REVIEWS Environmental remediation by photocatalysis R. Vinu AND Giridhar Madras
... a major role (reaction (2)), and the contribution of reactions (8)–(14) for the overall oxidation of the substrate is negligible. Once the active species are generated, the reactants are adsorbed onto the surface of the photocatalyst (reactions (15)–(17)). This is followed by the oxidation of the re ...
... a major role (reaction (2)), and the contribution of reactions (8)–(14) for the overall oxidation of the substrate is negligible. Once the active species are generated, the reactants are adsorbed onto the surface of the photocatalyst (reactions (15)–(17)). This is followed by the oxidation of the re ...
C07C - Cooperative Patent Classification
... – a compound is considered to be saturated if it does not contain carbon atoms bound to each other by multiple bonds; – a compound is considered to be unsaturated if it contains carbon atoms bound to each other by multiple bonds, which includes six-membered aromatic ring, unless otherwise specified ...
... – a compound is considered to be saturated if it does not contain carbon atoms bound to each other by multiple bonds; – a compound is considered to be unsaturated if it contains carbon atoms bound to each other by multiple bonds, which includes six-membered aromatic ring, unless otherwise specified ...
Ethers, Epoxides and Sulfides
... ¾ Similar to alkanes of comparable MW. ¾ Much lower than alcohols of comparable MW. ...
... ¾ Similar to alkanes of comparable MW. ¾ Much lower than alcohols of comparable MW. ...
Competing Intramolecular vs. Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonds in
... mutual penetration of the hydrogen and the acceptor atoms. This characteristic of a H-bond guarantees that polar X–H and Y groups cannot form an intramolecular hydrogen bond if they are far from each other in the space. For a rigid system, e.g., 1,4-dihydroxy benzene, the chemical structure itself p ...
... mutual penetration of the hydrogen and the acceptor atoms. This characteristic of a H-bond guarantees that polar X–H and Y groups cannot form an intramolecular hydrogen bond if they are far from each other in the space. For a rigid system, e.g., 1,4-dihydroxy benzene, the chemical structure itself p ...
HIGHLY SELECTIVE RHODIUM–CATALYZED C–H BORYLATIONS IN
... Scheme 1-5. Photolytic oxidative addition of metal to alkyl C–H bond ....................................... 9 Scheme 1-6. Pathways for the cyclometalation process via electrophilic bond activation (EBA) (Pathway A) and concerted metalation–deprotonation (CMD) (Pathway B) .......... 11 Scheme 1-7. G ...
... Scheme 1-5. Photolytic oxidative addition of metal to alkyl C–H bond ....................................... 9 Scheme 1-6. Pathways for the cyclometalation process via electrophilic bond activation (EBA) (Pathway A) and concerted metalation–deprotonation (CMD) (Pathway B) .......... 11 Scheme 1-7. G ...
PowerPoint ******
... 1,2-Shifts of migrating groups to empty orbitals in carbocations or toward partially empty orbitals in developing carbocations are the most common rearrangements of organic molecules. Especially, migration of hydrogen atom or alkyl or aryl groups in carbocations are called “WagnerMeerwein Rearrangem ...
... 1,2-Shifts of migrating groups to empty orbitals in carbocations or toward partially empty orbitals in developing carbocations are the most common rearrangements of organic molecules. Especially, migration of hydrogen atom or alkyl or aryl groups in carbocations are called “WagnerMeerwein Rearrangem ...
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS, PHENOLS, AND THIOLS
... All three compounds are alcohols. 1-pentanol has the lowest molar mass and hence the lowest boiling point. 1-octanol has a higher molar mass and therefore a higher boiling point than 1-pentanol. 1,2-pentanediol has two ¬ OH groups and therefore forms more hydrogen bonds than the other two alcohols w ...
... All three compounds are alcohols. 1-pentanol has the lowest molar mass and hence the lowest boiling point. 1-octanol has a higher molar mass and therefore a higher boiling point than 1-pentanol. 1,2-pentanediol has two ¬ OH groups and therefore forms more hydrogen bonds than the other two alcohols w ...
Aldehydes and Ketones The Carbonyl Group
... Other Nomenclature Rules • In cyclic ketones, the carbonyl group is always numbered “1”; this does not need to be included in the name. The numbering continues clockwise or counterclockwise to give the lowest number for the next substituent. • Molecules with more than one ketone group are named by p ...
