ap chemistry 2005/2006
... 1-2 days of lab activity. Labs may exceed one 90 minute class, depending on the requirements of the specific lab activity. In addition, some sections/objectives are more conducive to lab activity than others and will have more lab activity. AP Chemistry Objectives: The AP Chemistry course is desig ...
... 1-2 days of lab activity. Labs may exceed one 90 minute class, depending on the requirements of the specific lab activity. In addition, some sections/objectives are more conducive to lab activity than others and will have more lab activity. AP Chemistry Objectives: The AP Chemistry course is desig ...
Lecture two
... covalent bonding by some common biological elements Hydrogen = valence 1; 1 electron needed; 1 covalent bond Oxygen = valence 2; 2 electrons needed; 2 covalent bonds Sulfur = valence 2; 2 electrons needed; 2, 4 or 6 covalent bonds Nitrogen = valence 3; 3 electrons needed; 3 or 4 covalent bonds Carbo ...
... covalent bonding by some common biological elements Hydrogen = valence 1; 1 electron needed; 1 covalent bond Oxygen = valence 2; 2 electrons needed; 2 covalent bonds Sulfur = valence 2; 2 electrons needed; 2, 4 or 6 covalent bonds Nitrogen = valence 3; 3 electrons needed; 3 or 4 covalent bonds Carbo ...
Document
... covalent bonding by some common biological elements Hydrogen = valence 1; 1 electron needed; 1 covalent bond Oxygen = valence 2; 2 electrons needed; 2 covalent bonds Sulfur = valence 2; 2 electrons needed; 2, 4 or 6 covalent bonds Nitrogen = valence 3; 3 electrons needed; 3 or 4 covalent bonds Carbo ...
... covalent bonding by some common biological elements Hydrogen = valence 1; 1 electron needed; 1 covalent bond Oxygen = valence 2; 2 electrons needed; 2 covalent bonds Sulfur = valence 2; 2 electrons needed; 2, 4 or 6 covalent bonds Nitrogen = valence 3; 3 electrons needed; 3 or 4 covalent bonds Carbo ...
CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
Chapter 4 - WordPress.com
... Types of Reactions • 4 different types of Reactions: – Combination: A + B AB – Decomposition: AB A + B – Single Replacement: A + BC AC + B ...
... Types of Reactions • 4 different types of Reactions: – Combination: A + B AB – Decomposition: AB A + B – Single Replacement: A + BC AC + B ...
Course Map_2011-2012 - Kenwood Academy High School
... increases. Understand how a hydraulic lift (such as the kind used to raise a car for repairs) confers mechanical advantage. 12.11.78 Understand the universal law of gravitation: that gravitation is a force that every mass exerts on every other mass. The strength of the gravitational attractive force ...
... increases. Understand how a hydraulic lift (such as the kind used to raise a car for repairs) confers mechanical advantage. 12.11.78 Understand the universal law of gravitation: that gravitation is a force that every mass exerts on every other mass. The strength of the gravitational attractive force ...
Double-Replacement Reactions - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • In double-replacement reactions, the ions of two compounds exchange places in an aqueous solution to form two new compounds. • One of the compounds formed is usually a precipitate, an insoluble gas that bubbles out of the solution, or a molecular compound, usually water. • The other compound is of ...
... • In double-replacement reactions, the ions of two compounds exchange places in an aqueous solution to form two new compounds. • One of the compounds formed is usually a precipitate, an insoluble gas that bubbles out of the solution, or a molecular compound, usually water. • The other compound is of ...
CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
effective nuclear charge
... good reducing agents, easy to oxidize very reactive, not found uncombined in nature react with nonmetals to form salts compounds generally soluble in water found in seawater ...
... good reducing agents, easy to oxidize very reactive, not found uncombined in nature react with nonmetals to form salts compounds generally soluble in water found in seawater ...
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CHEMISTRY (043) CLASS XII (2013-14)
... (b) Metals of very high purity can be obtained by this method. The impure metal rod is mounted horizontally and heated by a circular electric heater at one end in an atmosphere of inert gas to form a thin molten zone. By slowly moving the heater, the molten zone is moved from one end of the rod to t ...
... (b) Metals of very high purity can be obtained by this method. The impure metal rod is mounted horizontally and heated by a circular electric heater at one end in an atmosphere of inert gas to form a thin molten zone. By slowly moving the heater, the molten zone is moved from one end of the rod to t ...
