GLOSSARY
... a carbon-atom chain 4. alkane a hydrocarbon that contains only single bonds 5. alkene a hydrocarbon that contains double covalent bonds 6. alkyl group a group of atoms that is formed when one hydrogen atom is removed from an alkane molecule 7. alkyl halide an organic compound in which one or more ha ...
... a carbon-atom chain 4. alkane a hydrocarbon that contains only single bonds 5. alkene a hydrocarbon that contains double covalent bonds 6. alkyl group a group of atoms that is formed when one hydrogen atom is removed from an alkane molecule 7. alkyl halide an organic compound in which one or more ha ...
Organic chemistry
... If more then one sidechain comes off the main chain, label each one, and write which carbon it branched from. ...
... If more then one sidechain comes off the main chain, label each one, and write which carbon it branched from. ...
1 - contentextra
... Saturated A compound which contains only single bonds between carbon atoms, no carbon–carbon double or triple bonds. Secondary carbon atom A carbon atom that is attached to the functional group and also to one hydrogen atom. SN1 Substitution nucleophilic unimolecular. A substitution reaction in whic ...
... Saturated A compound which contains only single bonds between carbon atoms, no carbon–carbon double or triple bonds. Secondary carbon atom A carbon atom that is attached to the functional group and also to one hydrogen atom. SN1 Substitution nucleophilic unimolecular. A substitution reaction in whic ...
Aromatic nitro compounds Background Nomenclature
... The simplest aromatic nitro compound, nitrobenzene, also known as nitrobenzol, molecular formula C6H5NO2. Often highly explosive, especially when the compound contains more than one nitro group. One of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used global ...
... The simplest aromatic nitro compound, nitrobenzene, also known as nitrobenzol, molecular formula C6H5NO2. Often highly explosive, especially when the compound contains more than one nitro group. One of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used global ...
Chemical Composition Notes
... OXIDATION NUMBERS __________________ – a number assigned to an atom in a molecular compound or ion that indicates the general distribution of electrons among the bonded atoms Rules in Assigning Oxidation Numbers Oxidation Number of Pure Element = Binary Molecular Compound Less electronegative atom = ...
... OXIDATION NUMBERS __________________ – a number assigned to an atom in a molecular compound or ion that indicates the general distribution of electrons among the bonded atoms Rules in Assigning Oxidation Numbers Oxidation Number of Pure Element = Binary Molecular Compound Less electronegative atom = ...
Nugget
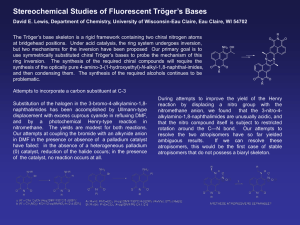
... Substitution of the halogen in the 3-bromo-4-alkylamino-1,8naphthalimides has been accomplished by Ullmann-type displacement with excess cuprous cyanide in refluxing DMF, and by a photochemical Henry-type reaction in nitromethane. The yields are modest for both reactions. Our attempts at coupling th ...
... Substitution of the halogen in the 3-bromo-4-alkylamino-1,8naphthalimides has been accomplished by Ullmann-type displacement with excess cuprous cyanide in refluxing DMF, and by a photochemical Henry-type reaction in nitromethane. The yields are modest for both reactions. Our attempts at coupling th ...
Organic Chemistry 25.2 Introduction to Hydrocarbons
... Alkenes are named in the same way as alkanes with the suffix -ene replacing the -ane in alkanes. The location of the double bond is indicated by a prefix ...
... Alkenes are named in the same way as alkanes with the suffix -ene replacing the -ane in alkanes. The location of the double bond is indicated by a prefix ...
7. In CCl 4 carbon is the “central atom”. In NF3 nitrogen is the
... 24 electrons instead of 22. (Where did the extra two electrons come from?) ...
... 24 electrons instead of 22. (Where did the extra two electrons come from?) ...
Carbon Compounds - Montgomery County Schools
... name? Give the ratio of carbons, hydrogens, & oxygens. 48. Name the 3 MOST common monosaccharides. 51. What are double sugars called? Name & describe the process that forms them. 52. Name a disaccharide. 53. What forms a polysaccharide? Name a polysaccharide found in animals. Name one found in plant ...