... Other Nomenclature Rules • In cyclic ketones, the carbonyl group is always numbered “1”; this does not need to be included in the name. The numbering continues clockwise or counterclockwise to give the lowest number for the next substituent. • Molecules with more than one ketone group are named by p ...
Chemical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
... • Both aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl group. Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen atom bonded to the carbonyl carbon. Ketones have only alkyl or aryl groups bonded to the carbonyl carbon. • The IUPAC naming of aldehydes and ketones follows a similar process to that used for other organic ...
... • Both aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl group. Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen atom bonded to the carbonyl carbon. Ketones have only alkyl or aryl groups bonded to the carbonyl carbon. • The IUPAC naming of aldehydes and ketones follows a similar process to that used for other organic ...
+2 - h2ochem
... including CHARGES! 2. Check to see if charges are balanced. (If so, skip to step 5) 3. Balance charges , if necessary, using subscripts. A. Cross over the charges by using the absolute value of each ion’s charge as the subscript for the other ion. B. Use parentheses if you need more than one of a po ...
... including CHARGES! 2. Check to see if charges are balanced. (If so, skip to step 5) 3. Balance charges , if necessary, using subscripts. A. Cross over the charges by using the absolute value of each ion’s charge as the subscript for the other ion. B. Use parentheses if you need more than one of a po ...
Organic – Nomenclature – III
... compound is alkanoic acid. Longest chain of six carbon atoms is available on both the directions from C-4. The chain containing two functional groups(-OH and -NH2) is taken as the correct longest chain. Note that although the other chain bears a higher priority group (-CHO), still it is not consider ...
... compound is alkanoic acid. Longest chain of six carbon atoms is available on both the directions from C-4. The chain containing two functional groups(-OH and -NH2) is taken as the correct longest chain. Note that although the other chain bears a higher priority group (-CHO), still it is not consider ...
Unit 5: Oragnic Chemistry Notes (answers)
... 25.2: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Saturated Hydrocarbons: - hydrocarbons that consist of all single bonds only. Unsaturated Bonds: - hydrocarbons that contain double or triple bond(s). Alkenes: - hydrocarbons that contain a C = C (double bond) - nomenclature of alkane involves the use of the suffix ~en ...
... 25.2: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Saturated Hydrocarbons: - hydrocarbons that consist of all single bonds only. Unsaturated Bonds: - hydrocarbons that contain double or triple bond(s). Alkenes: - hydrocarbons that contain a C = C (double bond) - nomenclature of alkane involves the use of the suffix ~en ...
Ch14_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... 44) As the molar mass of these alcohols increases, the water solubility decreases. This occurs because the polarity of the hydroxyl group, which is the reason for the interaction with the polar water molecules, becomes less important as the size of the nonpolar hydrocarbon portion of the molecule in ...
... 44) As the molar mass of these alcohols increases, the water solubility decreases. This occurs because the polarity of the hydroxyl group, which is the reason for the interaction with the polar water molecules, becomes less important as the size of the nonpolar hydrocarbon portion of the molecule in ...
1049-1060 Reeder.pm - Mineralogical Society of America
... symmetry 3. Cell six Ca-O distances are identical (2.36 Å), and the CaO6 octahedron is only slightly trigonally elongated (cf. Reeder 1983). Unlike Ng2+, Co2+, Zn2+, Fe2+, and Mn2+, all of which occure commonly in octahedral coordination, the larger ions Sr2+, Pb2+, and Ba2+ usually have a higher co ...
... symmetry 3. Cell six Ca-O distances are identical (2.36 Å), and the CaO6 octahedron is only slightly trigonally elongated (cf. Reeder 1983). Unlike Ng2+, Co2+, Zn2+, Fe2+, and Mn2+, all of which occure commonly in octahedral coordination, the larger ions Sr2+, Pb2+, and Ba2+ usually have a higher co ...
Modern Organic Chemistry
... Terminal carbons condense to CH3 with the hydrogens usually to the right of the carbon. Interior carbons condense to CH2 . ...
... Terminal carbons condense to CH3 with the hydrogens usually to the right of the carbon. Interior carbons condense to CH2 . ...
06. Alcohols. Phenols. Ethers
... III. The carbinol system. In this system, the simplest alcohol, СН3ОН, is called carbinol. More complex alcohols are named as alkyl substituted carbinols. The names are written as one word. ...
