Course Outline School of Business and Economics ECON 1950
... Principles of Macroeconomics (3,0,0) Calendar Description Students examine economic behaviour at the aggregate level, and the measurement and determination of national income. Topics include an introduction to economics; measuring macroeconomic variables including gross domestic product, unemploymen ...
... Principles of Macroeconomics (3,0,0) Calendar Description Students examine economic behaviour at the aggregate level, and the measurement and determination of national income. Topics include an introduction to economics; measuring macroeconomic variables including gross domestic product, unemploymen ...
Are We in a Recession? What Will It Look Like If We Have One?
... The Federal Reserve—stuck between a rock and a hard place Doesn't want to lose its price-stability credibility by cutting interest rates too far too fast and igniting inflation both through a misjudgment of domestic demand and because cutting interest rates means a weaker dollar, higher dollar price ...
... The Federal Reserve—stuck between a rock and a hard place Doesn't want to lose its price-stability credibility by cutting interest rates too far too fast and igniting inflation both through a misjudgment of domestic demand and because cutting interest rates means a weaker dollar, higher dollar price ...
833-2869-1-SP
... Source: Viñals J., Gray S. & Eckhold, K.(2016), The Broader View: The Positive Effects of Negative Nominal Interest Rates, IMF Global Economy Forum ...
... Source: Viñals J., Gray S. & Eckhold, K.(2016), The Broader View: The Positive Effects of Negative Nominal Interest Rates, IMF Global Economy Forum ...
Izmir University of Economics Name: Department of
... (c) decrease the government deficit. (d) increase investment spending. 3) Each of the following might be a specific fiscal policy action EXCEPT (a) reducing interest rates to stimulate consumer demand. (b) increasing government spending on military hardware. (c) increasing transfer payments (d) impo ...
... (c) decrease the government deficit. (d) increase investment spending. 3) Each of the following might be a specific fiscal policy action EXCEPT (a) reducing interest rates to stimulate consumer demand. (b) increasing government spending on military hardware. (c) increasing transfer payments (d) impo ...
Chapter 14
... Fed buys bonds, lowers reserve ratio, lowers the discount rate, or increases reserve auctions Excess reserves increase Federal funds rate falls Money supply rises Interest rate falls ...
... Fed buys bonds, lowers reserve ratio, lowers the discount rate, or increases reserve auctions Excess reserves increase Federal funds rate falls Money supply rises Interest rate falls ...
Economic History of the US
... Commercial Banks Industrial Age…rise of Investment Banks Peculiar to US Big companies raise money from savers directly… …by issuing stocks and bonds Underwriting and trading ...
... Commercial Banks Industrial Age…rise of Investment Banks Peculiar to US Big companies raise money from savers directly… …by issuing stocks and bonds Underwriting and trading ...
Presentation to the Pasadena Business Community co-sponsored by
... We injected massive amount of liquidity into the financial system. ...
... We injected massive amount of liquidity into the financial system. ...
“The Great Recession of 2007-2009 and The Great Depression of
... Troubled Asset Relief Program • Allocated $700 billion for Treasury to buy up toxic assets from financial institutions. In effect government buys stakes in private companies. • December 2008, Bush mandates that TARP funds can be used to support any industry government deems needs it to avert system ...
... Troubled Asset Relief Program • Allocated $700 billion for Treasury to buy up toxic assets from financial institutions. In effect government buys stakes in private companies. • December 2008, Bush mandates that TARP funds can be used to support any industry government deems needs it to avert system ...
EconomicPolicy AP2013
... Result: Banks have MORE money to lend, and consumers have MORE money to spend! ...
... Result: Banks have MORE money to lend, and consumers have MORE money to spend! ...
The Great Depression 1929
... – Biggest drop in first year – Biggest drop peak to trough – Biggest drop in the last year. ...
... – Biggest drop in first year – Biggest drop peak to trough – Biggest drop in the last year. ...
money problems in the new republic
... • Thomas Jefferson and Madison argue that: 1) National Bank is unconstitutional 2) Protective Tariff is unfair to southerners Is the National Bank Constitutional? If so how? ...
... • Thomas Jefferson and Madison argue that: 1) National Bank is unconstitutional 2) Protective Tariff is unfair to southerners Is the National Bank Constitutional? If so how? ...
Answers to Chapter 12 Questions
... the accumulation of assets, liabilities, and equity as of a specific point in time. The Report of Income refers to the bank's income statement which presents information about the flow of revenues and expenses between two points in time. 2. a-3; b-1; c-2. 3. a-5,6,12; b-2,10; c-3, 13; d-1,8,15; e-9, ...
... the accumulation of assets, liabilities, and equity as of a specific point in time. The Report of Income refers to the bank's income statement which presents information about the flow of revenues and expenses between two points in time. 2. a-3; b-1; c-2. 3. a-5,6,12; b-2,10; c-3, 13; d-1,8,15; e-9, ...
week_5_assignment
... major component of M1; the other major component is (currency, checkable deposits) _______. 18. M2 is equal to M1 plus (checking, savings) _______ deposits that include money market (deposit accounts, mutual funds) _______, plus (small, large) _______ time deposits, and plus money market (deposit ac ...
... major component of M1; the other major component is (currency, checkable deposits) _______. 18. M2 is equal to M1 plus (checking, savings) _______ deposits that include money market (deposit accounts, mutual funds) _______, plus (small, large) _______ time deposits, and plus money market (deposit ac ...
