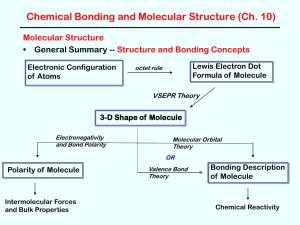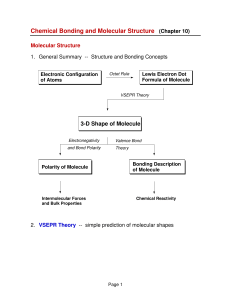
3-D Shape of Molecule
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
Chemistry - StudyTime NZ
... From this informa>on, we can tell that Magnesium has three electron shells, the last of which contains 2 electrons. We can assume that the first two electron shells are full with 2 electrons and 8 ...
... From this informa>on, we can tell that Magnesium has three electron shells, the last of which contains 2 electrons. We can assume that the first two electron shells are full with 2 electrons and 8 ...
Biology\Ch 2 Chemistry
... When combining substances, we can use a chemical equation to show what atoms, etc. are present and how many of each. The chemicals we are adding together are called the “reactants.” The result of the combination is called the “product.” Ex: 2 Na + Cl2 2 NaCl *Note: an arrow is used instead of an ...
... When combining substances, we can use a chemical equation to show what atoms, etc. are present and how many of each. The chemicals we are adding together are called the “reactants.” The result of the combination is called the “product.” Ex: 2 Na + Cl2 2 NaCl *Note: an arrow is used instead of an ...
Question Paper
... PART-A Answer any NINE questions. (Answer each question in one word or in one sentence) 9 x 1 =9 ...
... PART-A Answer any NINE questions. (Answer each question in one word or in one sentence) 9 x 1 =9 ...
transition metals
... 11.) Does the Qc for the formation of 1 mole of NO from its elements differ from the Qc of the decomposition of 1 mole of NO into its elements? Explain and give the relationship between the two Qc values. 12.) Balance the reaction and write the Qc a. ________NaHCO3 (s) ________Na2CO3 (s) + _______ ...
... 11.) Does the Qc for the formation of 1 mole of NO from its elements differ from the Qc of the decomposition of 1 mole of NO into its elements? Explain and give the relationship between the two Qc values. 12.) Balance the reaction and write the Qc a. ________NaHCO3 (s) ________Na2CO3 (s) + _______ ...
Unit 2 - Biochemistry Notes
... Molecule – when two or more atoms bond. CO2 , O2 , H2 and H2O are all molecules. Compound – when different elements combine. CO2 and H2O are molecules, but they are also compounds because they are molecules containing more than one element. ...
... Molecule – when two or more atoms bond. CO2 , O2 , H2 and H2O are all molecules. Compound – when different elements combine. CO2 and H2O are molecules, but they are also compounds because they are molecules containing more than one element. ...
1 - kurtniedenzu
... c. are emitted by the nucleus as beta particles d. move to higher energy levels 2. Compared with an atom of C-12, an atom of C-14 has a. More protons b. Fewer protons c. More neutrons d. Fewer neutrons 3. How many electrons are present in the electron-dot diagram of an atom with atomic number 9? a. ...
... c. are emitted by the nucleus as beta particles d. move to higher energy levels 2. Compared with an atom of C-12, an atom of C-14 has a. More protons b. Fewer protons c. More neutrons d. Fewer neutrons 3. How many electrons are present in the electron-dot diagram of an atom with atomic number 9? a. ...
7R CHEMISTRY 1 REVIEW
... 3. Protons are the sub-atomic particles that have a _______________ charge and are situated in the nucleus of the atom. 4. Neutrons are the sub-atomic particles that are ______________ and are situated in the nucleus of the atom. 5. Electrons have a _______________ charge and are situated outside of ...
... 3. Protons are the sub-atomic particles that have a _______________ charge and are situated in the nucleus of the atom. 4. Neutrons are the sub-atomic particles that are ______________ and are situated in the nucleus of the atom. 5. Electrons have a _______________ charge and are situated outside of ...
First Semester complete review with answers
... 33. How do you determine an element’s oxidation number? Use potassium and nitrogen as examples. Oxidation number is determined y how many electrons an atom takes or gives to become an ion. K oxidation number is +1. Potassium (K) is in group 1 and has 1 valence electron. K gives up that 1 electron be ...
... 33. How do you determine an element’s oxidation number? Use potassium and nitrogen as examples. Oxidation number is determined y how many electrons an atom takes or gives to become an ion. K oxidation number is +1. Potassium (K) is in group 1 and has 1 valence electron. K gives up that 1 electron be ...
