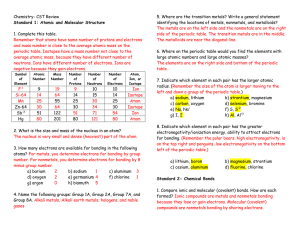
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on the food label are if they are not elements? ...
... • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on the food label are if they are not elements? ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... (a)The nitrate ion (NO3-1) bears one negative charge, so the copper ion must have two positive charges. Copper (II) nitrate. (b)The cation is K+ and the anion is PO4-3 (phosphate). Because potassium only forms one type of ion (K+), there is no need to use potassium (I) in the name. The compound is p ...
... (a)The nitrate ion (NO3-1) bears one negative charge, so the copper ion must have two positive charges. Copper (II) nitrate. (b)The cation is K+ and the anion is PO4-3 (phosphate). Because potassium only forms one type of ion (K+), there is no need to use potassium (I) in the name. The compound is p ...
Chapter 2 - Molecules of Life (Biochemistry) Periodic Table of
... • Electrons not shared equally! • One atom “hogs” the electrons! • This leads to the formation of hydrogen bonds.! ...
... • Electrons not shared equally! • One atom “hogs” the electrons! • This leads to the formation of hydrogen bonds.! ...
2002 local exam - Virginia Section
... 59. Which of the following statements are correct? I In a family of elements, the largest atom has the highest electronegativity II In the third row of elements the halogen element has the highest electronegativity III For all elements its second ionization energy is greater than its first ionizatio ...
... 59. Which of the following statements are correct? I In a family of elements, the largest atom has the highest electronegativity II In the third row of elements the halogen element has the highest electronegativity III For all elements its second ionization energy is greater than its first ionizatio ...
Oxidation Numbers and Ionic Compounds
... Remember… Constructing Dot Diagrams for the polyatomic ions is the same as constructing Dot Diagrams for molecules, except the difference in charge (+ or -) must be accounted for. STEPS: 1. Count the total number of valence e-. 2. Determine the central atom. The following are guides: Often the uni ...
... Remember… Constructing Dot Diagrams for the polyatomic ions is the same as constructing Dot Diagrams for molecules, except the difference in charge (+ or -) must be accounted for. STEPS: 1. Count the total number of valence e-. 2. Determine the central atom. The following are guides: Often the uni ...
Describe properties of particles and thermochemical - Mr
... There are three major trends in the periodic table that you will need to explain. They are atomic and ionic radii, ionisation energy, and electronegativity. When attempting to explain these trends you will need to consider the relative size of the electrostatic attraction between the protons in the ...
... There are three major trends in the periodic table that you will need to explain. They are atomic and ionic radii, ionisation energy, and electronegativity. When attempting to explain these trends you will need to consider the relative size of the electrostatic attraction between the protons in the ...
The s-Block Elements - GCG-42
... BeCl2 is essentially covalent, with comparatively low m.pt. The lower members in group II form essentially ionic chlorides, with Mg having intermediate properties. ...
... BeCl2 is essentially covalent, with comparatively low m.pt. The lower members in group II form essentially ionic chlorides, with Mg having intermediate properties. ...
Chemistry for BIOS 302
... which means that they have the same number of electrons (- charge) as protons (+ charge). Electrons circle the nucleus at defined positions called shells. The innermost shell of every atom holds 2 electrons. The next two shells hold up to 8 electrons. The first three shells thus hold 2 + 8 + 8 = 18 ...
... which means that they have the same number of electrons (- charge) as protons (+ charge). Electrons circle the nucleus at defined positions called shells. The innermost shell of every atom holds 2 electrons. The next two shells hold up to 8 electrons. The first three shells thus hold 2 + 8 + 8 = 18 ...
Introduction to Chemical Bonding
... Ions and Ionic Bonding The bond of Sodium and Fluorine is an example of Ionic bonding: electrons have been transferred in order for the atoms to have a full outer level. When an atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes what is called an ion. An ion is no longer neutrally charged because it has diff ...
... Ions and Ionic Bonding The bond of Sodium and Fluorine is an example of Ionic bonding: electrons have been transferred in order for the atoms to have a full outer level. When an atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes what is called an ion. An ion is no longer neutrally charged because it has diff ...
Unit 1 Notes
... 2) Compounds – substances that contain atoms of more than one element combined in a definite, fixed proportion. Compounds are represented by chemical formulas that contain two or more different symbols. e.g. Water’s chemical formula is H2O – (2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom make 1 water molecul ...
