Unit 2: Carbon Compounds
... A homologous series is a set of compounds with the same general formula and similar chemical properties. ...
... A homologous series is a set of compounds with the same general formula and similar chemical properties. ...
Organic Chem Slideshow Part 1
... labeled with prefixes in table P. All end in –ane. 29. AKLENES: hydrocarbons with only one double C=C bond. Only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms. Chains of 1 to 10 labeled with prefixes in table P. All end in –ene. In college molecules can have multiple double bonding, but we have a single double ...
... labeled with prefixes in table P. All end in –ane. 29. AKLENES: hydrocarbons with only one double C=C bond. Only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms. Chains of 1 to 10 labeled with prefixes in table P. All end in –ene. In college molecules can have multiple double bonding, but we have a single double ...
organic compound containing nitrogen
... Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi – 110 018, Ph. : 9312629035, 8527112111 ...
... Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi – 110 018, Ph. : 9312629035, 8527112111 ...
Structural Effects on Acidity
... Acidity is associated not only with the tendency of compound to yield hydrogen in H2O but also to accept an electron pair to form a covalent bond. ...
... Acidity is associated not only with the tendency of compound to yield hydrogen in H2O but also to accept an electron pair to form a covalent bond. ...
Study_guide_2010-01
... This is a list of topics we will be covering to help you in preparation for exams. Topics from Clayden are indicated clearly by chapter and page numbers where necessary. Topics NOT from Clayden are listed in italics. PLTL topics are in CAPS. This document will be updated throughout the term. The goa ...
... This is a list of topics we will be covering to help you in preparation for exams. Topics from Clayden are indicated clearly by chapter and page numbers where necessary. Topics NOT from Clayden are listed in italics. PLTL topics are in CAPS. This document will be updated throughout the term. The goa ...
PPTB&W - Gmu - George Mason University
... The diversity of organic compounds is based on the ability of Carbon atoms to bond to each other (catenation) to form straight chains, branched chains, and cyclic structures – aliphatic, aromatic Carbon is in group 4 of the Periodic Chart and has 4 valence electrons – 2s22p2 This configuration ...
... The diversity of organic compounds is based on the ability of Carbon atoms to bond to each other (catenation) to form straight chains, branched chains, and cyclic structures – aliphatic, aromatic Carbon is in group 4 of the Periodic Chart and has 4 valence electrons – 2s22p2 This configuration ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... Unlike alcohols, phenols are acidic enough to dissolve in NaOH(aq), and be re-precipitated on the addition of HCl(aq) [The intrinsic solubility of phenol in water sometimes masks this effect - the use of the less soluble thymol makes for a more impressive demonstration]. Phenol reacts vigorously wit ...
... Unlike alcohols, phenols are acidic enough to dissolve in NaOH(aq), and be re-precipitated on the addition of HCl(aq) [The intrinsic solubility of phenol in water sometimes masks this effect - the use of the less soluble thymol makes for a more impressive demonstration]. Phenol reacts vigorously wit ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... Unlike alcohols, phenols are acidic enough to dissolve in NaOH(aq), and be re-precipitated on the addition of HCl(aq) [The intrinsic solubility of phenol in water sometimes masks this effect - the use of the less soluble thymol makes for a more impressive demonstration]. Phenol reacts vigorously wit ...
... Unlike alcohols, phenols are acidic enough to dissolve in NaOH(aq), and be re-precipitated on the addition of HCl(aq) [The intrinsic solubility of phenol in water sometimes masks this effect - the use of the less soluble thymol makes for a more impressive demonstration]. Phenol reacts vigorously wit ...
GROUP 13 ELEMENTS -THE BORON FAMILY -
... important because it forms gallium arsenide (GaAs), which can convert light directly into electricity. Also due to thermite reaction, aluminum can extract oxygen from water and hydrogen is released. However, as mentioned above, aluminum forms a protective coat in the presence of water. By combining ...
... important because it forms gallium arsenide (GaAs), which can convert light directly into electricity. Also due to thermite reaction, aluminum can extract oxygen from water and hydrogen is released. However, as mentioned above, aluminum forms a protective coat in the presence of water. By combining ...
Article Reference - Archive ouverte UNIGE
... mechanism is correct. The first attempt5 to use correlated electronic structure theory to ...
... mechanism is correct. The first attempt5 to use correlated electronic structure theory to ...
