Chemistry Content Standards
... e. Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds (i.e. ionic, covalent). f. Relate light emission and the movement of electrons to element identification. SC4. Students will use the organization of the Periodic Table to predict properties of elements. a. Use the Periodic Table to predict periodic tre ...
... e. Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds (i.e. ionic, covalent). f. Relate light emission and the movement of electrons to element identification. SC4. Students will use the organization of the Periodic Table to predict properties of elements. a. Use the Periodic Table to predict periodic tre ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONS
... Recall that an element consists of atoms which have the same number of protons, and therefore, the same Atomic Number. Chemical properties of elements depend on the atomic number of the element. A complete Periodic Table lists the elements, their symbols and atomic numbers as well as atomic masses. ...
... Recall that an element consists of atoms which have the same number of protons, and therefore, the same Atomic Number. Chemical properties of elements depend on the atomic number of the element. A complete Periodic Table lists the elements, their symbols and atomic numbers as well as atomic masses. ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... 1. __Condensation___ occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. 2. All matter is made up of tiny particles called __atoms___. 3. When a solid becomes a liquid, _melting_____ occurs. 4. An _element_____ is made up of only one type of atom. 5. __freezing___ changes a liquid into a solid. 6. A mixture is made ...
... 1. __Condensation___ occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. 2. All matter is made up of tiny particles called __atoms___. 3. When a solid becomes a liquid, _melting_____ occurs. 4. An _element_____ is made up of only one type of atom. 5. __freezing___ changes a liquid into a solid. 6. A mixture is made ...
Two valence electrons.
... elements by increasing atomic mass, leaving blank spaces where he was sure elements Dmitri yet to be discovered Mendeleev would fit. ...
... elements by increasing atomic mass, leaving blank spaces where he was sure elements Dmitri yet to be discovered Mendeleev would fit. ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry comes alive
... produces polar molecules Atoms with six or seven valence shell electrons are electronegative Atoms with one or two valence shell electrons are electropositive ...
... produces polar molecules Atoms with six or seven valence shell electrons are electronegative Atoms with one or two valence shell electrons are electropositive ...
Exam 3 Review
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
Solon City Schools
... • In the formula you put a dot and then write the number of molecules. • Calcium chloride dihydrate = CaCl22O • Chromium (III) nitrate hexahydrate = Cr(NO3)3 6H2O ...
... • In the formula you put a dot and then write the number of molecules. • Calcium chloride dihydrate = CaCl22O • Chromium (III) nitrate hexahydrate = Cr(NO3)3 6H2O ...
Chapter 2
... • In the formula you put a dot and then write the number of molecules. • Calcium chloride dihydrate = CaCl22O • Chromium (III) nitrate hexahydrate = Cr(NO3)3 6H2O ...
... • In the formula you put a dot and then write the number of molecules. • Calcium chloride dihydrate = CaCl22O • Chromium (III) nitrate hexahydrate = Cr(NO3)3 6H2O ...
Name - Madison County Schools
... Li – because it’s one valence electron is in energy level 2 which is close to the nucleus resulting in a much stronger magnetic pull on it than on the valence electrons of other members of the group which as in higher energy level. J. Define Electronegativity? Which element has the highest electrone ...
... Li – because it’s one valence electron is in energy level 2 which is close to the nucleus resulting in a much stronger magnetic pull on it than on the valence electrons of other members of the group which as in higher energy level. J. Define Electronegativity? Which element has the highest electrone ...
Notes - Organization of Matter
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
Honors Chemistry
... 2. Write the nuclear equation for the bombardment of uranium with beta particles (show equations for both positron and electron bombardment.) 3. Titanium-51 decays by negative emission with a half-life of 6 minutes. How much of a 48.0 gram sample would be left after one hour? 4. Compare and contra ...
