physical setting chemistry
... 37 Which general trends in first ionization energy and electronegativity values are demonstrated by Group 15 elements as they are considered in order from top to bottom? (1) The first ionization energy decreases and the electronegativity decreases. (2) The first ionization energy increases and the ...
... 37 Which general trends in first ionization energy and electronegativity values are demonstrated by Group 15 elements as they are considered in order from top to bottom? (1) The first ionization energy decreases and the electronegativity decreases. (2) The first ionization energy increases and the ...
Science Focus 9 Matter and Chemical Change Class Notes Topic 1
... electricity through water, they discovered hydrogen and oxygen gases could be produced and the water level dropped slightly. Using electricity to split molecules into their elements was a process called electrolysis. Scientists used electrolysis to isolate the elements potassium, sodium, magnesium, ...
... electricity through water, they discovered hydrogen and oxygen gases could be produced and the water level dropped slightly. Using electricity to split molecules into their elements was a process called electrolysis. Scientists used electrolysis to isolate the elements potassium, sodium, magnesium, ...
Chemistry - Sanskriti School
... Plasma is an ionized gas, a gas into which sufficient energy is provided to free electrons from atoms or molecules and to allow species, ions and electrons, to coexist. In effect plasma is a cloud of protons, neutrons and electrons where all the electrons have come loose from their respective molecu ...
... Plasma is an ionized gas, a gas into which sufficient energy is provided to free electrons from atoms or molecules and to allow species, ions and electrons, to coexist. In effect plasma is a cloud of protons, neutrons and electrons where all the electrons have come loose from their respective molecu ...
Export To Word
... experiment), and Bohr (planetary model of atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern atomic theory. Florida Standards Connections: MAFS.K12.MP.4: Model with mathematics. Explore the scientific theory of atoms (also known as atomic theory) by describing the structure of atoms in terms o ...
... experiment), and Bohr (planetary model of atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern atomic theory. Florida Standards Connections: MAFS.K12.MP.4: Model with mathematics. Explore the scientific theory of atoms (also known as atomic theory) by describing the structure of atoms in terms o ...
Cooling and Trapping Neutral Atoms
... Introduction and overview Bose-Einstein condensation of atoms was achieved in 1995 and had a major impact of atomic physics. New techniques were developed to prepare atomic samples at nanokelvin temperature, to control their properties and to diagnose them with a variety of powerful techniques. Sinc ...
... Introduction and overview Bose-Einstein condensation of atoms was achieved in 1995 and had a major impact of atomic physics. New techniques were developed to prepare atomic samples at nanokelvin temperature, to control their properties and to diagnose them with a variety of powerful techniques. Sinc ...
On inelastic hydrogen atom collisions in stellar atmospheres
... the deflection of the incident electron results in an energy transfer between electrons corresponding precisely to the ionization potential. All collisions inside this impact parameter will have a larger energy transfer and thus lead to ionization and so the cross section can be easily calculated. E ...
... the deflection of the incident electron results in an energy transfer between electrons corresponding precisely to the ionization potential. All collisions inside this impact parameter will have a larger energy transfer and thus lead to ionization and so the cross section can be easily calculated. E ...
Chem-130 Test Lecture
... position of an electron only the probability of finding it in a given location. The probability of finding the electron in a given location is the electron density and is given by the square of the wave function for that location, y2. ...
... position of an electron only the probability of finding it in a given location. The probability of finding the electron in a given location is the electron density and is given by the square of the wave function for that location, y2. ...
8
... In classical physics, a particle moves along a well-de®ned trajectory. A quantum object, however, reveals its wave character in interference experiments in which the object seems to move from one place to another along several different paths simultaneously. It is essential that these ways are indis ...
... In classical physics, a particle moves along a well-de®ned trajectory. A quantum object, however, reveals its wave character in interference experiments in which the object seems to move from one place to another along several different paths simultaneously. It is essential that these ways are indis ...
Document
... Atoms can be represented as shown in this example: Mass number 23 Na Atomic number 11 The relative masses of protons, neutrons and electrons are: Name of particle Mass Proton 1 Neutron 1 Electron Very small The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is called its mass number. Atoms of the s ...
... Atoms can be represented as shown in this example: Mass number 23 Na Atomic number 11 The relative masses of protons, neutrons and electrons are: Name of particle Mass Proton 1 Neutron 1 Electron Very small The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is called its mass number. Atoms of the s ...