SAT Practice Test 3
... Neutrons and protons are both located in the principal energy levels of the atom HCl is a proton donor Powdered zinc has a greater surface area NH3 is a polar substance Water boils when the vapor pressure of the water is equal to the atmospheric pressure In an exothermic reaction the products have l ...
... Neutrons and protons are both located in the principal energy levels of the atom HCl is a proton donor Powdered zinc has a greater surface area NH3 is a polar substance Water boils when the vapor pressure of the water is equal to the atmospheric pressure In an exothermic reaction the products have l ...
CHEMISTRY Academic Standards Statement
... substances or to understand how substances are formed and removed in the environment. Chemistry is the science of analysing, transforming or manipulating substances and the molecular interpretation of the world around us. It is at the molecular level that major advances are made in many diverse area ...
... substances or to understand how substances are formed and removed in the environment. Chemistry is the science of analysing, transforming or manipulating substances and the molecular interpretation of the world around us. It is at the molecular level that major advances are made in many diverse area ...
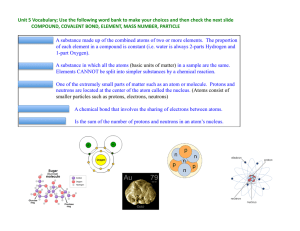
3 molecules
... Valence Electrons in Ionic Compounds • The A-group (representative) elements follow the OCTET RULE; they obtain an inert gas valence (outer) shell that contains 8 electrons • Metals - lose # electrons = group number e.g. Ca Ca2+ + 2e- (Ar outer shell) • Nonmetals - gain electrons = 8 - group # e. ...
... Valence Electrons in Ionic Compounds • The A-group (representative) elements follow the OCTET RULE; they obtain an inert gas valence (outer) shell that contains 8 electrons • Metals - lose # electrons = group number e.g. Ca Ca2+ + 2e- (Ar outer shell) • Nonmetals - gain electrons = 8 - group # e. ...
Review Unit 5
... 11) How many protons, neutrons, and electrons in the ion Mg+2 Atomic number = Protons = 12, Atomic Mass = 24; Neutrons = 12; Electrons must be 2 less than the protons. Electrons = 10 ...
... 11) How many protons, neutrons, and electrons in the ion Mg+2 Atomic number = Protons = 12, Atomic Mass = 24; Neutrons = 12; Electrons must be 2 less than the protons. Electrons = 10 ...
Bio 102 Lecture - chapter 2 The Chemical Basis of Life
... Chemical Bonding If 3 or less electrons in the outer most shell – ...
... Chemical Bonding If 3 or less electrons in the outer most shell – ...
Writing Chemical Equations - Mrs. Procee's Online Classroom
... At the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Translate chemical word equations into formula ...
... At the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Translate chemical word equations into formula ...
Final Exam Study Guide Page 1 Quiz
... c. 1.5 x 1025 moles d. none of the above 2. How many grams are in 6.2 moles of NH4? a. .34 g b. 111.8 g c. 6.2 g d. 11.6 g 3. One mole of CaCO3 is equal to how many molecules of CaCO3? a. 765 molecules b. 249 molecules c. 7.6 x 1024 molecules d. 6.02 x 1023 molecules 4. How many grams of sodium are ...
... c. 1.5 x 1025 moles d. none of the above 2. How many grams are in 6.2 moles of NH4? a. .34 g b. 111.8 g c. 6.2 g d. 11.6 g 3. One mole of CaCO3 is equal to how many molecules of CaCO3? a. 765 molecules b. 249 molecules c. 7.6 x 1024 molecules d. 6.02 x 1023 molecules 4. How many grams of sodium are ...
AQA C2 revision book
... Most of these catalysts are solid substances, used to catalyse reactions between gases. They do this by allowing the gas molecules to collect on their surface where they are close enough to react quickly. Catalysts are very valuable in chemical industry, since they can be reused and they provide a m ...
... Most of these catalysts are solid substances, used to catalyse reactions between gases. They do this by allowing the gas molecules to collect on their surface where they are close enough to react quickly. Catalysts are very valuable in chemical industry, since they can be reused and they provide a m ...
Document
... – No chemical bonding between components – Can be separated by physical means, such as straining or filtering – Heterogeneous or homogeneous ...
... – No chemical bonding between components – Can be separated by physical means, such as straining or filtering – Heterogeneous or homogeneous ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.