CHEM 1405 Practice Exam 3 (2015)
... 5) Hydrogen has an electronegativity value of 2.1. Given the electronegativity of N, O, and P (3.0, 3.5, and 2.1, respectively), predict which of the following has nonpolar bonds. ...
... 5) Hydrogen has an electronegativity value of 2.1. Given the electronegativity of N, O, and P (3.0, 3.5, and 2.1, respectively), predict which of the following has nonpolar bonds. ...
AP Chemistry Summer Study Guide
... Dipole-Dipole: Permanent IMF present in polar molecules Direct Relationship: Relationship between two variables where when one changes, the other changes in the same manner Dissociate: To break into ions Dissolve: To break into smaller pieces Distillation: Process of separating liquids based on diff ...
... Dipole-Dipole: Permanent IMF present in polar molecules Direct Relationship: Relationship between two variables where when one changes, the other changes in the same manner Dissociate: To break into ions Dissolve: To break into smaller pieces Distillation: Process of separating liquids based on diff ...
Periodic table Periodic Trends
... Electronegativity (χ) is defined as the relative attraction that an atom has for the shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond. Linus Pauling proposed concept of electronegativity and defined it as “the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself.” The Pauling Scale (χp) is found ...
... Electronegativity (χ) is defined as the relative attraction that an atom has for the shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond. Linus Pauling proposed concept of electronegativity and defined it as “the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself.” The Pauling Scale (χp) is found ...
Answers to Final Exam Review
... Sodium because they are in the same group; elements in the same group have similar properties 28. Which pair of elements is both brittle and not able to conduct heat? a. Bromine and silver c. Iron and bromine d. Silver and iron b. Iodine and neon 29. An atom of which element has the weakest attracti ...
... Sodium because they are in the same group; elements in the same group have similar properties 28. Which pair of elements is both brittle and not able to conduct heat? a. Bromine and silver c. Iron and bromine d. Silver and iron b. Iodine and neon 29. An atom of which element has the weakest attracti ...
Chemistry -- Oxidation
... compounds is +2. The oxidation number of F is -1 in all its compounds. 5. The oxidation number of H is +1 in most compounds. Exceptions are H2 (where H = 0) and the ionic hydrides, such as NaH (where H = ...
... compounds is +2. The oxidation number of F is -1 in all its compounds. 5. The oxidation number of H is +1 in most compounds. Exceptions are H2 (where H = 0) and the ionic hydrides, such as NaH (where H = ...
Question, hints, and answers. Look at hints if you need help. Look at
... between N and H. But the N "wants" the electrons more than the H does, so it pulls them closer to itself. You end up with a little more than half the negative charge from the bond on the N, and a little less than half on the H. That means N has a partial negative charge and H has a partial positive ...
... between N and H. But the N "wants" the electrons more than the H does, so it pulls them closer to itself. You end up with a little more than half the negative charge from the bond on the N, and a little less than half on the H. That means N has a partial negative charge and H has a partial positive ...
Lesson 1 - Working With Chemicals
... When one orbit is filled the remaining electrons go to the next orbit – you cannot exceed the maximum allowed. We can draw the Bohr diagram for any element. It must have a nucleus showing the number of protons and neutrons and circles outside the nucleus showing the number of electrons. Reminder: # ...
... When one orbit is filled the remaining electrons go to the next orbit – you cannot exceed the maximum allowed. We can draw the Bohr diagram for any element. It must have a nucleus showing the number of protons and neutrons and circles outside the nucleus showing the number of electrons. Reminder: # ...
The Periodic table and subatomic particles
... Periodic table and its organization, subatomic particles, Bohr-Rutherford diagrams, ions, counting atoms, chemical reactions, names an formulas, balancing chemical equations, law of conservation of mass, reaction types, words and chemical equations, acids and bases, process of scientific inquiry, sa ...
... Periodic table and its organization, subatomic particles, Bohr-Rutherford diagrams, ions, counting atoms, chemical reactions, names an formulas, balancing chemical equations, law of conservation of mass, reaction types, words and chemical equations, acids and bases, process of scientific inquiry, sa ...
CHAPTER 1 -Chemistry -Matter -Elements -Atoms
... (d) I(e) Cl4) For which of the following pairs are the atoms most likely to form an ionic compound? (a) Carbon and Oxygen (b) Calcium and Chlorine (c) Chlorine and Oxygen (d) Sodium and Magnesium (e) Chlorine and Neon 5) The discovery of the electron came from: (a) The gold foil experiment (b) Dalto ...
... (d) I(e) Cl4) For which of the following pairs are the atoms most likely to form an ionic compound? (a) Carbon and Oxygen (b) Calcium and Chlorine (c) Chlorine and Oxygen (d) Sodium and Magnesium (e) Chlorine and Neon 5) The discovery of the electron came from: (a) The gold foil experiment (b) Dalto ...