Chemical Reactions and The Mole
... Generally, you will work with quantities of atoms greater than one. A new unit was developed from work by the Italian Chemist Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo Avogadro. The unit is named the mole or Avogadro’s number. This unit is nothing more than a number, a very big number. The mole works no different ...
... Generally, you will work with quantities of atoms greater than one. A new unit was developed from work by the Italian Chemist Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo Avogadro. The unit is named the mole or Avogadro’s number. This unit is nothing more than a number, a very big number. The mole works no different ...
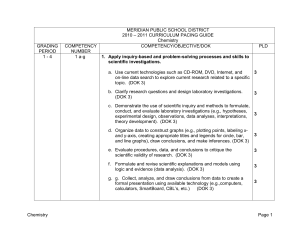
MERIDIAN PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT
... explaining atomic structure and chemical bonding. b. Research and explain crucial contributions and critical experiments of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, de Broglie, and Schrődinger and describe how each discovery contributed to the current model of atomic and nuclear structure. (DOK 2) dWrite ...
... explaining atomic structure and chemical bonding. b. Research and explain crucial contributions and critical experiments of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, de Broglie, and Schrődinger and describe how each discovery contributed to the current model of atomic and nuclear structure. (DOK 2) dWrite ...
CHEM 1411 EXAM I (Chapters 1, 2, 3): 25
... Thus, 223.7 + 0.27 = 223.97 from calculator, which must be corrected with the least decimal points of the components, and thus it is 224.0. So the question turns to 224.0 ÷ 4.21 = 53.20665083 from calculator, which must be corrected with the lease digit of the significant figures of the components ...
... Thus, 223.7 + 0.27 = 223.97 from calculator, which must be corrected with the least decimal points of the components, and thus it is 224.0. So the question turns to 224.0 ÷ 4.21 = 53.20665083 from calculator, which must be corrected with the lease digit of the significant figures of the components ...
2005/6 - SAASTA
... electrons and upon oxidation, loses 2 electrons. Thus, for Ca2+, there are only 18 electrons to distribute in all orbitals according to the Aufbau principle. Only option 3 is correct. Option 4 is incorrect because it is for elemental calcium with 20 electrons. Ca2+ has the same number of electrons a ...
... electrons and upon oxidation, loses 2 electrons. Thus, for Ca2+, there are only 18 electrons to distribute in all orbitals according to the Aufbau principle. Only option 3 is correct. Option 4 is incorrect because it is for elemental calcium with 20 electrons. Ca2+ has the same number of electrons a ...
Stoichiometry
... Dalton’s law of partial pressure: The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases, that do not interact, equals sum of partial pressures of all gases, if each gas occupies the container on its own. P total = P1 + P2 + P3 + ………… ...
... Dalton’s law of partial pressure: The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases, that do not interact, equals sum of partial pressures of all gases, if each gas occupies the container on its own. P total = P1 + P2 + P3 + ………… ...
pages 851-900 - Light and Matter
... numbers of photons: four photons in figure i/3, for example. A wrong interpretation: photons interfering with each other One possible interpretation of wave-particle duality that occurred to physicists early in the game was that perhaps the interference effects came from photons interacting with eac ...
... numbers of photons: four photons in figure i/3, for example. A wrong interpretation: photons interfering with each other One possible interpretation of wave-particle duality that occurred to physicists early in the game was that perhaps the interference effects came from photons interacting with eac ...
Quantum dynamics of open systems governed by the Milburn equation
... which is caused by the nonunitary evolution of the system on a short time scale ~here ‘‘short’’ is specified by the value of g ). This freezing of the time evolution is analogous to the quantum Zeno effect @5#. The difference is that the nonunitarity in the quantum Zeno effect is caused by a sequenc ...
... which is caused by the nonunitary evolution of the system on a short time scale ~here ‘‘short’’ is specified by the value of g ). This freezing of the time evolution is analogous to the quantum Zeno effect @5#. The difference is that the nonunitarity in the quantum Zeno effect is caused by a sequenc ...
Strongly perturbed Stark states and electron correlation in Ba F. Robicheaux,
... formalism. In this formalism, even a simple alkali-metal atom like Li has a multichannel behavior because the multiple channels are the channels in parabolic coordinates and the coupling between channels is provided by the nonhydrogenic potential generated by the core electrons; the coupling between ...
... formalism. In this formalism, even a simple alkali-metal atom like Li has a multichannel behavior because the multiple channels are the channels in parabolic coordinates and the coupling between channels is provided by the nonhydrogenic potential generated by the core electrons; the coupling between ...