... 2. Write the nuclear equation for the bombardment of uranium with beta particles (show equations for both positron and electron bombardment.) 3. Titanium-51 decays by negative emission with a half-life of 6 minutes. How much of a 48.0 gram sample would be left after one hour? 4. Compare and contra ...
GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS IN THE MYSTERY OF MATTER
... when they combine with water. They include lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium. Any of a group of metallic elements that includes beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium. A positively charged particle, indistinguishable from a helium atom nucleus and consi ...
... when they combine with water. They include lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium. Any of a group of metallic elements that includes beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium. A positively charged particle, indistinguishable from a helium atom nucleus and consi ...
Gateway Chemistry Review (Answer Key) Structure and Properties
... Two atoms contain the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes are atoms of the same element, but have different masses. Isotopes with an unstable nucleus will tend to breakdown or decay; these atoms are called radioactive and will release energy in the form of nuclea ...
... Two atoms contain the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes are atoms of the same element, but have different masses. Isotopes with an unstable nucleus will tend to breakdown or decay; these atoms are called radioactive and will release energy in the form of nuclea ...
2A Final Exam Review Worksheet
... A. If there is 10.0 g of P4O10, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. B. If there is also 10.0 g of perchloric acid, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. C. Considering A & B, how much of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete. D. Find the number of phosphorus atoms in 10. ...
... A. If there is 10.0 g of P4O10, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. B. If there is also 10.0 g of perchloric acid, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. C. Considering A & B, how much of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete. D. Find the number of phosphorus atoms in 10. ...
Nature of Atoms Atomic Structure
... • Chemical reactions involve the formation or breaking of chemical bonds • Atoms shift from one molecule to another without any change in number or identity of atoms • Reactants = original molecules • Products = molecules resulting from reaction ...
... • Chemical reactions involve the formation or breaking of chemical bonds • Atoms shift from one molecule to another without any change in number or identity of atoms • Reactants = original molecules • Products = molecules resulting from reaction ...
Stoichiometry 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10-24 g The amu mass of an atom
... Stoichiometry 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10-24 g The amu mass of an atom of carbon-12 is 12 amu 1 mole = count multiplier = 6.022 x 1023 items subscript to the right of an element symbol = atom count multiplier = the number of atoms of the element in a chemical formula number before chemical formula in a chem ...
... Stoichiometry 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10-24 g The amu mass of an atom of carbon-12 is 12 amu 1 mole = count multiplier = 6.022 x 1023 items subscript to the right of an element symbol = atom count multiplier = the number of atoms of the element in a chemical formula number before chemical formula in a chem ...
8th Grade: First Semester Final Review
... 29. do not form natural compounds 32. nonmetals in your body 30. nonmetal from group 14 33. semiconductors 31. reacts with a metal to form a salt Choose the letter of the term that matches it correctly. Not all terms are used. a. metallic bond e. polar molecule b. electron dot diagram f. ion c. ioni ...
... 29. do not form natural compounds 32. nonmetals in your body 30. nonmetal from group 14 33. semiconductors 31. reacts with a metal to form a salt Choose the letter of the term that matches it correctly. Not all terms are used. a. metallic bond e. polar molecule b. electron dot diagram f. ion c. ioni ...
Periodic Table
... All atoms of a given element are ____________ , having the same size, mass, and chemical properties. Atoms of a specific element are ____________ from other elements Atoms cannot be ____________ , ____________ , or ...
... All atoms of a given element are ____________ , having the same size, mass, and chemical properties. Atoms of a specific element are ____________ from other elements Atoms cannot be ____________ , ____________ , or ...
Year 11 Chemistry Balancing Equations
... 9. Sr 10. C 11. O 12. S 13. F 14. Cl 15. Br 16. I 17. He 18. Ne 19. Ar 20. Kr 21. Xe 22. F ...
