Unit - III - E
... Steric attraction occurs when molecules have shapes or geometries that are optimized for interaction with one another. In these cases molecules will react with each other most often in specific arrangements. Chain crossing — A random coil can't change from one conformation to a closely related shap ...
... Steric attraction occurs when molecules have shapes or geometries that are optimized for interaction with one another. In these cases molecules will react with each other most often in specific arrangements. Chain crossing — A random coil can't change from one conformation to a closely related shap ...
Unit 2 Spiraling
... 8.. Dalton’s atomic theory was not correct in every detail. Should this be taken as criticism of Dalton as a scientist? Explain. 9. What was inadequate about Rutherford’s model of the atom? 10. What did Bohr assume about the motions of electrons? Subscripts in a chemical formula represent the relati ...
... 8.. Dalton’s atomic theory was not correct in every detail. Should this be taken as criticism of Dalton as a scientist? Explain. 9. What was inadequate about Rutherford’s model of the atom? 10. What did Bohr assume about the motions of electrons? Subscripts in a chemical formula represent the relati ...
1st mid unit test formative (pre-test)
... Is a substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by chemical means. Iron, oxygen and neon are examples. ...
... Is a substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by chemical means. Iron, oxygen and neon are examples. ...
1st mid unit test formative (pre-test)
... Is a substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by chemical means. Iron, oxygen and neon are examples. ...
... Is a substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by chemical means. Iron, oxygen and neon are examples. ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
name
... CHAPTER 5 CHARACTERISTICS OF ELEMENTS Use a periodic table of the elements to help you answer the following questions. 1. a) ...
... CHAPTER 5 CHARACTERISTICS OF ELEMENTS Use a periodic table of the elements to help you answer the following questions. 1. a) ...
Standards Practice
... Read each question, and choose the best answer. Then, on your answer sheet, mark the answer choice that you think is best. •Students that atoms combine to form . molecules know by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging electrons to form ionic bonds. 1. Potassium (K) an ...
... Read each question, and choose the best answer. Then, on your answer sheet, mark the answer choice that you think is best. •Students that atoms combine to form . molecules know by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging electrons to form ionic bonds. 1. Potassium (K) an ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... with its charge? (1) A neutron has a negative charge. (2) A proton has a negative charge. (3) A neutron has no charge. (4) A proton has no charge. ...
... with its charge? (1) A neutron has a negative charge. (2) A proton has a negative charge. (3) A neutron has no charge. (4) A proton has no charge. ...
Chapters 1-4 Numbers and Measurements in Chemistry Units SI
... • Each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms. • The atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms of different elements are different in some fundamental way or ways. • Chemical compounds are formed when atoms combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative num ...
... • Each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms. • The atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms of different elements are different in some fundamental way or ways. • Chemical compounds are formed when atoms combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative num ...
Writing formulas and naming ionic bonds
... What type of nuclear reaction occurs in the sun? Fusion What type of nuclear reaction produces electricity? Fission When a chemical reaction occurs, the mass of the reactants ___ the mass of the products. Equals If the mass of the reactants is 10 g, then the mass of the products is ___ g. ...
... What type of nuclear reaction occurs in the sun? Fusion What type of nuclear reaction produces electricity? Fission When a chemical reaction occurs, the mass of the reactants ___ the mass of the products. Equals If the mass of the reactants is 10 g, then the mass of the products is ___ g. ...
Final Exam - W09
... A civil engineer wants to reduce odors at a wastewater treatment plant by adding hydrogen peroxide to the sewage. The hydrogen peroxide is delivered as 50% by mass solution, but for maintenance and safety issues, the H2O2 is diluted to a 3% by mass solution. If the engineer needs 20.0 gallons of the ...
... A civil engineer wants to reduce odors at a wastewater treatment plant by adding hydrogen peroxide to the sewage. The hydrogen peroxide is delivered as 50% by mass solution, but for maintenance and safety issues, the H2O2 is diluted to a 3% by mass solution. If the engineer needs 20.0 gallons of the ...
29.2 Chemical Bonds
... benzene have six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms shaped in a ring. An atom can make one chemical bond for each valence electron. Bonds can also involve two or more valence electrons. ...