幻灯片 1 - Sun Yat-sen University
... • Cyclic Alkynes and Polyalkynes: 1. The linear nature of the -C≡C- group small ring alkynes are not stable. 2. Since the −C ≡ C− group is very reactive, poly-ynes are not common. CH3 CH3 ...
... • Cyclic Alkynes and Polyalkynes: 1. The linear nature of the -C≡C- group small ring alkynes are not stable. 2. Since the −C ≡ C− group is very reactive, poly-ynes are not common. CH3 CH3 ...
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... (ii) Metal-Carbon Bridge Bonding : The light electropositive elements (e.g. Li, Be, Mg, Al) form organometallic compounds such as MeLi, Me2Mg , Ph3Al etc. These compounds do not exist as monomers rather form oligomers, or polymers, namely, (MeLi)4, (Me2Mg)n, (Ph3Al)2 involving bridging by alkyl or a ...
... (ii) Metal-Carbon Bridge Bonding : The light electropositive elements (e.g. Li, Be, Mg, Al) form organometallic compounds such as MeLi, Me2Mg , Ph3Al etc. These compounds do not exist as monomers rather form oligomers, or polymers, namely, (MeLi)4, (Me2Mg)n, (Ph3Al)2 involving bridging by alkyl or a ...
Chromatographic and Spectroscopic Methods of Identification for the
... spectrum. Methamphetamine and phentermine (5) are regioisomeric, based on the substitution of a methyl group on nitrogen or carbon of the side-chain. The street drug 4-bromo-2,5dimethoxyphenethylamine (“Nexus”) would have several regioisomers based on other aromatic ring substitution patterns (8). A ...
... spectrum. Methamphetamine and phentermine (5) are regioisomeric, based on the substitution of a methyl group on nitrogen or carbon of the side-chain. The street drug 4-bromo-2,5dimethoxyphenethylamine (“Nexus”) would have several regioisomers based on other aromatic ring substitution patterns (8). A ...
Nugget
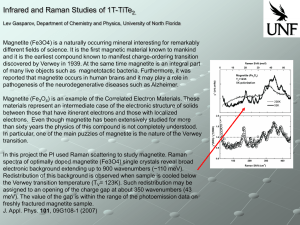
... Magnetite (Fe3O4) is a naturally occurring mineral interesting for remarkably different fields of science. It is the first magnetic material known to mankind and it is the earliest compound known to manifest charge-ordering transition discovered by Verwey in 1939. At the same time magnetite is an in ...
... Magnetite (Fe3O4) is a naturally occurring mineral interesting for remarkably different fields of science. It is the first magnetic material known to mankind and it is the earliest compound known to manifest charge-ordering transition discovered by Verwey in 1939. At the same time magnetite is an in ...
A Lead-Filled G-Quadruplex: Insight into the G
... cations with affinity and selectivity. In addition to represent(8) Zimmerman, S. C.; Schmitt, P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 1076910770. (9) Sessler, J. L.; Sathiosatham, M.; Doerr, K.; Lynch, V.; Abboud, K. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 2000, 39, 1300-1303. (10) (a) Forman, S. L.; Fettinger, J. ...
... cations with affinity and selectivity. In addition to represent(8) Zimmerman, S. C.; Schmitt, P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 1076910770. (9) Sessler, J. L.; Sathiosatham, M.; Doerr, K.; Lynch, V.; Abboud, K. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 2000, 39, 1300-1303. (10) (a) Forman, S. L.; Fettinger, J. ...
PP IR Spectroscopy
... organic molecules have a lot of C-C and C-H bonds within their structure spectra obtained will have peaks in the 1400 cm-1 to 800 cm-1 range this is referred to as the “fingerprint” region the pattern obtained is characteristic of a particular compound the frequency of any absorption is also affecte ...
... organic molecules have a lot of C-C and C-H bonds within their structure spectra obtained will have peaks in the 1400 cm-1 to 800 cm-1 range this is referred to as the “fingerprint” region the pattern obtained is characteristic of a particular compound the frequency of any absorption is also affecte ...
COMPOUNDS OF CARBON CONTAINING NITROGEN
... oxygen atom as a part of the functional group. Now, you will learn about organic compounds containing nitrogen atom as a part of the functional group. An historical importance can be associated with these compounds as the first ever organic compound synthesised in the laboratory was urea which conta ...
