Chapter 6
... The principle- originally deduced from the atomic milieu - later on has been applied as common rules for all sorts of matter. The principle has been used in the atomic nucleus when describing the fundamental nature of the strong nuclear force for instance) and even in the particle physics when descr ...
... The principle- originally deduced from the atomic milieu - later on has been applied as common rules for all sorts of matter. The principle has been used in the atomic nucleus when describing the fundamental nature of the strong nuclear force for instance) and even in the particle physics when descr ...
Quantum gases in optical lattices
... rectly. However, a periodic pattern can show striking interference effects when illuminated with coherent waves, and we can use this approach to check that the condensate has indeed been transferred. We can also turn off the lattice potential and use the diffraction pattern to follow how the atoms o ...
... rectly. However, a periodic pattern can show striking interference effects when illuminated with coherent waves, and we can use this approach to check that the condensate has indeed been transferred. We can also turn off the lattice potential and use the diffraction pattern to follow how the atoms o ...
Quantum critical phenomena and stability of atomic and molecular
... not to the spatial dimension but to the number of elements in a complete basis set used to expand the exact eigenfunction of a given Hamiltonian. In this method we assumed that the two lowest eigenvalues of the quantum Hamiltonian can be taken as the leading eigenvalues of a transfer matrix of a cla ...
... not to the spatial dimension but to the number of elements in a complete basis set used to expand the exact eigenfunction of a given Hamiltonian. In this method we assumed that the two lowest eigenvalues of the quantum Hamiltonian can be taken as the leading eigenvalues of a transfer matrix of a cla ...
Probing a scattering resonance in Rydberg molecules with a Bose
... with a detuning in this range are not shifted as much as the theory predicts, leading to an underestimated theory signal between -40 and 0 MHz. There are several simplifications in the model, which could lead to these discrepancies at intermediate detunings. All atoms are treated as point-like parti ...
... with a detuning in this range are not shifted as much as the theory predicts, leading to an underestimated theory signal between -40 and 0 MHz. There are several simplifications in the model, which could lead to these discrepancies at intermediate detunings. All atoms are treated as point-like parti ...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
... Laws/ Dalton’s Atomic Theory John Dalton (1808) “Father of Atomic Theory” Essentials of his theory. . . 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary c ...
... Laws/ Dalton’s Atomic Theory John Dalton (1808) “Father of Atomic Theory” Essentials of his theory. . . 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary c ...
MU08-CHAPTER6.doc
... De Broglie's formula D = n.h/(2. .p), applied as a universal rule for particles, or particle systems. Many experiments have been performed but there are no exact knowledge about size parameters of particles. XXX In our theory we regard electrons, as well as protons, as point particles having vortex ...
... De Broglie's formula D = n.h/(2. .p), applied as a universal rule for particles, or particle systems. Many experiments have been performed but there are no exact knowledge about size parameters of particles. XXX In our theory we regard electrons, as well as protons, as point particles having vortex ...
11 Two and many electron atoms - FU Berlin
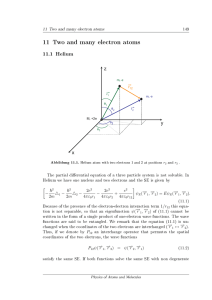
... state (1s)(2s) is metastable, since relaxation to (1s)2 is not possible upon light emission (intercombination lines are forbidden). Excitation of triplet states is possible upon collisions of atoms, spin-orbit coupling (which is very weak for helium) and magnetic dipole transitions. Interaction with ...
... state (1s)(2s) is metastable, since relaxation to (1s)2 is not possible upon light emission (intercombination lines are forbidden). Excitation of triplet states is possible upon collisions of atoms, spin-orbit coupling (which is very weak for helium) and magnetic dipole transitions. Interaction with ...
Measuring the Rydberg Constant Using Circular Rydberg Atoms in
... (relative uncertainty of 2.1 × 10−11 ) and a proposal involving circular states of lithium [7] (expected relative uncertainty of about 10−10 ). The approaches involving low-lying states and circular states deal with significantly different frequency regimes: optical versus microwave. Therefore, meas ...
... (relative uncertainty of 2.1 × 10−11 ) and a proposal involving circular states of lithium [7] (expected relative uncertainty of about 10−10 ). The approaches involving low-lying states and circular states deal with significantly different frequency regimes: optical versus microwave. Therefore, meas ...
1 Data Provided: Formula sheet and physical constants
... Answer question ONE (compulsory) and TWO other questions. Please clearly indicate the question numbers on which you would like to be examined on the front cover of your answer book. Cross through any work that you do not wish to be examined. The total number of marks for the exam paper is 50. Questi ...
... Answer question ONE (compulsory) and TWO other questions. Please clearly indicate the question numbers on which you would like to be examined on the front cover of your answer book. Cross through any work that you do not wish to be examined. The total number of marks for the exam paper is 50. Questi ...
Lecture Notes Part A
... Atoms become stable through shared electrons Single covalent bonds share one pair of electrons Double covalent bonds share two pairs of electrons ...
... Atoms become stable through shared electrons Single covalent bonds share one pair of electrons Double covalent bonds share two pairs of electrons ...
Standard - Santee Education Complex
... place in NaCl is different than that in HCl. This gives NaCl and HCl very different structures, appearances, and properties.What other differences are noticeable among molecules that result from different types of chemical bonding? Think about what happens when a bunch of sodium and chlorine ions jo ...
... place in NaCl is different than that in HCl. This gives NaCl and HCl very different structures, appearances, and properties.What other differences are noticeable among molecules that result from different types of chemical bonding? Think about what happens when a bunch of sodium and chlorine ions jo ...
Ionization Energies of the Elements Manifest Natural Harmonies of
... ionization of He: EII = 13.6 (2/1)2 = 13.6 × 4 = 54.4 eV. Johnson: This is quite close to being a 1: 4 proportion, within 1/20 of one percent! We might then look at the Lithium II value of 122.454353 and see that it is remarkably close to NINE times the hydrogen value, again around a match of around ...
... ionization of He: EII = 13.6 (2/1)2 = 13.6 × 4 = 54.4 eV. Johnson: This is quite close to being a 1: 4 proportion, within 1/20 of one percent! We might then look at the Lithium II value of 122.454353 and see that it is remarkably close to NINE times the hydrogen value, again around a match of around ...
Fall 2012 Chem106 Final Review Name: Test 1 Materials Question
... 1. A patient receives 250 mL of a 4% (m/v) mannitol solution every hour. The number of grams of mannitol is_______. a) 8 b) 10 c) 15 d) 20 2. Write the balanced equation for dissociating the following solid ionic salts in water: a) Na2CO3(s) b) (NH4)3PO4(s) 3. (15pts) Which of the following reaction ...
... 1. A patient receives 250 mL of a 4% (m/v) mannitol solution every hour. The number of grams of mannitol is_______. a) 8 b) 10 c) 15 d) 20 2. Write the balanced equation for dissociating the following solid ionic salts in water: a) Na2CO3(s) b) (NH4)3PO4(s) 3. (15pts) Which of the following reaction ...