... 9. Sr 10. C 11. O 12. S 13. F 14. Cl 15. Br 16. I 17. He 18. Ne 19. Ar 20. Kr 21. Xe 22. F ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
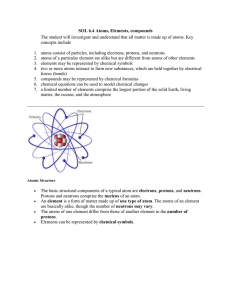
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
Name: Date: Period: Who is the Father of Atomic Theory? What
... 9. Why do elements in a group have similar chemical properties? 10. What can the number of valence electrons tell us about and element? 11. What is the most reactive group on the periodic table? The least? ...
... 9. Why do elements in a group have similar chemical properties? 10. What can the number of valence electrons tell us about and element? 11. What is the most reactive group on the periodic table? The least? ...
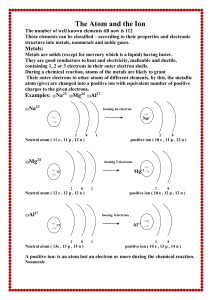
The Atom and the Ion
... atom (give) are changed into a positive ion with equivalent number of positive charges to the given electrons. ...
... atom (give) are changed into a positive ion with equivalent number of positive charges to the given electrons. ...
MID-TERM EXAM REVIEW! Unit 1 Convert the following: 1.) 2.02 x
... 34.) Write out the four quantum numbers for the last electron added to nickel and selenium. (Honors only) 35.) Draw the dot diagram for nickel and selenium. 36.) Identify the H.O.E.L. and # of valence electrons for nickel and selenium. Unit 5 * Define the following terms: 37.) Ionization energy 38.) ...
... 34.) Write out the four quantum numbers for the last electron added to nickel and selenium. (Honors only) 35.) Draw the dot diagram for nickel and selenium. 36.) Identify the H.O.E.L. and # of valence electrons for nickel and selenium. Unit 5 * Define the following terms: 37.) Ionization energy 38.) ...
Electronegativity

Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The term ""electronegativity"" was introduced by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1811,though the concept was known even before that and was studied by many chemists including Avogadro.In spite of its long history, an accurate scale of electronegativity had to wait till 1932, when Linus Pauling proposed an electronegativity scale, which depends on bond energies, as a development of valence bond theory. It has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties. Electronegativity cannot be directly measured and must be calculated from other atomic or molecular properties. Several methods of calculation have been proposed, and although there may be small differences in the numerical values of the electronegativity, all methods show the same periodic trends between elements. The most commonly used method of calculation is that originally proposed by Linus Pauling. This gives a dimensionless quantity, commonly referred to as the Pauling scale, on a relative scale running from around 0.7 to 3.98 (hydrogen = 2.20). When other methods of calculation are used, it is conventional (although not obligatory) to quote the results on a scale that covers the same range of numerical values: this is known as an electronegativity in Pauling units. As it is usually calculated, electronegativity is not a property of an atom alone, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule. Properties of a free atom include ionization energy and electron affinity. It is to be expected that the electronegativity of an element will vary with its chemical environment, but it is usually considered to be a transferable property, that is to say that similar values will be valid in a variety of situations.On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more ""pull"" it will have on electrons) and the number/location of other electrons present in the atomic shells (the more electrons an atom has, the farther from the nucleus the valence electrons will be, and as a result the less positive charge they will experience—both because of their increased distance from the nucleus, and because the other electrons in the lower energy core orbitals will act to shield the valence electrons from the positively charged nucleus).The opposite of electronegativity is electropositivity: a measure of an element's ability to donate electrons.Caesium is the least electronegative element in the periodic table (=0.79), while fluorine is most electronegative (=3.98). (Francium and caesium were originally assigned both assigned 0.7; caesium's value was later refined to 0.79, but no experimental data allows a similar refinement for francium. However, francium's ionization energy is known to be slightly higher than caesium's, in accordance with the relativistic stabilization of the 7s orbital, and this in turn implies that caesium is in fact more electronegative than francium.)