Ch3 notes - Midway ISD
... Same compound always same ratio of elements Water is always 2 H and 1 O ...
... Same compound always same ratio of elements Water is always 2 H and 1 O ...
Carbon-12 Stable
... Compounds are made of chemically bound elements, but their properties can be different than the properties of the elements that make them. dangerous elements can make harmless compounds and vice versa ...
... Compounds are made of chemically bound elements, but their properties can be different than the properties of the elements that make them. dangerous elements can make harmless compounds and vice versa ...
2.5 THE NAMES AND FORMULAS OF COMPOUNDS
... compounds are weaker in comparison — adding a relatively small amount of heat will cause a solid molecular compound to change state from a solid to a liquid, and then to a gas. (b) Ionic compounds (many of which dissolve readily in water) form solutions that conduct electricity. Because the ionic bo ...
... compounds are weaker in comparison — adding a relatively small amount of heat will cause a solid molecular compound to change state from a solid to a liquid, and then to a gas. (b) Ionic compounds (many of which dissolve readily in water) form solutions that conduct electricity. Because the ionic bo ...
Haley CHM2045 Final Review
... 2. Place the following in order of decreasing electron affinity. Na, F, Cl, Ge, N 3. Place the the same elements in order of increasing metallic character. 4. Use the periodic table to identify the element of each electron configuration 1. [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p6 2. [Kr] 5s2 5. Choose the larger atom of e ...
... 2. Place the following in order of decreasing electron affinity. Na, F, Cl, Ge, N 3. Place the the same elements in order of increasing metallic character. 4. Use the periodic table to identify the element of each electron configuration 1. [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p6 2. [Kr] 5s2 5. Choose the larger atom of e ...
PSI AP Chemistry Name Unit 4: Chemical Bonding MC Review Part
... (A) regions of electron density on an atom will organize themselves so as to maximize s-character (B) regions of electron density in the valence shell of an atom will arrange themselves so as to maximize overlap (C) atomic orbitals of the bonding atoms must overlap for a bond to form (D) electron pa ...
... (A) regions of electron density on an atom will organize themselves so as to maximize s-character (B) regions of electron density in the valence shell of an atom will arrange themselves so as to maximize overlap (C) atomic orbitals of the bonding atoms must overlap for a bond to form (D) electron pa ...
Chapter 2 Expanded Notes
... The Atomic Number: This is more important for chemistry. Note as mentioned earlier that atoms are classified into elements based on certain characteristics, which we call identity, and they retain this identity through chemical reactions. Atoms of one element are different from atoms of another ele ...
... The Atomic Number: This is more important for chemistry. Note as mentioned earlier that atoms are classified into elements based on certain characteristics, which we call identity, and they retain this identity through chemical reactions. Atoms of one element are different from atoms of another ele ...
FirstSemesterReviewHonors
... 4. How many unpaired electrons are in a sulfur atom (atomic number 16)? 5. Be able to do the electron configuration for a given atom. 6. According to the aufbau principle, how many electrons may occupy an orbital? Chapter 6 1. Who arranged the elements according to atomic mass, and used the arrangem ...
... 4. How many unpaired electrons are in a sulfur atom (atomic number 16)? 5. Be able to do the electron configuration for a given atom. 6. According to the aufbau principle, how many electrons may occupy an orbital? Chapter 6 1. Who arranged the elements according to atomic mass, and used the arrangem ...
Prior knowledge catch-up student sheet for Chapter 3 Quantitative
... Number of neutrons = mass number − atomic number For example, the atomic number of sodium is 11 and the mass number is 23. Number of protons = 11 Number of electrons = 11 Number of neutrons = 23 − 11 = 12 Chemical reactions can be represented using a formula to show reactants and products in a chemi ...
... Number of neutrons = mass number − atomic number For example, the atomic number of sodium is 11 and the mass number is 23. Number of protons = 11 Number of electrons = 11 Number of neutrons = 23 − 11 = 12 Chemical reactions can be represented using a formula to show reactants and products in a chemi ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of Matter
... – (a) atoms can slide past each other without breaking their bonds ...
... – (a) atoms can slide past each other without breaking their bonds ...
Atoms and Molecules
... Elements in the same family have the same valence e-config, and thus similar properties When moving down a group the distance (# of energy levels) between the nucleus and the valence e’s increases causing the attraction between them to decrease, so atomic radius increases down a group while the ...
... Elements in the same family have the same valence e-config, and thus similar properties When moving down a group the distance (# of energy levels) between the nucleus and the valence e’s increases causing the attraction between them to decrease, so atomic radius increases down a group while the ...
