CHEM 1411 NAME: PRACTICE EXAM #3 (Chapters 6
... In which of the series of elements listed below would the elements have most nearly the same atomic radius? A) Sc, Ti, V, Cr B) Na, K, Rb, Cs C) B, Si, As, Te D) F, Cl, Br, I E) Na, Mg, Al, Si ...
... In which of the series of elements listed below would the elements have most nearly the same atomic radius? A) Sc, Ti, V, Cr B) Na, K, Rb, Cs C) B, Si, As, Te D) F, Cl, Br, I E) Na, Mg, Al, Si ...
Final Exam Review Answers
... • According to Hund’s rule, when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbit until • a. all the orbitals contain one electron, with spins parallel. • b. all the orbitals contain one electron, with opposite spins. • c. there are two electrons in each orbital. • d. electr ...
... • According to Hund’s rule, when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbit until • a. all the orbitals contain one electron, with spins parallel. • b. all the orbitals contain one electron, with opposite spins. • c. there are two electrons in each orbital. • d. electr ...
Quiz 1 - sample quiz
... The masses of protons and neutrons are approximately the same. Calcium commonly forms the Ca2+ and cation. If an atom gains electrons it becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. The xenon atom has 54 protons. Different isotopes of the same element have different chemical behaviour. ...
... The masses of protons and neutrons are approximately the same. Calcium commonly forms the Ca2+ and cation. If an atom gains electrons it becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. The xenon atom has 54 protons. Different isotopes of the same element have different chemical behaviour. ...
unit 2 - chemistry
... A. Basic definitions 1. matter – anything that occupies space and has mass 2. element – basic unit of all matter (109 total) a. 92 natural elements b. 4 basic – H, C, O, N, -96% of human mass Ca, P -> 99% (3%) K, S, Cl, Mg, I, FE, (16 other)1% -> ...
... A. Basic definitions 1. matter – anything that occupies space and has mass 2. element – basic unit of all matter (109 total) a. 92 natural elements b. 4 basic – H, C, O, N, -96% of human mass Ca, P -> 99% (3%) K, S, Cl, Mg, I, FE, (16 other)1% -> ...
Ch 8 Bonding and Molecular Structure 06-Nov
... down so the hydrogen-hydrogen angle is no longer 109.5o, but is 107.5o. Water is similar with the two lone pair pushing the two hydrogen back so their angle is 104.5o. Central atoms with more than 4 valence electron pair. When a central atom has 5 or 6 equivalent bonds, all angles are not equal. The ...
... down so the hydrogen-hydrogen angle is no longer 109.5o, but is 107.5o. Water is similar with the two lone pair pushing the two hydrogen back so their angle is 104.5o. Central atoms with more than 4 valence electron pair. When a central atom has 5 or 6 equivalent bonds, all angles are not equal. The ...
PIB and HH - Unit 4 - Chemical Names and Formulas
... Bonded atoms attain the stable electron configuration of a noble gas. The noble gases themselves exist as isolated atoms because that is their most stable condition. For the representative elements, the number of valence electrons is equal to the element’s group number in the periodic table. The tra ...
... Bonded atoms attain the stable electron configuration of a noble gas. The noble gases themselves exist as isolated atoms because that is their most stable condition. For the representative elements, the number of valence electrons is equal to the element’s group number in the periodic table. The tra ...
MIDTERM EXAM – JANUARY, 2003
... 73. Describe how ionization energy changes as you move across the periodic table. 74. Describe how electronegativity changes as you move across the periodic table. 75. The transition metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy t ...
... 73. Describe how ionization energy changes as you move across the periodic table. 74. Describe how electronegativity changes as you move across the periodic table. 75. The transition metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy t ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... react with other forms of matter. For example, some substances are flammable. If they are heated with oxygen, they will react and burst into flames. The ability of a substance to combine with oxygen is an example of chemical property. ...
... react with other forms of matter. For example, some substances are flammable. If they are heated with oxygen, they will react and burst into flames. The ability of a substance to combine with oxygen is an example of chemical property. ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... react with other forms of matter. For example, some substances are flammable. If they are heated with oxygen, they will react and burst into flames. The ability of a substance to combine with oxygen is an example of chemical property. ...
... react with other forms of matter. For example, some substances are flammable. If they are heated with oxygen, they will react and burst into flames. The ability of a substance to combine with oxygen is an example of chemical property. ...
