The Atomic Theory of Matter
... other properties. Atoms of one element are different from that of another element. • Atoms are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither changed nor destroyed during chemical reactions. ...
... other properties. Atoms of one element are different from that of another element. • Atoms are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither changed nor destroyed during chemical reactions. ...
Review Notes - Biochemistry
... The goal of all atoms is to have a _STABLE_ outer energy level. The goal leads to bonding of atoms. 2 types of bonding: 1. Ionic Bonding: When _1_ or more electrons are _TRANSFERRED_ from one atom to another. Ion: an atom with a_CHARGE_. When an electron is gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged ...
... The goal of all atoms is to have a _STABLE_ outer energy level. The goal leads to bonding of atoms. 2 types of bonding: 1. Ionic Bonding: When _1_ or more electrons are _TRANSFERRED_ from one atom to another. Ion: an atom with a_CHARGE_. When an electron is gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged ...
希臘 - 中正大學化生系
... first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of modern chemistry, and one of the pioneers of modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...
... first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of modern chemistry, and one of the pioneers of modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...
Chemical Bonds
... compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...
... compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...
File
... • Atomic Number-the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of a particular element. • Chemical Formula-an expression of the elements in a compound and their ratios in which the elements are denoted by their chemical ...
... • Atomic Number-the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of a particular element. • Chemical Formula-an expression of the elements in a compound and their ratios in which the elements are denoted by their chemical ...
Chemistry of Life
... Chemistry of Life – the SMALLEST particle that can exist and still be considered matter ...
... Chemistry of Life – the SMALLEST particle that can exist and still be considered matter ...
8.5C Vocabulary
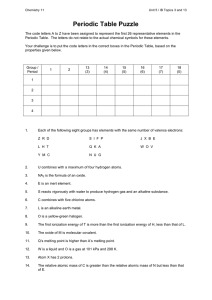
... The columns on a Periodic Table that arrange the elements by the number of electrons that are in the outermost shell (valence electrons) A specific area where electrons (e-) of the same energy level are found Either filled or partially filled last energy level of an atom that determine the chemical ...
... The columns on a Periodic Table that arrange the elements by the number of electrons that are in the outermost shell (valence electrons) A specific area where electrons (e-) of the same energy level are found Either filled or partially filled last energy level of an atom that determine the chemical ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Conservation of Mass- Mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. ...
... Conservation of Mass- Mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Conservation of Mass- Mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. ...
... Conservation of Mass- Mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. ...
Atomic History Notes.notebook
... Democritus - 460 - 370 BC Often credited with being the father of atomic theory. Proposed that matter was made up of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Democritus' theory was largely ignored in his time and wasn't revived until the early 1800's by John Dalton. ...
... Democritus - 460 - 370 BC Often credited with being the father of atomic theory. Proposed that matter was made up of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Democritus' theory was largely ignored in his time and wasn't revived until the early 1800's by John Dalton. ...
CHM 2045C - State College of Florida
... (5 Credit Hours) (A.A.) Three hours lecture, three hours laboratory per week. Prerequisites: Completion of MAC 1105. Completion of CHM 1025C with a grade of “C” or better or one year of high school college preparatory honors or AP chemistry within last three years. This course meets Area V for the A ...
... (5 Credit Hours) (A.A.) Three hours lecture, three hours laboratory per week. Prerequisites: Completion of MAC 1105. Completion of CHM 1025C with a grade of “C” or better or one year of high school college preparatory honors or AP chemistry within last three years. This course meets Area V for the A ...
Notes
... Key Questions: • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
... Key Questions: • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
history of the atom ppt student copy
... Atoms making up compounds can be separated, or combined ...
... Atoms making up compounds can be separated, or combined ...
atoms, molecules, and matter (2)
... 5. Ether = QUINTESSENCE (Latin) – substance whose natural motion is that most symmetrical and eternal of all conceivable motion = endless circles ...
... 5. Ether = QUINTESSENCE (Latin) – substance whose natural motion is that most symmetrical and eternal of all conceivable motion = endless circles ...
Chemical Change
... energy changes that take place when atoms lose, gain or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. ...
... energy changes that take place when atoms lose, gain or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. ...
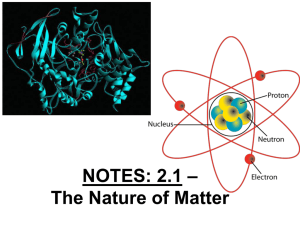
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... ● MATTER can be defined as anything that has mass and takes up space…this includes individual atoms!! ...
... ● MATTER can be defined as anything that has mass and takes up space…this includes individual atoms!! ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... John Dalton (in 1805) proposes his Atomic Theory to explain the results of the quantitative studies of several scientists (including Lavoisier, Proust, and himself, among many others). Dalton’s Atomic Theory a. Elements consist of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. b. All the atoms of a given ...
... John Dalton (in 1805) proposes his Atomic Theory to explain the results of the quantitative studies of several scientists (including Lavoisier, Proust, and himself, among many others). Dalton’s Atomic Theory a. Elements consist of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. b. All the atoms of a given ...
Chemistry Unit Study Guide Key
... 5) examples of physical changes – Breaking glass; melting ice; Cutting; Boiling 6) difference between physical and chemical changes – In a physical change, nothing new is formed. In a chemical change, a new substance is formed. 7) what it means if elements are in the same family/group – They have si ...
... 5) examples of physical changes – Breaking glass; melting ice; Cutting; Boiling 6) difference between physical and chemical changes – In a physical change, nothing new is formed. In a chemical change, a new substance is formed. 7) what it means if elements are in the same family/group – They have si ...
Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... combine to form materials. So chemistry puts more attention to atoms (and electrons in atoms) but not the nucleus. The change of atoms through the change of nucleus is not the center of chemistry. It belongs to Nuclear Science and Technology. ...
... combine to form materials. So chemistry puts more attention to atoms (and electrons in atoms) but not the nucleus. The change of atoms through the change of nucleus is not the center of chemistry. It belongs to Nuclear Science and Technology. ...
Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... combine to form materials. So chemistry puts more attention to atoms (and electrons in atoms) but not the nucleus. The change of atoms through the change of nucleus is not the center of chemistry. It belongs to Nuclear Science and Technology. ...
... combine to form materials. So chemistry puts more attention to atoms (and electrons in atoms) but not the nucleus. The change of atoms through the change of nucleus is not the center of chemistry. It belongs to Nuclear Science and Technology. ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.