are about the SAME distance from Earth Open cluster loose, disorganized, only a few thousand stars Globular cluster large groupings of older stars ...
... Star Clusters larger groupings stars belong to All stars in a cluster formed from the SAME nebula at about the SAME time and are about the SAME distance from Earth Open cluster loose, disorganized, only a few thousand stars Globular cluster large groupings of older stars ...
Planet Finding
... It was more than 200 years ago—on June 6, 1761, to be precise—that a Russian scientist named Mikhail Lomonosov observed what looked like a black dot crossing the surface of the Sun. The dot was Venus, making a rare direct passage between the Sun and Earth, and Lomonosov noticed something odd about t ...
... It was more than 200 years ago—on June 6, 1761, to be precise—that a Russian scientist named Mikhail Lomonosov observed what looked like a black dot crossing the surface of the Sun. The dot was Venus, making a rare direct passage between the Sun and Earth, and Lomonosov noticed something odd about t ...
powerpoint version
... silicate dust seasoned with metals. Stir well. Hammer to a lumpy consistency. Stars will form and bake. In other words... Gas and dust cloud is compressed by shock wave from a supernova, gravity takes over so cloud condenses, getting hotter and smaller. Cloud becomes a T Tauri star, lowish mass, red ...
... silicate dust seasoned with metals. Stir well. Hammer to a lumpy consistency. Stars will form and bake. In other words... Gas and dust cloud is compressed by shock wave from a supernova, gravity takes over so cloud condenses, getting hotter and smaller. Cloud becomes a T Tauri star, lowish mass, red ...
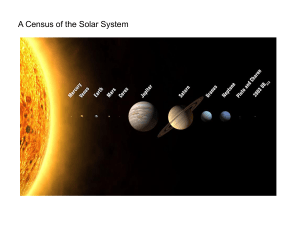
A Census of the Solar System
... The Kepler Mission Designed to constantly survey the same region of sky 105 sg deg ...
... The Kepler Mission Designed to constantly survey the same region of sky 105 sg deg ...
Early Observers (The Beginnings of Astronomy)
... The time it takes for a group of stars (constellation) to return to the same part of the sky at a certain time of day What we know: Time required for the Earth to revolve around the sun. ...
... The time it takes for a group of stars (constellation) to return to the same part of the sky at a certain time of day What we know: Time required for the Earth to revolve around the sun. ...
Galileo`s Telescope - YEAR 11 EBSS PHYSICS DETAILED STUDIES
... examined the optics of the system. The Galilean telescope works on the same principles, however, it uses a concave eyepiece, this results in an image that is upright, this is more important for terrestrial use, but not for astronomy. Though the magnification of a telescope is important, the ligh ...
... examined the optics of the system. The Galilean telescope works on the same principles, however, it uses a concave eyepiece, this results in an image that is upright, this is more important for terrestrial use, but not for astronomy. Though the magnification of a telescope is important, the ligh ...
Astronomy - AG Web Services
... b. What direction does the moon travel? c. What causes the moon to have different shapes, called phases? d. What causes the moon to “move” in the sky during the night? 9. Do ONE of the following: a. With a small telescope or binoculars, study the moon, stars, and planets on three different nights. K ...
... b. What direction does the moon travel? c. What causes the moon to have different shapes, called phases? d. What causes the moon to “move” in the sky during the night? 9. Do ONE of the following: a. With a small telescope or binoculars, study the moon, stars, and planets on three different nights. K ...
ASTR 1120H – Spring Semester 2010 Exam 1 – Answers The AU is
... 1. The angular size of the Moon as seen from the Earth is α = 1,867″ (about ½°). What was the angular size of the Earth as seen by the Apollo astronauts who walked on the Moon? (The Earth's diameter is 12,756 km. The Moon's diameter is 3,476 km.) ...
... 1. The angular size of the Moon as seen from the Earth is α = 1,867″ (about ½°). What was the angular size of the Earth as seen by the Apollo astronauts who walked on the Moon? (The Earth's diameter is 12,756 km. The Moon's diameter is 3,476 km.) ...
An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light
... People use telescopes and binoculars for activities such as observational astronomy, ornithology, pilotage and reconnaissance, and watching sports or performance arts. The basic scheme is that the primary light-gathering element focuses that light from the distant object to a focal plane where it fo ...
... People use telescopes and binoculars for activities such as observational astronomy, ornithology, pilotage and reconnaissance, and watching sports or performance arts. The basic scheme is that the primary light-gathering element focuses that light from the distant object to a focal plane where it fo ...
Introduction to Astronomy - Northumberland Astronomical Society
... We’ll also examine how our location on the Earth affects the stars and constellations we can see and how changes in the tilt of the Earth’s axis change the view over long time periods. ...