... 2) Compounds – substances that contain atoms of more than one element combined in a definite, fixed proportion. Compounds are represented by chemical formulas that contain two or more different symbols. e.g. Water’s chemical formula is H2O – (2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom make 1 water molecul ...
Problem
... (a) Depict the electron configuration of manganese, Mn, and its 4+ cation, Mn4+, using noble gas configuration and orbital diagrams. (b) Determine the magnetic properties of MnO2. Will this substance be more or less magnetic than solid manganese Mn (s) ...
... (a) Depict the electron configuration of manganese, Mn, and its 4+ cation, Mn4+, using noble gas configuration and orbital diagrams. (b) Determine the magnetic properties of MnO2. Will this substance be more or less magnetic than solid manganese Mn (s) ...
Chapter 3 - WebAssign
... other valence electrons. Thus, in going from one atom to the next in a period, Z increases by one as one proton is added, but σ increases by less than one because the additional valence electron does not shield with its full charge. Therefore, as shown in Figure 3.2, the effective nuclear charge exp ...
... other valence electrons. Thus, in going from one atom to the next in a period, Z increases by one as one proton is added, but σ increases by less than one because the additional valence electron does not shield with its full charge. Therefore, as shown in Figure 3.2, the effective nuclear charge exp ...
star test review
... (a) low ionization energy and low electronegativity (b) low ionization energy and high electronegativity (c) high ionization energy and low electronegativity (d) high ionization energy and high electronegativity ...
... (a) low ionization energy and low electronegativity (b) low ionization energy and high electronegativity (c) high ionization energy and low electronegativity (d) high ionization energy and high electronegativity ...
Chapter 10. Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry and
... Describe the bonding in CH4 molecule. experimental fact -- CH4 is tetrahedral (H-C-H angle = 109.5°) VSEPR theory "explains" this with 4 e- pairs, ∴ tetrahedral however, if only s and p orbitals are used, the angles ought to be 90° since the p orbitals are mutually perpendicular! ...
... Describe the bonding in CH4 molecule. experimental fact -- CH4 is tetrahedral (H-C-H angle = 109.5°) VSEPR theory "explains" this with 4 e- pairs, ∴ tetrahedral however, if only s and p orbitals are used, the angles ought to be 90° since the p orbitals are mutually perpendicular! ...
Chemistry at Karlsruhe 1860
... • Prof. Justus Liebig and his group developed methods to analyze organic chemical • Like the Berzelians they dealt only with empirical data and equivalent weights • Organic Compounds generally are made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen • Organic compounds when combusted in air form water, and carbon ...
... • Prof. Justus Liebig and his group developed methods to analyze organic chemical • Like the Berzelians they dealt only with empirical data and equivalent weights • Organic Compounds generally are made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen • Organic compounds when combusted in air form water, and carbon ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... (E) 84 Which element contains 3 half-filled orbitals? 37. (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 38. Which element has the highest electronegativity? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 39. Which element is a metalloid? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 40. Which element does not form compounds? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) ...
... (E) 84 Which element contains 3 half-filled orbitals? 37. (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 38. Which element has the highest electronegativity? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 39. Which element is a metalloid? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 40. Which element does not form compounds? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) ...
Dalton Model Reading
... Law of Definite Proportions Near the end of the 18th century, two laws about chemical reactions emerged without referring to the notion of an atomic theory. The first was the law of conservation of mass, formulated by Antoine Lavoisier in 1789, which states that the total mass in a chemical reactio ...
... Law of Definite Proportions Near the end of the 18th century, two laws about chemical reactions emerged without referring to the notion of an atomic theory. The first was the law of conservation of mass, formulated by Antoine Lavoisier in 1789, which states that the total mass in a chemical reactio ...
Chemistry- CST Review
... Standard 4 – Gases and their Properties 1. What causes gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory? Gas pressure is caused by the random motion of the gas molecules. 2. If someone sprays perfume at the front of the room, will the people in the back of the room eventually be able to smell it? Why? Expla ...
... Standard 4 – Gases and their Properties 1. What causes gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory? Gas pressure is caused by the random motion of the gas molecules. 2. If someone sprays perfume at the front of the room, will the people in the back of the room eventually be able to smell it? Why? Expla ...
Chapter Two:
... combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. ...
... combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. ...