Presentation to the Association of Trade and Forfaiting in the... Ritz Carlton, San Francisco, CA
... Of course, nothing in life is certain, and there are factors outside our control that could get in the way—heightened geopolitical tensions, for instance, or instability in foreign financial markets, particularly in emerging economies. We’ll continue to keep an eye on those developments, but as thin ...
... Of course, nothing in life is certain, and there are factors outside our control that could get in the way—heightened geopolitical tensions, for instance, or instability in foreign financial markets, particularly in emerging economies. We’ll continue to keep an eye on those developments, but as thin ...
Fed Delays Interest
... The decision left uncertain for a while longer just when the Fed would raise its benchmark rate, which has been near zero since December 2008. Most of the policy makers at the meeting, 13 of 17, indicated they still expect to move this year, but that was down from the 15 who held that view in June. ...
... The decision left uncertain for a while longer just when the Fed would raise its benchmark rate, which has been near zero since December 2008. Most of the policy makers at the meeting, 13 of 17, indicated they still expect to move this year, but that was down from the 15 who held that view in June. ...
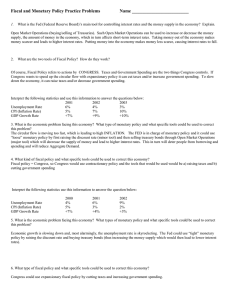
Answer Key--Fiscal and Monetary Policy Practice
... Economic growth is slowing down and, most alarmingly, the unemployment rate is skyrocketing. The Fed could use “tight” monetary policy by raising the discount rate and buying treasury bonds (thus increasing the money supply which would then lead to lower interest rates). ...
... Economic growth is slowing down and, most alarmingly, the unemployment rate is skyrocketing. The Fed could use “tight” monetary policy by raising the discount rate and buying treasury bonds (thus increasing the money supply which would then lead to lower interest rates). ...
Final Exam
... net gain of about $25 billion. • The government purchased $205 billion worth of preferred stock from 707 financial institutions. Of that investment, those institutions paid back $192 billion, or 94%. The CBO believes that taxpayers will see a net gain of $18 billion from that program. ...
... net gain of about $25 billion. • The government purchased $205 billion worth of preferred stock from 707 financial institutions. Of that investment, those institutions paid back $192 billion, or 94%. The CBO believes that taxpayers will see a net gain of $18 billion from that program. ...
Review Sheet - Syracuse University
... (a) what sellers generally accept and buyers generally use to pay for goods and services. (b) an asset that can be used to transport purchasing power from one period of time to another. (c) a standard unit that provides a consistent way of quoting prices. (d) the ability to buy something today but t ...
... (a) what sellers generally accept and buyers generally use to pay for goods and services. (b) an asset that can be used to transport purchasing power from one period of time to another. (c) a standard unit that provides a consistent way of quoting prices. (d) the ability to buy something today but t ...
assignment #2
... b) How much new money has been created? Total money created is $52233.28 million ...
... b) How much new money has been created? Total money created is $52233.28 million ...
Problem Set 3 Answers - University of Wisconsin–Madison
... If the U.S. interest rate is raised today by one percentage point, but inflationary expectations are also rising simultaneously also by one percentage point, then the real interest rate stays constant, and the dollar does not change value. ...
... If the U.S. interest rate is raised today by one percentage point, but inflationary expectations are also rising simultaneously also by one percentage point, then the real interest rate stays constant, and the dollar does not change value. ...
Ch14-- Monetary Policy
... money supply is growing at 5% per year, and real GDP is growing at 2% per year, what must the inflation rate (P%) be? ...
... money supply is growing at 5% per year, and real GDP is growing at 2% per year, what must the inflation rate (P%) be? ...
Slide 1
... Unconventional tool today is “quantitative easing 2” (QE2) FOMC statement on Wednesday: “To promote a stronger pace of economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at levels consistent with its mandate, the Committee decided today to expand its holdings of securities. …. In add ...
... Unconventional tool today is “quantitative easing 2” (QE2) FOMC statement on Wednesday: “To promote a stronger pace of economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at levels consistent with its mandate, the Committee decided today to expand its holdings of securities. …. In add ...
A Hands-off Central Banker? Marriner S. Eccles and the
... Eccles considered the role of the Federal Reserve as fiscal agent of the Treasury as the essential one, in a situation that only expansionary fiscal policy could turn the economy around; Prebisch considered that an independent central bank could minimize the effects of external crises in smooth out ...
... Eccles considered the role of the Federal Reserve as fiscal agent of the Treasury as the essential one, in a situation that only expansionary fiscal policy could turn the economy around; Prebisch considered that an independent central bank could minimize the effects of external crises in smooth out ...
Dollar Weakens Against Euro But Off Lows
... fiscal gap and is even dragging out the potential recovery further with the Brazilian real expected to remain under pressure," said Arnaud Masset, an analyst at Swissquote Bank SA in Gland, Switzerland. Brazilians returned to the streets in nationwide protests on Sunday against Rousseff’s government ...
... fiscal gap and is even dragging out the potential recovery further with the Brazilian real expected to remain under pressure," said Arnaud Masset, an analyst at Swissquote Bank SA in Gland, Switzerland. Brazilians returned to the streets in nationwide protests on Sunday against Rousseff’s government ...
2013 Spring Sample Final Solutions
... 3) the increase in the overall money supply would be smaller than the Bank of Canada may have intended. A) 1 or 2 B) 2 or 3 C) 2 only D) 3 only E) 1 only ...
... 3) the increase in the overall money supply would be smaller than the Bank of Canada may have intended. A) 1 or 2 B) 2 or 3 C) 2 only D) 3 only E) 1 only ...