... We’ll also examine how our location on the Earth affects the stars and constellations we can see and how changes in the tilt of the Earth’s axis change the view over long time periods. ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Fall 2011
... compared to its brightness as seen from the Earth? The brightness is given by the flux you see. From slide 8 of Lecture 7, the flux goes as the luminosity over the distance squared. For the earth d = 1AU, while for Mercury d = 0.39AU. The sun’s luminosity is the same for both, so the flux at Mercury ...
... compared to its brightness as seen from the Earth? The brightness is given by the flux you see. From slide 8 of Lecture 7, the flux goes as the luminosity over the distance squared. For the earth d = 1AU, while for Mercury d = 0.39AU. The sun’s luminosity is the same for both, so the flux at Mercury ...
QUINN_2004 - Armagh Observatory
... During my 6 week placement at Armagh observatory, I was set the project of studying the change in magnitude of a variable star, KPD 1930+2752. KPD 1930+2752 is actually 2 stars, known as a binary system, it consists of 2 stars, one hot, bright sub-dwarf B star orbiting round a smaller, denser white ...
... During my 6 week placement at Armagh observatory, I was set the project of studying the change in magnitude of a variable star, KPD 1930+2752. KPD 1930+2752 is actually 2 stars, known as a binary system, it consists of 2 stars, one hot, bright sub-dwarf B star orbiting round a smaller, denser white ...
Chapter 1 - Humble ISD
... • Eclipses occur when Earth, Moon, and Sun form a ______________________ • Lunar eclipse: • Earth is between __________________________ • Partial when only part of Moon is in shadow • Total when it all is in shadow • Solar eclipse: Moon is between ________________________ • Partial when only part of ...
... • Eclipses occur when Earth, Moon, and Sun form a ______________________ • Lunar eclipse: • Earth is between __________________________ • Partial when only part of Moon is in shadow • Total when it all is in shadow • Solar eclipse: Moon is between ________________________ • Partial when only part of ...
Astronomy Unit Test Review Sheet
... 7. Compare and contrast apparent and absolute magnitude? Which is most useful to scientists? Apparent magnitude is the brightness a star appears from earth and absolute magnitude is the actual brightness if stars were all the same distance away. The absolute magnitude tells a scientist more about a ...
... 7. Compare and contrast apparent and absolute magnitude? Which is most useful to scientists? Apparent magnitude is the brightness a star appears from earth and absolute magnitude is the actual brightness if stars were all the same distance away. The absolute magnitude tells a scientist more about a ...
The coolest White Dwarf— older than the age of the universe?
... steadily loses its outer gasses and ends its life as a ball of compact degenerate electron gas or a White Dwarf (WD). It may begin this stage with a very high temperature, say 50,000 K and it steadily cools over time following a well-known cooling rate. Eventually this object will cool so much that ...
... steadily loses its outer gasses and ends its life as a ball of compact degenerate electron gas or a White Dwarf (WD). It may begin this stage with a very high temperature, say 50,000 K and it steadily cools over time following a well-known cooling rate. Eventually this object will cool so much that ...
File
... A collection of gas, stars and dust held together by gravity. About 125 billion galaxies are estimated to exist in the universe What galaxy do we live in? The Milky Way The number of galaxies in the universe According to the textbook, the number of sand grains that would fill a toothpaste cap repres ...
... A collection of gas, stars and dust held together by gravity. About 125 billion galaxies are estimated to exist in the universe What galaxy do we live in? The Milky Way The number of galaxies in the universe According to the textbook, the number of sand grains that would fill a toothpaste cap repres ...
Famous astronomers - sydney-13
... known for his Copernican theory. His theory started that the sun rest near the centre of the earth, which spin daily on its axis revolved around the sun. The process is now known as the heliocentric or suncentered system. ...
... known for his Copernican theory. His theory started that the sun rest near the centre of the earth, which spin daily on its axis revolved around the sun. The process is now known as the heliocentric or suncentered system. ...
AY 20 Fall 2010
... Example 2.2.1 Carroll and Ostlie: force exerted on a point mass by a spherically symmetric mass also F= GMm/r2 (all mass of larger body in effect concentrated at center) ...
... Example 2.2.1 Carroll and Ostlie: force exerted on a point mass by a spherically symmetric mass also F= GMm/r2 (all mass of larger body in effect concentrated at center) ...
Chapter 30 Notes
... Chapter 30 What is Astronomy? X-ray telescopes are designed to detect high-energy radiation (X-rays) from space. Xrays from space cannot penetrate our atmosphere, so X-ray telescopes must be placed on an object that leaves Earth’s atmosphere (like a satellite). An observatory is an observing sit ...
... Chapter 30 What is Astronomy? X-ray telescopes are designed to detect high-energy radiation (X-rays) from space. Xrays from space cannot penetrate our atmosphere, so X-ray telescopes must be placed on an object that leaves Earth’s atmosphere (like a satellite). An observatory is an observing sit ...
Chapter 28 Vocabulary
... Absolute Magnitude – The measure of how bright a star would be if it were located 10 parsecs from Earth. ...
... Absolute Magnitude – The measure of how bright a star would be if it were located 10 parsecs from Earth. ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.