... benzene have six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms shaped in a ring. An atom can make one chemical bond for each valence electron. Bonds can also involve two or more valence electrons. ...
Document
... benzene have six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms shaped in a ring. An atom can make one chemical bond for each valence electron. Bonds can also involve two or more valence electrons. ...
... benzene have six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms shaped in a ring. An atom can make one chemical bond for each valence electron. Bonds can also involve two or more valence electrons. ...
History and Current Status of the Plastics Industry
... Polymer chains with atoms other than carbon – Usually polymer chains with C and N, O, S, F, and Cl • PVC has Cl; Nylon has O and N; Polyurethane has O and N • PET has O and benzene ring; PC has O and benzene ring ...
... Polymer chains with atoms other than carbon – Usually polymer chains with C and N, O, S, F, and Cl • PVC has Cl; Nylon has O and N; Polyurethane has O and N • PET has O and benzene ring; PC has O and benzene ring ...
Chemical Bonding Quiz
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
Chemistry Readings
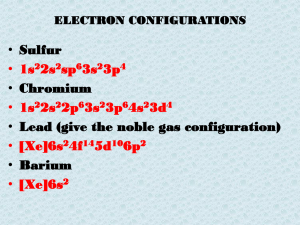
... is 32. An atom that has a full outer shell will be stable. Being stable means the atom will not react with other atoms. The Noble Gases in the right hand column of the Periodic Table are stable because they have full outer shells. The two inner shells of an atom must be full before the outer shells ...
... is 32. An atom that has a full outer shell will be stable. Being stable means the atom will not react with other atoms. The Noble Gases in the right hand column of the Periodic Table are stable because they have full outer shells. The two inner shells of an atom must be full before the outer shells ...
chemisty_ass_2
... electrons by inner electrons overcomes the influence on the increasing nuclear charge, thus the outer electron is shielded from the nucleus by the repelling effect of the inner electrons. Across the group, the reverse is the case; the increasing nuclear charge has greater effect. In general, the scr ...
... electrons by inner electrons overcomes the influence on the increasing nuclear charge, thus the outer electron is shielded from the nucleus by the repelling effect of the inner electrons. Across the group, the reverse is the case; the increasing nuclear charge has greater effect. In general, the scr ...
File
... A. The number of protons equals the number of electrons. B. The number of protons equals the number of neutrons. C. The number of neutrons equals the number of electrons. D. The number of neutrons is greater than the number of protons. 5. Consider the spectrum for the hydrogen atom. In which situati ...
... A. The number of protons equals the number of electrons. B. The number of protons equals the number of neutrons. C. The number of neutrons equals the number of electrons. D. The number of neutrons is greater than the number of protons. 5. Consider the spectrum for the hydrogen atom. In which situati ...
chem final review
... B) Cs, 55 protons, 132.9 electrons C) Zn, 30 protons, 60 electrons D) He, 4 protons, 4 electrons E) F, 19 protons, 19 electrons 31) Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass number of 20 is 25% abundant; the isotope ...
... B) Cs, 55 protons, 132.9 electrons C) Zn, 30 protons, 60 electrons D) He, 4 protons, 4 electrons E) F, 19 protons, 19 electrons 31) Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass number of 20 is 25% abundant; the isotope ...
Matter and Energy
... Properties of Matter Practice 1. Describe each of the following properties as physical or chemical: a. neon is a color gas at room temperature b. apple slices turn brown when exposed to air c. phosphorus will ignite when exposed to air d. at room temperature, mercury is a liquid e. propane gas is c ...
... Properties of Matter Practice 1. Describe each of the following properties as physical or chemical: a. neon is a color gas at room temperature b. apple slices turn brown when exposed to air c. phosphorus will ignite when exposed to air d. at room temperature, mercury is a liquid e. propane gas is c ...
Honors Chemistry Exam Review Questions
... carbon dioxide and water a single product an element and a compound two ionic compounds ...
... carbon dioxide and water a single product an element and a compound two ionic compounds ...
Preview Sample 1
... D) are always some form of carbohydrate. E) are naturally similar to sugars. 102) Alaska Natives have a lower incidence of heart disease even though their diets are high in fat and cholesterol. This may be due to the large amount of ________ in their diets. A) steroids B) omega-3 fatty acids C) trig ...