... name? Give the ratio of carbons, hydrogens, & oxygens. 48. Name the 3 MOST common monosaccharides. 51. What are double sugars called? Name & describe the process that forms them. 52. Name a disaccharide. 53. What forms a polysaccharide? Name a polysaccharide found in animals. Name one found in plant ...
Active Reading 3.1: Matter and Substances
... Carbohydrates are organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in the proportion of 1:2:1. 2 Carbohydrates are a key source of energy, and they are found in most foods—especially fruits, vegetables, and grains. 3 The building blocks of carbohydrates are single sugars called monosacch ...
... Carbohydrates are organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in the proportion of 1:2:1. 2 Carbohydrates are a key source of energy, and they are found in most foods—especially fruits, vegetables, and grains. 3 The building blocks of carbohydrates are single sugars called monosacch ...
Chapter 2 - A
... Carbon forms strong covalent bonds Carbon atoms can bond to other carbon atoms Carbon has the ability to form millions of different large and complex structures No other element can come close to matching carbon’s versatility ...
... Carbon forms strong covalent bonds Carbon atoms can bond to other carbon atoms Carbon has the ability to form millions of different large and complex structures No other element can come close to matching carbon’s versatility ...
CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS
... H2O: -Atomic number of O is 8. Its electronic configuration is 2,6 and thus requires two electrons to complete its octet (8). Atomic number of H is 1. Its electronic configuration is 1 and thus requires 1 electron to complete the K shell.(duplet) Thus O shares two of its valence electrons with each ...
... H2O: -Atomic number of O is 8. Its electronic configuration is 2,6 and thus requires two electrons to complete its octet (8). Atomic number of H is 1. Its electronic configuration is 1 and thus requires 1 electron to complete the K shell.(duplet) Thus O shares two of its valence electrons with each ...
Ionic bonds
... Atoms are lonely hearts that are constantly in search of partners to bring stability to their lives. Your job is to play matchmaker and make each atom stable by determining how many valence eeach element needs & finding a partner that will complete the valence energy level! ...
... Atoms are lonely hearts that are constantly in search of partners to bring stability to their lives. Your job is to play matchmaker and make each atom stable by determining how many valence eeach element needs & finding a partner that will complete the valence energy level! ...
Spectroscopy WS 2
... There are four isomeric Alcohols with the molecular formula C 4H10O. They can be distinguished using a variety of analytical techniques. (a) ...
... There are four isomeric Alcohols with the molecular formula C 4H10O. They can be distinguished using a variety of analytical techniques. (a) ...
04_lecture_presentation
... Overview: Carbon: The Backbone of Life • Living organisms consist mostly of carbon-based compounds • Carbon is unparalleled in its ability to form large, complex, and diverse molecules • Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter are all composed of carbon comp ...
... Overview: Carbon: The Backbone of Life • Living organisms consist mostly of carbon-based compounds • Carbon is unparalleled in its ability to form large, complex, and diverse molecules • Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter are all composed of carbon comp ...
ppt
... Found to be teratogen Was found in some animals that only the S stereoisomer is teratogenic – but turns out they both are. ...
... Found to be teratogen Was found in some animals that only the S stereoisomer is teratogenic – but turns out they both are. ...
Crazy Carbon - Cloudfront.net
... ex. Vision involves light changing chemical rhodopsin from one geometric isomer to another. ...
... ex. Vision involves light changing chemical rhodopsin from one geometric isomer to another. ...
Metallic and nonmetallic double perovskites: A case study of A $ _2
... the t2g orbitals. Moreover, the greater covalency of Ca-O bonds would directly compete with the t2g orbitals of the transition metal B, B’ cations for the O: 2pπ electrons and also reduce the Re-Re overlap. However, it is not clear that this would reduce the Fe-Fe superexchange, since the change in ...
... the t2g orbitals. Moreover, the greater covalency of Ca-O bonds would directly compete with the t2g orbitals of the transition metal B, B’ cations for the O: 2pπ electrons and also reduce the Re-Re overlap. However, it is not clear that this would reduce the Fe-Fe superexchange, since the change in ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.