Lecture 24 (Slides) October 18
... • 1. Which of the following atoms and ions are paramagnetic (i.e. have unpaired electrons). Note: An even number of electrons does not indicate that all electrons are paired. (a) He atom, (b) F atom, (c) As atom, (d) F- ion (e) Al3+ ion and (f) Fe atom. • 2. Arrange the following in order of increas ...
... • 1. Which of the following atoms and ions are paramagnetic (i.e. have unpaired electrons). Note: An even number of electrons does not indicate that all electrons are paired. (a) He atom, (b) F atom, (c) As atom, (d) F- ion (e) Al3+ ion and (f) Fe atom. • 2. Arrange the following in order of increas ...
08_lecture_ppt - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Electronic Quantum Numbers in Atoms 1. Principle quantum number, n – Energy level – Average distance from nucleus ...
... Electronic Quantum Numbers in Atoms 1. Principle quantum number, n – Energy level – Average distance from nucleus ...
An element`s properties depend on the structure of its atoms
... A. An element is composed of atoms; a molecule is not. B. An element is composed of only one kind of atom; molecules can be composed of more than one kind of atom. C. Elements always have lower atomic weights than molecules. D. Elements exist in nature only as parts of molecules. ...
... A. An element is composed of atoms; a molecule is not. B. An element is composed of only one kind of atom; molecules can be composed of more than one kind of atom. C. Elements always have lower atomic weights than molecules. D. Elements exist in nature only as parts of molecules. ...
Bonding Web Practice Trupia - Trupia
... Bromine is the only liquid nonmetallic element at room temperature. It is a heavy, mobile, reddish-brown liquid, volatilizing readily at room temperature to a red vapor with a strong disagreeable odor, resembling chlorine, and having a very irritating effect on the eyes and throat; it is readily sol ...
... Bromine is the only liquid nonmetallic element at room temperature. It is a heavy, mobile, reddish-brown liquid, volatilizing readily at room temperature to a red vapor with a strong disagreeable odor, resembling chlorine, and having a very irritating effect on the eyes and throat; it is readily sol ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Atomic Theory
... Multivalent: some transition metals have more than one charge. Roman numerals are used after the metal name to indicate which ion was used Ex. 1 What is the formula manganese(III) sulphide? This manganese is Mn3+ Sulphur is S2– Lowest common multiple of 3 and 2 is 6 2 Mn3+ ions and 3 S2– i ...
... Multivalent: some transition metals have more than one charge. Roman numerals are used after the metal name to indicate which ion was used Ex. 1 What is the formula manganese(III) sulphide? This manganese is Mn3+ Sulphur is S2– Lowest common multiple of 3 and 2 is 6 2 Mn3+ ions and 3 S2– i ...
Atoms in Combination: The Chemical Bond
... electron to chlorine, which is one electron shy of the “magic” number 18. The result is the ionic compound sodium chloride—ordinary table salt. In these diagrams, electrons are represented as dots in shells around a nucleus. ...
... electron to chlorine, which is one electron shy of the “magic” number 18. The result is the ionic compound sodium chloride—ordinary table salt. In these diagrams, electrons are represented as dots in shells around a nucleus. ...
Atomic Theory - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
Chemistry Major Understandings
... 4.1c Energy released or absorbed during a chemical reaction can be represented by a potential energy diagram. 4.1d Energy released or absorbed during a chemical reaction (heat of reaction) is equal to the difference between the potential energy of the products and potential energy of the reactants. ...
... 4.1c Energy released or absorbed during a chemical reaction can be represented by a potential energy diagram. 4.1d Energy released or absorbed during a chemical reaction (heat of reaction) is equal to the difference between the potential energy of the products and potential energy of the reactants. ...
Test Objectives: Unit 1 – Measurement
... Determine the percent water in a hydrate, given the formula of the hydrate Determine the number of atoms of each element in a formula when the formula is preceded by a coefficient Recognize that subscripts & coefficients in chemical formulas can refer to atom ratios or mole ratios, depending on the ...
... Determine the percent water in a hydrate, given the formula of the hydrate Determine the number of atoms of each element in a formula when the formula is preceded by a coefficient Recognize that subscripts & coefficients in chemical formulas can refer to atom ratios or mole ratios, depending on the ...
form revision a
... Check your key area statements. If not green you need to do more work! Knowledge of the structure of the periodic table, groups and periods. All matter is made of atoms. When a substance contains only one kind of atom it is known as an element. Atoms contain protons, neutrons and electrons each with ...
... Check your key area statements. If not green you need to do more work! Knowledge of the structure of the periodic table, groups and periods. All matter is made of atoms. When a substance contains only one kind of atom it is known as an element. Atoms contain protons, neutrons and electrons each with ...
