One- and two-center physical space partitioning of the energy Salvador
... Hartree-Fock case to the fuzzy atom DFT energy decomposition did not give satisfactory results at all. In fact, one could anticipate that if one uses the same simple direct approaches in DFT which were successful in HF, then one may get difficulties: there is no obvious way to decompose the exchange ...
... Hartree-Fock case to the fuzzy atom DFT energy decomposition did not give satisfactory results at all. In fact, one could anticipate that if one uses the same simple direct approaches in DFT which were successful in HF, then one may get difficulties: there is no obvious way to decompose the exchange ...
Electron spectroscopy of atoms and molecules using synchrotron
... itself. It is therefore natural that the understanding of the electronic properties of atoms is very important for the understanding of the natural world around us. Electron spectroscopy analyzes the electrons emitted or scattered by the studied sample when bombarded using excitation beams (electron ...
... itself. It is therefore natural that the understanding of the electronic properties of atoms is very important for the understanding of the natural world around us. Electron spectroscopy analyzes the electrons emitted or scattered by the studied sample when bombarded using excitation beams (electron ...
CHEM 250Q
... 77. A researcher uses several procedures to separate a rock sample into different chemicals. A mass of 50 grams of one chemical is produced. If this chemical cannot be separated into other chemicals, then it is best described as A. ...
... 77. A researcher uses several procedures to separate a rock sample into different chemicals. A mass of 50 grams of one chemical is produced. If this chemical cannot be separated into other chemicals, then it is best described as A. ...
Answers to Selected Exercises
... 1.0 g of pure water should always contain the same relative amounts of hydrogen and oxygen, no matter where or how the sample is obtained. 1.38 (a) 0.5711 g O>1 g N; 1.142 g O>1 g N; 2.284 g O>1 g N; 2.855 g O>1 g N (b) The numbers in part (a) obey the law of multiple proportions. Multiple proportio ...
... 1.0 g of pure water should always contain the same relative amounts of hydrogen and oxygen, no matter where or how the sample is obtained. 1.38 (a) 0.5711 g O>1 g N; 1.142 g O>1 g N; 2.284 g O>1 g N; 2.855 g O>1 g N (b) The numbers in part (a) obey the law of multiple proportions. Multiple proportio ...
"Effects of quantum chemistry models for bound electrons on positron annihilation spectra for atoms and small molecules" New J. Phys. , 14 , 085022 (2012). F. Wang, X. Ma, L. Selvam, G. F. Gribakin, and C. M Surko (PDF)
... simulated γ-ray annihilation spectra of a target, which depends on the electron wavefunctions, will be the same when using either HF or post-HF models, but will be different from those simulated using the DFT models. The choice of basis set is also important for the development of an accurate model. ...
... simulated γ-ray annihilation spectra of a target, which depends on the electron wavefunctions, will be the same when using either HF or post-HF models, but will be different from those simulated using the DFT models. The choice of basis set is also important for the development of an accurate model. ...
Alkali D Line Data
... recommended values, as listed in [2]. Some of the overall physical properties of 87 Rb are given in Table 2. Rubidium 87 has 37 electrons, only one of which is in the outermost shell. 87 Rb is not a stable isotope of rubidium, decaying to β − + 87 Sr with a total disintegration energy of 0.283 MeV [ ...
... recommended values, as listed in [2]. Some of the overall physical properties of 87 Rb are given in Table 2. Rubidium 87 has 37 electrons, only one of which is in the outermost shell. 87 Rb is not a stable isotope of rubidium, decaying to β − + 87 Sr with a total disintegration energy of 0.283 MeV [ ...
Atomistic description of wave function localization effects in InxGa1
... k = 0. The charge density is shown in red at 25% of the maximum charge density. In atoms are indicated in green, Ga atoms in silver and N atoms are given in blue. Figure 1 reflects the trends observed in Table 1. The CBE exhibits only very weak indications of wave function localization effects, sinc ...
... k = 0. The charge density is shown in red at 25% of the maximum charge density. In atoms are indicated in green, Ga atoms in silver and N atoms are given in blue. Figure 1 reflects the trends observed in Table 1. The CBE exhibits only very weak indications of wave function localization effects, sinc ...
physical setting chemistry
... In 1897, J. J. Thomson demonstrated in an experiment that cathode rays were deflected by an electric field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in ...
... In 1897, J. J. Thomson demonstrated in an experiment that cathode rays were deflected by an electric field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in ...
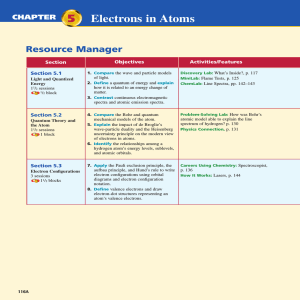
Electrons in Atoms CHAPTER
... Figure 5-1b, also is a gas. Argon, however, is so unreactive that it is considered a noble gas. Potassium is a reactive metal at room temperature. In fact, as you can see in Figure 5-1c, because potassium is so reactive, it must be stored under kerosene or oil to prevent its atoms from reacting with ...
... Figure 5-1b, also is a gas. Argon, however, is so unreactive that it is considered a noble gas. Potassium is a reactive metal at room temperature. In fact, as you can see in Figure 5-1c, because potassium is so reactive, it must be stored under kerosene or oil to prevent its atoms from reacting with ...