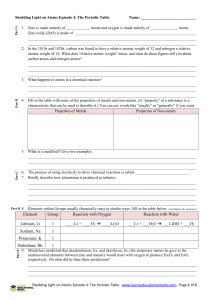
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... 1. Zinc is made entirely of ____________ atoms and oxygen is made entirely of ______________ atoms. Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ...
... 1. Zinc is made entirely of ____________ atoms and oxygen is made entirely of ______________ atoms. Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ...
File
... • Atoms gain and lose electrons to form bonds. When atoms become electrically charged particles, they are called ions. Metals lose electrons and become positive ions (called cations). Some metals (multivalent) lose electrons in different ways. For example, iron, Fe, loses either two (Fe2+) o ...
... • Atoms gain and lose electrons to form bonds. When atoms become electrically charged particles, they are called ions. Metals lose electrons and become positive ions (called cations). Some metals (multivalent) lose electrons in different ways. For example, iron, Fe, loses either two (Fe2+) o ...
Elements (NonMetals)
... Lowest density of any chemical substance Used in blimps in 1930s but flammable Gas at room Temp B.P. –253°C (20K) and M.P.-259°C (14K) Insoluble in water: 2mL gas/ 1L of water Found in H2O, organic and biological molecules Most common element in universe H2 (H-H) isoelectronic with He H has a small ...
... Lowest density of any chemical substance Used in blimps in 1930s but flammable Gas at room Temp B.P. –253°C (20K) and M.P.-259°C (14K) Insoluble in water: 2mL gas/ 1L of water Found in H2O, organic and biological molecules Most common element in universe H2 (H-H) isoelectronic with He H has a small ...
CHEMISTRY: MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW SPRING 2013 Multiple
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
HighFour Chemistry Round 1 Category C: Grades 9 – 10 Thursday
... Reviewing the data provided, it is clear that iodine gas (I2) has the largest molecular weight, and consequently, has the greatest strength of van der Waals’ forces. It would need a higher energy to break apart these forces. This translates into a higher boiling point. In conclusion, iodine gas (I2) ...
... Reviewing the data provided, it is clear that iodine gas (I2) has the largest molecular weight, and consequently, has the greatest strength of van der Waals’ forces. It would need a higher energy to break apart these forces. This translates into a higher boiling point. In conclusion, iodine gas (I2) ...
Dec. 15 , 2012, 9:00 am – noon - Dr. K. Brown
... d. Answer multiple choice questions in Section A by circling a response on this paper AND by filling in the corresponding response on the blue opscan sheet USING ONLY A SOFT-LEAD PENCIL. No deductions will be made for incorrect answer. Multiple answers will be treated as NO answer; if you change you ...
... d. Answer multiple choice questions in Section A by circling a response on this paper AND by filling in the corresponding response on the blue opscan sheet USING ONLY A SOFT-LEAD PENCIL. No deductions will be made for incorrect answer. Multiple answers will be treated as NO answer; if you change you ...
Electronegativity

Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The term ""electronegativity"" was introduced by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1811,though the concept was known even before that and was studied by many chemists including Avogadro.In spite of its long history, an accurate scale of electronegativity had to wait till 1932, when Linus Pauling proposed an electronegativity scale, which depends on bond energies, as a development of valence bond theory. It has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties. Electronegativity cannot be directly measured and must be calculated from other atomic or molecular properties. Several methods of calculation have been proposed, and although there may be small differences in the numerical values of the electronegativity, all methods show the same periodic trends between elements. The most commonly used method of calculation is that originally proposed by Linus Pauling. This gives a dimensionless quantity, commonly referred to as the Pauling scale, on a relative scale running from around 0.7 to 3.98 (hydrogen = 2.20). When other methods of calculation are used, it is conventional (although not obligatory) to quote the results on a scale that covers the same range of numerical values: this is known as an electronegativity in Pauling units. As it is usually calculated, electronegativity is not a property of an atom alone, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule. Properties of a free atom include ionization energy and electron affinity. It is to be expected that the electronegativity of an element will vary with its chemical environment, but it is usually considered to be a transferable property, that is to say that similar values will be valid in a variety of situations.On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more ""pull"" it will have on electrons) and the number/location of other electrons present in the atomic shells (the more electrons an atom has, the farther from the nucleus the valence electrons will be, and as a result the less positive charge they will experience—both because of their increased distance from the nucleus, and because the other electrons in the lower energy core orbitals will act to shield the valence electrons from the positively charged nucleus).The opposite of electronegativity is electropositivity: a measure of an element's ability to donate electrons.Caesium is the least electronegative element in the periodic table (=0.79), while fluorine is most electronegative (=3.98). (Francium and caesium were originally assigned both assigned 0.7; caesium's value was later refined to 0.79, but no experimental data allows a similar refinement for francium. However, francium's ionization energy is known to be slightly higher than caesium's, in accordance with the relativistic stabilization of the 7s orbital, and this in turn implies that caesium is in fact more electronegative than francium.)