NM Strand
... 50. A student spills a chemical in the laboratory. What should he do first? 51. A sour candy has a pH of: 52. A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the sample’s composition is 53. An experiment that determines the maximum number of grams of a substance that will dissolve ...
... 50. A student spills a chemical in the laboratory. What should he do first? 51. A sour candy has a pH of: 52. A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the sample’s composition is 53. An experiment that determines the maximum number of grams of a substance that will dissolve ...
Atomic Structure Study Guide
... Definite _____________, and the Law of __________ Proportions. The Law of Conservation of Mass states that the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products of any chemical reaction – mass is ___________ in all chemical reactions. The Law of __________ Proportions states tha ...
... Definite _____________, and the Law of __________ Proportions. The Law of Conservation of Mass states that the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products of any chemical reaction – mass is ___________ in all chemical reactions. The Law of __________ Proportions states tha ...
bonding notes for votech
... Ca1Cl2 ---- CaCl2 Sodium Oxide Na+1 O-2 -> Na1 O2 Na2O1 -> Na2O ...
... Ca1Cl2 ---- CaCl2 Sodium Oxide Na+1 O-2 -> Na1 O2 Na2O1 -> Na2O ...
File
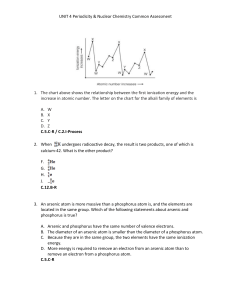
... UNIT 4 Periodicity & Nuclear Chemistry Common Assessment 16. In the figure below, what type of nuclear activity is represented? ...
... UNIT 4 Periodicity & Nuclear Chemistry Common Assessment 16. In the figure below, what type of nuclear activity is represented? ...
2.1 Atoms and Bonds
... Lewis structures show the number of valence electrons in an atom Procedure: 1. Write the atomic symbol 2. Determine the number of valence electrons 3. Place the valence electrons (dots) around all 4 sides of the atomic symbol – not pairing up until necessary! ...
... Lewis structures show the number of valence electrons in an atom Procedure: 1. Write the atomic symbol 2. Determine the number of valence electrons 3. Place the valence electrons (dots) around all 4 sides of the atomic symbol – not pairing up until necessary! ...
Atomic number
... Element: a substance made of only one kind of atom, cannot be chemically or physically separated into other substances. ...
... Element: a substance made of only one kind of atom, cannot be chemically or physically separated into other substances. ...
Electronegativity

Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The term ""electronegativity"" was introduced by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1811,though the concept was known even before that and was studied by many chemists including Avogadro.In spite of its long history, an accurate scale of electronegativity had to wait till 1932, when Linus Pauling proposed an electronegativity scale, which depends on bond energies, as a development of valence bond theory. It has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties. Electronegativity cannot be directly measured and must be calculated from other atomic or molecular properties. Several methods of calculation have been proposed, and although there may be small differences in the numerical values of the electronegativity, all methods show the same periodic trends between elements. The most commonly used method of calculation is that originally proposed by Linus Pauling. This gives a dimensionless quantity, commonly referred to as the Pauling scale, on a relative scale running from around 0.7 to 3.98 (hydrogen = 2.20). When other methods of calculation are used, it is conventional (although not obligatory) to quote the results on a scale that covers the same range of numerical values: this is known as an electronegativity in Pauling units. As it is usually calculated, electronegativity is not a property of an atom alone, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule. Properties of a free atom include ionization energy and electron affinity. It is to be expected that the electronegativity of an element will vary with its chemical environment, but it is usually considered to be a transferable property, that is to say that similar values will be valid in a variety of situations.On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more ""pull"" it will have on electrons) and the number/location of other electrons present in the atomic shells (the more electrons an atom has, the farther from the nucleus the valence electrons will be, and as a result the less positive charge they will experience—both because of their increased distance from the nucleus, and because the other electrons in the lower energy core orbitals will act to shield the valence electrons from the positively charged nucleus).The opposite of electronegativity is electropositivity: a measure of an element's ability to donate electrons.Caesium is the least electronegative element in the periodic table (=0.79), while fluorine is most electronegative (=3.98). (Francium and caesium were originally assigned both assigned 0.7; caesium's value was later refined to 0.79, but no experimental data allows a similar refinement for francium. However, francium's ionization energy is known to be slightly higher than caesium's, in accordance with the relativistic stabilization of the 7s orbital, and this in turn implies that caesium is in fact more electronegative than francium.)