Chemistry in Biology
... • Compounds are pure substances formed when two or more different elements combine. -Ex: H20, CO2, and C6H12O6 • Compounds are always formed from a specific combination of elements in a fixed ratio. • Compounds cannot be broken down into simpler compounds or elements by physical means. -can be broke ...
... • Compounds are pure substances formed when two or more different elements combine. -Ex: H20, CO2, and C6H12O6 • Compounds are always formed from a specific combination of elements in a fixed ratio. • Compounds cannot be broken down into simpler compounds or elements by physical means. -can be broke ...
specimen
... The student had added the exact amount of calcium required to react with the hydrochloric acid used. After carrying out the experiment, the student accidentally added some more calcium. The student was surprised that the extra calcium still reacted. Explain this observation. Include an equation in y ...
... The student had added the exact amount of calcium required to react with the hydrochloric acid used. After carrying out the experiment, the student accidentally added some more calcium. The student was surprised that the extra calcium still reacted. Explain this observation. Include an equation in y ...
2007 - SolPass
... relationship between the concentration of alcohol dissolved in water and its density. The relationship was expected to be linear. Which of the data points most likely resulted from an error in procedure? F G H J ...
... relationship between the concentration of alcohol dissolved in water and its density. The relationship was expected to be linear. Which of the data points most likely resulted from an error in procedure? F G H J ...
Final Exam - Dawson College
... Smallest atomic radius in Group 6A Largest atomic radius in Period 6 Condensed ground-state electron configuration is [Ne] 3s23p2 The period 4 member whose (2-) ion is isoelectronic with Kr A transition metal ion with a charge of 1+ having 5 unpaired “4d” electrons The element with the highest first ...
... Smallest atomic radius in Group 6A Largest atomic radius in Period 6 Condensed ground-state electron configuration is [Ne] 3s23p2 The period 4 member whose (2-) ion is isoelectronic with Kr A transition metal ion with a charge of 1+ having 5 unpaired “4d” electrons The element with the highest first ...
Chapter 4 - Mr. Fischer.com
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. A. Early philosophers believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. B. Dalton’s Atomic theory. Dalton used experimental methods, to transform Democritus’s ideas on atoms into scientific theory ...
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. A. Early philosophers believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. B. Dalton’s Atomic theory. Dalton used experimental methods, to transform Democritus’s ideas on atoms into scientific theory ...
Electronegativity

Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The term ""electronegativity"" was introduced by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1811,though the concept was known even before that and was studied by many chemists including Avogadro.In spite of its long history, an accurate scale of electronegativity had to wait till 1932, when Linus Pauling proposed an electronegativity scale, which depends on bond energies, as a development of valence bond theory. It has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties. Electronegativity cannot be directly measured and must be calculated from other atomic or molecular properties. Several methods of calculation have been proposed, and although there may be small differences in the numerical values of the electronegativity, all methods show the same periodic trends between elements. The most commonly used method of calculation is that originally proposed by Linus Pauling. This gives a dimensionless quantity, commonly referred to as the Pauling scale, on a relative scale running from around 0.7 to 3.98 (hydrogen = 2.20). When other methods of calculation are used, it is conventional (although not obligatory) to quote the results on a scale that covers the same range of numerical values: this is known as an electronegativity in Pauling units. As it is usually calculated, electronegativity is not a property of an atom alone, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule. Properties of a free atom include ionization energy and electron affinity. It is to be expected that the electronegativity of an element will vary with its chemical environment, but it is usually considered to be a transferable property, that is to say that similar values will be valid in a variety of situations.On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more ""pull"" it will have on electrons) and the number/location of other electrons present in the atomic shells (the more electrons an atom has, the farther from the nucleus the valence electrons will be, and as a result the less positive charge they will experience—both because of their increased distance from the nucleus, and because the other electrons in the lower energy core orbitals will act to shield the valence electrons from the positively charged nucleus).The opposite of electronegativity is electropositivity: a measure of an element's ability to donate electrons.Caesium is the least electronegative element in the periodic table (=0.79), while fluorine is most electronegative (=3.98). (Francium and caesium were originally assigned both assigned 0.7; caesium's value was later refined to 0.79, but no experimental data allows a similar refinement for francium. However, francium's ionization energy is known to be slightly higher than caesium's, in accordance with the relativistic stabilization of the 7s orbital, and this in turn implies that caesium is in fact more electronegative than francium.)