... oxygen atom as a part of the functional group. Now, you will learn about organic compounds containing nitrogen atom as a part of the functional group. An historical importance can be associated with these compounds as the first ever organic compound synthesised in the laboratory was urea which conta ...
How QuikSoil 2600 works
... potential of the mass while maintaining good structure, 2600 promotes increased facultative proliferation throughout the interior of the substrate. Concurrently, aerobes, micro-aerophiles and existing facultative microbes utilize (by respiration {oxidation}) any molecular oxygen which approaches the ...
... potential of the mass while maintaining good structure, 2600 promotes increased facultative proliferation throughout the interior of the substrate. Concurrently, aerobes, micro-aerophiles and existing facultative microbes utilize (by respiration {oxidation}) any molecular oxygen which approaches the ...
100 Problems and Exercises in Organometallic Chemistry Anil J. Elias
... 30. The reaction of Mo(CO)6 with dicyclopentadiene (C10H12) under microwave conditions yields a stable compound A with the empirical formula C8H5O3Mo along with evolution of CO and H2 gas. The infrared spectrum of this compound gives peaks in the range of 1859-1960 cm-1. Compound A on refluxing in t ...
... 30. The reaction of Mo(CO)6 with dicyclopentadiene (C10H12) under microwave conditions yields a stable compound A with the empirical formula C8H5O3Mo along with evolution of CO and H2 gas. The infrared spectrum of this compound gives peaks in the range of 1859-1960 cm-1. Compound A on refluxing in t ...
Chapter 4 - Jenkins Independent Schools
... other atoms. When carbon atoms form covalent bonds, they obtain the stability of a noble gas with eight electrons in their outer energy level. One of carbon’s most frequent partners in forming covalent bonds is hydrogen. Substances can be classified into two groups—those derived from living things a ...
... other atoms. When carbon atoms form covalent bonds, they obtain the stability of a noble gas with eight electrons in their outer energy level. One of carbon’s most frequent partners in forming covalent bonds is hydrogen. Substances can be classified into two groups—those derived from living things a ...
O - Imperial College London
... “The enzyme’s role is most likely to shield intermediate carbocations… thereby allowing the hydride and methyl group migrations to proceed down a thermodynamically favorable and kinetically facile cascade” ...
... “The enzyme’s role is most likely to shield intermediate carbocations… thereby allowing the hydride and methyl group migrations to proceed down a thermodynamically favorable and kinetically facile cascade” ...
chapter 9 - chemical bonds
... The most widely used electronegativity values are those introduced by Linus Pauling (1901 – 1995), in which fluorine, which is the most electronegative atom in the periodic table, is given an electronegativity value of 4.0. In general, electronegativity increases from left to right across periods an ...
... The most widely used electronegativity values are those introduced by Linus Pauling (1901 – 1995), in which fluorine, which is the most electronegative atom in the periodic table, is given an electronegativity value of 4.0. In general, electronegativity increases from left to right across periods an ...
Mass Spectrometry
... Other suitable examples include series such as a) C7H14, C6H10O, C5H6O2, C5H10N2; b) NO, H2C=0, H2N2; or c) C2H8N2, C3H8O, C2O2. For this course we will limit our discussion essentially to: a) electron impact MS b) positive ion MS and c) low resolution MS. Fragmentation of molecular ions Many molecu ...
... Other suitable examples include series such as a) C7H14, C6H10O, C5H6O2, C5H10N2; b) NO, H2C=0, H2N2; or c) C2H8N2, C3H8O, C2O2. For this course we will limit our discussion essentially to: a) electron impact MS b) positive ion MS and c) low resolution MS. Fragmentation of molecular ions Many molecu ...
organic revision nots
... 2. In Phenol, the –OH group activates the benzene ring towards elecrophilic substitution and directs the substituents to Ortho and para positions in benzene ring. 3. The –OH group in phenols is more strongly held as compared to –OH group in alcohols. 4. Phenol does not undergo protonation easily. 5. ...
... 2. In Phenol, the –OH group activates the benzene ring towards elecrophilic substitution and directs the substituents to Ortho and para positions in benzene ring. 3. The –OH group in phenols is more strongly held as compared to –OH group in alcohols. 4. Phenol does not undergo protonation easily. 5. ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.