... D) are always some form of carbohydrate. E) are naturally similar to sugars. 102) Alaska Natives have a lower incidence of heart disease even though their diets are high in fat and cholesterol. This may be due to the large amount of ________ in their diets. A) steroids B) omega-3 fatty acids C) trig ...
Atomic Concepts
... 17. Noble gases- (fat and happy) stable valence configurations; tend to not bond 18. Hydrogen bonding- H and FON; strong; high melting/boiling points; low vapor pressure 19. Dipole forces- (polar molecules) weak; low melting points, high vapor pressure; soluble in water, conduct as aqueous 20. Nonpo ...
... 17. Noble gases- (fat and happy) stable valence configurations; tend to not bond 18. Hydrogen bonding- H and FON; strong; high melting/boiling points; low vapor pressure 19. Dipole forces- (polar molecules) weak; low melting points, high vapor pressure; soluble in water, conduct as aqueous 20. Nonpo ...
Chemistry Notes
... Example of Bonds Let's look at Sodium Hydroxide (Na-OH)... You can see that on the left is the Sodium part and the right has the Oxygen/Hydrogen part. The bond which binds the Hydrogen to the Oxygen is covalent. The Sodium is bonded to the HYDROXIDE part of the compound with an ionic bond. This is a ...
... Example of Bonds Let's look at Sodium Hydroxide (Na-OH)... You can see that on the left is the Sodium part and the right has the Oxygen/Hydrogen part. The bond which binds the Hydrogen to the Oxygen is covalent. The Sodium is bonded to the HYDROXIDE part of the compound with an ionic bond. This is a ...
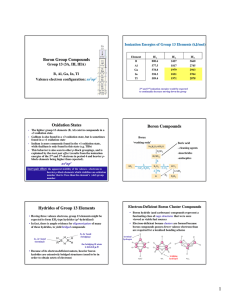
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... +3 oxidation state. Gallium is also found in a +3 oxidation state, but is sometimes found in a +1 oxidation state Indium is more commonly found in the +1 oxidation state, while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by ...
... +3 oxidation state. Gallium is also found in a +3 oxidation state, but is sometimes found in a +1 oxidation state Indium is more commonly found in the +1 oxidation state, while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by ...
Electronegativity

Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The term ""electronegativity"" was introduced by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1811,though the concept was known even before that and was studied by many chemists including Avogadro.In spite of its long history, an accurate scale of electronegativity had to wait till 1932, when Linus Pauling proposed an electronegativity scale, which depends on bond energies, as a development of valence bond theory. It has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties. Electronegativity cannot be directly measured and must be calculated from other atomic or molecular properties. Several methods of calculation have been proposed, and although there may be small differences in the numerical values of the electronegativity, all methods show the same periodic trends between elements. The most commonly used method of calculation is that originally proposed by Linus Pauling. This gives a dimensionless quantity, commonly referred to as the Pauling scale, on a relative scale running from around 0.7 to 3.98 (hydrogen = 2.20). When other methods of calculation are used, it is conventional (although not obligatory) to quote the results on a scale that covers the same range of numerical values: this is known as an electronegativity in Pauling units. As it is usually calculated, electronegativity is not a property of an atom alone, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule. Properties of a free atom include ionization energy and electron affinity. It is to be expected that the electronegativity of an element will vary with its chemical environment, but it is usually considered to be a transferable property, that is to say that similar values will be valid in a variety of situations.On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more ""pull"" it will have on electrons) and the number/location of other electrons present in the atomic shells (the more electrons an atom has, the farther from the nucleus the valence electrons will be, and as a result the less positive charge they will experience—both because of their increased distance from the nucleus, and because the other electrons in the lower energy core orbitals will act to shield the valence electrons from the positively charged nucleus).The opposite of electronegativity is electropositivity: a measure of an element's ability to donate electrons.Caesium is the least electronegative element in the periodic table (=0.79), while fluorine is most electronegative (=3.98). (Francium and caesium were originally assigned both assigned 0.7; caesium's value was later refined to 0.79, but no experimental data allows a similar refinement for francium. However, francium's ionization energy is known to be slightly higher than caesium's, in accordance with the relativistic stabilization of the 7s orbital, and this in turn implies that caesium is in fact more electronegative than francium.)