AP Semester I Review: Free Response Questions
... water to produce 100. mL of solution. A 20.0 mL portion of the solution was titrated with KMnO4 (aq). The balanced equation for the reaction that occurred is as follows: 16 H+ (aq) + 2 MnO4- (aq) + 5 C2O42- (aq) 2 Mn2+ (aq) + 10 CO2 (g) + 8 H2O (l) The volume of 0.0150 M KMnO4 (aq) required to rea ...
... water to produce 100. mL of solution. A 20.0 mL portion of the solution was titrated with KMnO4 (aq). The balanced equation for the reaction that occurred is as follows: 16 H+ (aq) + 2 MnO4- (aq) + 5 C2O42- (aq) 2 Mn2+ (aq) + 10 CO2 (g) + 8 H2O (l) The volume of 0.0150 M KMnO4 (aq) required to rea ...
Chem BIG REVIEW - Jones-wiki
... When the atoms in a bond are the same, the electrons are shared equally. This results in a nonpolar covalent bond. Diatomic elements (Br2, I2 N2, Cl2, H2, O2 and F2) have pure nonpolar covalent bonds. Nonpolar molecules are symmetrical because there are no unshared electrons around the central atom. ...
... When the atoms in a bond are the same, the electrons are shared equally. This results in a nonpolar covalent bond. Diatomic elements (Br2, I2 N2, Cl2, H2, O2 and F2) have pure nonpolar covalent bonds. Nonpolar molecules are symmetrical because there are no unshared electrons around the central atom. ...
PAP Chemistry - Fall Final Review
... 6. What did Rutherford discover from the Gold Foil Experiment – p.72 The nucleus and that the atom was mostly empty space 7. When is a bright-line spectrum produced by an atom? IE – How does an atom give off color (especially when burned)? The resting state or the ground state is when the electron i ...
... 6. What did Rutherford discover from the Gold Foil Experiment – p.72 The nucleus and that the atom was mostly empty space 7. When is a bright-line spectrum produced by an atom? IE – How does an atom give off color (especially when burned)? The resting state or the ground state is when the electron i ...
IPC – First Semester Exam Review Be able to classify an example
... Potassium (K) is in group 1 and has 1 valence electron. K gives up that 1 electron because it is easier to give up 1 electron than to gain 7 electrons to get a full outer shell. When K gives up the electron, it has one more positive proton than negative electron. Potassium starts with 19 positive pr ...
... Potassium (K) is in group 1 and has 1 valence electron. K gives up that 1 electron because it is easier to give up 1 electron than to gain 7 electrons to get a full outer shell. When K gives up the electron, it has one more positive proton than negative electron. Potassium starts with 19 positive pr ...
File - Mr. Walsh`s AP Chemistry
... o Ionic compounds are soluble in water if the sum of all of their attractions to the water molecules is greater than their attraction to each other. A good rule of thumb (though there are exceptions) is that almost all compounds with alkali metal and halogen ions are soluble. Most (but not all) comp ...
... o Ionic compounds are soluble in water if the sum of all of their attractions to the water molecules is greater than their attraction to each other. A good rule of thumb (though there are exceptions) is that almost all compounds with alkali metal and halogen ions are soluble. Most (but not all) comp ...
Chapter1011
... • Write the MO diagram for HCl. Predict the bond order and sketch the bonding and antibonding MO’s. [note: H 1s energy = -13 eV, Cl 3s energy = -25 eV, Cl 3p energy = -14 ...
... • Write the MO diagram for HCl. Predict the bond order and sketch the bonding and antibonding MO’s. [note: H 1s energy = -13 eV, Cl 3s energy = -25 eV, Cl 3p energy = -14 ...
Ionic Bonding - petersonORHS
... • Valence- refers to the outer electrons in an atom. These are the electrons on the outer shell, which is the highest energy level. ...
... • Valence- refers to the outer electrons in an atom. These are the electrons on the outer shell, which is the highest energy level. ...
2 - grade11chemistry
... 1. Determine the number of valence electrons of the element. Recall: The number of valence electrons (outermost electrons) of an element is equal to its group number. 2. Draw the symbol of the element. The symbol of the element is used to represent the core (protons and neutrons) and the inner elect ...
... 1. Determine the number of valence electrons of the element. Recall: The number of valence electrons (outermost electrons) of an element is equal to its group number. 2. Draw the symbol of the element. The symbol of the element is used to represent the core (protons and neutrons) and the inner elect ...
Chapter 2 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry This chapter deals with
... 2. in chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed 3. atoms of each element have unique properties - all atoms of a given atom are identical and have identical masses and other properties 4. chemical reactions involve the uniting or the separation of atoms of different elements Dalton ...