... III. The carbinol system. In this system, the simplest alcohol, СН3ОН, is called carbinol. More complex alcohols are named as alkyl substituted carbinols. The names are written as one word. ...
Chapter #14 Newest CD
... 1) The names of the alkanes beyond butane are obtained by adding the suffix –ane to the Greek root for the number of carbon atoms (pentfor five, hex- for six, and so on). For a branched hydrocarbon, the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms determines the root name for the hydrocarbon. For exampl ...
... 1) The names of the alkanes beyond butane are obtained by adding the suffix –ane to the Greek root for the number of carbon atoms (pentfor five, hex- for six, and so on). For a branched hydrocarbon, the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms determines the root name for the hydrocarbon. For exampl ...
Introduction
... Treatment of [M(BH4)3(THF)3] with NEt3HBPh4 in THF afforded the cationic complexes [M(BH4)2(THF)5][BPh4] [M = U (1), Nd (2), Ce (3)] which were transformed into [M(BH4)2(18-crown-6)][BPh4] [M = U (4), Nd (5), Ce (6)] in the presence of 18-crown-6; [U(BH4)2(18-thiacrown-6)][BPh4] (7) was obtained fro ...
... Treatment of [M(BH4)3(THF)3] with NEt3HBPh4 in THF afforded the cationic complexes [M(BH4)2(THF)5][BPh4] [M = U (1), Nd (2), Ce (3)] which were transformed into [M(BH4)2(18-crown-6)][BPh4] [M = U (4), Nd (5), Ce (6)] in the presence of 18-crown-6; [U(BH4)2(18-thiacrown-6)][BPh4] (7) was obtained fro ...
Chem E2b - Organic Chemistry II What is Organic Chemistry?
... Lewis Acids and Bases • Lewis acid: non-proton-donating acid; will accept two electrons • Lewis base: electron pair donors ...
... Lewis Acids and Bases • Lewis acid: non-proton-donating acid; will accept two electrons • Lewis base: electron pair donors ...
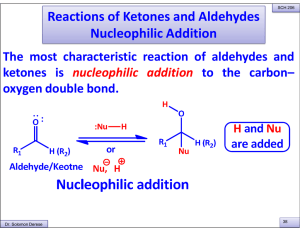
Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes Nucleophilic Addition
... Five or six-membered cyclic hemiacetals are relatively strain free and thus form spontaneously from the corresponding hydroxy aldehydes in water. ...
... Five or six-membered cyclic hemiacetals are relatively strain free and thus form spontaneously from the corresponding hydroxy aldehydes in water. ...
Unit 2
... Hydrocarbon Derivatives are carbon compounds in which any hydrogen atom has been replaced by another atom (ex. F, P, Br, Cl, N). Organic compounds generally share some common physical and chemical properties. Most carbon compounds are _________ electrolytes or are very ________electrolytes, and tend ...
... Hydrocarbon Derivatives are carbon compounds in which any hydrogen atom has been replaced by another atom (ex. F, P, Br, Cl, N). Organic compounds generally share some common physical and chemical properties. Most carbon compounds are _________ electrolytes or are very ________electrolytes, and tend ...
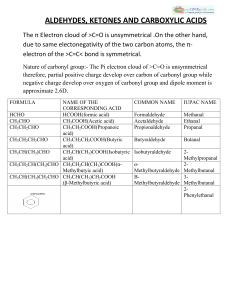
ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
... :-Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids are important classes of organic compounds containing carbonyl groups. :-They are highly polar molecules. :-They boil at higher temperatures than the corresponding hydrocarbons and weakly polar compounds such as ethers. :-Lower members are soluble in water b ...
... :-Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids are important classes of organic compounds containing carbonyl groups. :-They are highly polar molecules. :-They boil at higher temperatures than the corresponding hydrocarbons and weakly polar compounds such as ethers. :-Lower members are soluble in water b ...
Solid-State 23Na Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of Sodium
... proton decoupling. Under such circumstances, the observed central-transition 23Na NMR spectra exhibit typical features arising from second-order quadrupole interaction. In most cases only a single Na+ site is present in each of the complexes, making it possible to analyze the 1D MAS spectra in a str ...
... proton decoupling. Under such circumstances, the observed central-transition 23Na NMR spectra exhibit typical features arising from second-order quadrupole interaction. In most cases only a single Na+ site is present in each of the complexes, making it possible to analyze the 1D MAS spectra in a str ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.