... 2. in chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed 3. atoms of each element have unique properties - all atoms of a given atom are identical and have identical masses and other properties 4. chemical reactions involve the uniting or the separation of atoms of different elements Dalton ...
Science-M2-Basic-Che..
... It may be useful to draw a carbon atom and one other atom to illustrate the difference between elements. You can use the carbon atom to show its atomic number and mass and then elicit the atomic number and mass of the other atom. Finally, draw an isotope of carbon (perhaps carbon 14) and one of the ...
... It may be useful to draw a carbon atom and one other atom to illustrate the difference between elements. You can use the carbon atom to show its atomic number and mass and then elicit the atomic number and mass of the other atom. Finally, draw an isotope of carbon (perhaps carbon 14) and one of the ...
File
... atomic emission spectra; Bohr model of the hydrogen atom including explanation of H line spectrum and orbits, electron cloud and the probability model, wave/particle duality of electrons revisited, relate electron configurations of atoms to the Bohr and electron cloud models, describe the concepts o ...
... atomic emission spectra; Bohr model of the hydrogen atom including explanation of H line spectrum and orbits, electron cloud and the probability model, wave/particle duality of electrons revisited, relate electron configurations of atoms to the Bohr and electron cloud models, describe the concepts o ...
Presentation
... that can be broken down by chemical methods When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. Made of molecules- two or more atoms ...
... that can be broken down by chemical methods When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. Made of molecules- two or more atoms ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... c. The atom that gained an electron (called reduction), is now negatively charged and is called an anion. Think “Angry people are negative.” Remember the Law of Conservation of Matter? Matter is neither created, nor destroyed; just transferred or transformed. Well the electrons have been transferr ...
... c. The atom that gained an electron (called reduction), is now negatively charged and is called an anion. Think “Angry people are negative.” Remember the Law of Conservation of Matter? Matter is neither created, nor destroyed; just transferred or transformed. Well the electrons have been transferr ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... 72) The hydrogen bonding that occurs in water is responsible for all of the following, except A) the low freezing point of water. B) the ability of water to dissolve nonpolar substances. C) the surface tension of water. D) the high boiling point of water. E) the ability of water to dissolve inorgan ...
... 72) The hydrogen bonding that occurs in water is responsible for all of the following, except A) the low freezing point of water. B) the ability of water to dissolve nonpolar substances. C) the surface tension of water. D) the high boiling point of water. E) the ability of water to dissolve inorgan ...
Grade 11 Chemistry Exam Review
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
Electronegativity

Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The term ""electronegativity"" was introduced by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1811,though the concept was known even before that and was studied by many chemists including Avogadro.In spite of its long history, an accurate scale of electronegativity had to wait till 1932, when Linus Pauling proposed an electronegativity scale, which depends on bond energies, as a development of valence bond theory. It has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties. Electronegativity cannot be directly measured and must be calculated from other atomic or molecular properties. Several methods of calculation have been proposed, and although there may be small differences in the numerical values of the electronegativity, all methods show the same periodic trends between elements. The most commonly used method of calculation is that originally proposed by Linus Pauling. This gives a dimensionless quantity, commonly referred to as the Pauling scale, on a relative scale running from around 0.7 to 3.98 (hydrogen = 2.20). When other methods of calculation are used, it is conventional (although not obligatory) to quote the results on a scale that covers the same range of numerical values: this is known as an electronegativity in Pauling units. As it is usually calculated, electronegativity is not a property of an atom alone, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule. Properties of a free atom include ionization energy and electron affinity. It is to be expected that the electronegativity of an element will vary with its chemical environment, but it is usually considered to be a transferable property, that is to say that similar values will be valid in a variety of situations.On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more ""pull"" it will have on electrons) and the number/location of other electrons present in the atomic shells (the more electrons an atom has, the farther from the nucleus the valence electrons will be, and as a result the less positive charge they will experience—both because of their increased distance from the nucleus, and because the other electrons in the lower energy core orbitals will act to shield the valence electrons from the positively charged nucleus).The opposite of electronegativity is electropositivity: a measure of an element's ability to donate electrons.Caesium is the least electronegative element in the periodic table (=0.79), while fluorine is most electronegative (=3.98). (Francium and caesium were originally assigned both assigned 0.7; caesium's value was later refined to 0.79, but no experimental data allows a similar refinement for francium. However, francium's ionization energy is known to be slightly higher than caesium's, in accordance with the relativistic stabilization of the 7s orbital, and this in turn implies that caesium is in fact more electronegative than francium.)