Accretion Disk
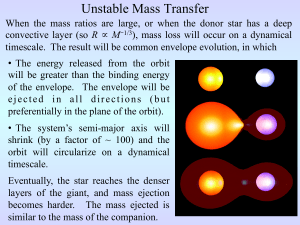
... still be two stars: a low mass star still burning hydrogen, and a helium proto-white dwarf. The separation will be very small, and the hot core will ionize the ejected envelope, producing a planetary nebula. ...
... still be two stars: a low mass star still burning hydrogen, and a helium proto-white dwarf. The separation will be very small, and the hot core will ionize the ejected envelope, producing a planetary nebula. ...
SM_Taurus - Cloudy Nights
... and high contrast. When embarked on your own investigation into the Pleiades nebulosity use low powers. Pay careful attention to the area around Merope - where the brightest swatch of nebula resides (the Merope Nebula). On a good night you may see nebulosity throughout the cluster. Be aware that a s ...
... and high contrast. When embarked on your own investigation into the Pleiades nebulosity use low powers. Pay careful attention to the area around Merope - where the brightest swatch of nebula resides (the Merope Nebula). On a good night you may see nebulosity throughout the cluster. Be aware that a s ...
- Europhysics News
... The huge diversity in the physical and orbital properties of exoplanets forces us to reconsider the model of planetary formation currently accepted for the solar system. This model is based upon the properties of planetary orbits, mostly coplanar, circular and concentric around the Sun. Following th ...
... The huge diversity in the physical and orbital properties of exoplanets forces us to reconsider the model of planetary formation currently accepted for the solar system. This model is based upon the properties of planetary orbits, mostly coplanar, circular and concentric around the Sun. Following th ...
Studying Variable stars using Small Telescopes Observational
... Light curve of Eclipsing Binaries - Algol A binary system of stars in which the orbital plane lies edge-on to us so that the component stars periodically eclipse one another. ...
... Light curve of Eclipsing Binaries - Algol A binary system of stars in which the orbital plane lies edge-on to us so that the component stars periodically eclipse one another. ...
Exercise 7
... declination (think of this as a space latitude). The declination runs from -90° (celestial south pole) to +90° (celestial north pole). Both of these coordinates are laminated to the metal pole bases. In addition, the stars have been colored according to their spectral classes; blue balls represent O ...
... declination (think of this as a space latitude). The declination runs from -90° (celestial south pole) to +90° (celestial north pole). Both of these coordinates are laminated to the metal pole bases. In addition, the stars have been colored according to their spectral classes; blue balls represent O ...
The First Thousand Exoplanets
... variation is inversely proportional to the square root of the orbital distance and proportional to the planet mass times the sin of the inclination angle of the orbit. Because of the uncertainty in inclination, a minimum mass is measured and for any sample of planet systems at random orientations t ...
... variation is inversely proportional to the square root of the orbital distance and proportional to the planet mass times the sin of the inclination angle of the orbit. Because of the uncertainty in inclination, a minimum mass is measured and for any sample of planet systems at random orientations t ...
H-R Diagram
... properties and life cycle can be determined. A simplified H-R diagram appears in your textbook. In this laboratory, you will construct an H-R diagram using data on the 20 stars that are nearest to our sun (Figure 21.1) and the 20 stars that appear brightest in our sky (Figure 21.2). Then you will us ...
... properties and life cycle can be determined. A simplified H-R diagram appears in your textbook. In this laboratory, you will construct an H-R diagram using data on the 20 stars that are nearest to our sun (Figure 21.1) and the 20 stars that appear brightest in our sky (Figure 21.2). Then you will us ...
Quantum Well Electron Gain Structures and Infrared
... • If planet is close in, orbit will be unstable and chaotic • Moving in/out of HZ is probably hard on life development • If planet is far away (orbiting BOTH stars), orbit is stable, but typically outside the HZ (!) ...
... • If planet is close in, orbit will be unstable and chaotic • Moving in/out of HZ is probably hard on life development • If planet is far away (orbiting BOTH stars), orbit is stable, but typically outside the HZ (!) ...
The Life and Times of a Neutron Star
... Exotic neutron stars may not be so rare. • Highly magnetized neutron stars may be as common as standard radio pulsars, but they don’t radio out their locations so they are harder to find. ...
... Exotic neutron stars may not be so rare. • Highly magnetized neutron stars may be as common as standard radio pulsars, but they don’t radio out their locations so they are harder to find. ...
HR Diagram - TeacherWeb
... In the early 1900s, astronomers identified many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will discover how some of these characteristics are related. Start by moving your cursor over the stars in the Star collect ...
... In the early 1900s, astronomers identified many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will discover how some of these characteristics are related. Start by moving your cursor over the stars in the Star collect ...
Astrophysics Outline—Option E
... E.1.2 Distinguish between a stellar cluster and a constellation. E.1.3 Define the light year. E.1.4 Compare the relative distances between stars within a galaxy and between galaxies, in terms of order of magnitude. E.1.5 Describe the apparent motion of the stars/constellations over a period of a nig ...
... E.1.2 Distinguish between a stellar cluster and a constellation. E.1.3 Define the light year. E.1.4 Compare the relative distances between stars within a galaxy and between galaxies, in terms of order of magnitude. E.1.5 Describe the apparent motion of the stars/constellations over a period of a nig ...
Chapter 8 - TeacherWeb
... Gravity pulls the dust and gas together into a sphere. As the sphere becomes denser it becomes hotter. Hydrogen changes to helium by a process called nuclear fusion. When a star dies its materials return to space---sometimes to form new stars. Stars can be classified by their size, mass, brightness, ...
... Gravity pulls the dust and gas together into a sphere. As the sphere becomes denser it becomes hotter. Hydrogen changes to helium by a process called nuclear fusion. When a star dies its materials return to space---sometimes to form new stars. Stars can be classified by their size, mass, brightness, ...
Supernova - Mid-Pacific Institute
... supported by the release of nuclear energy. If the star is particularly massive, then its core will collapse and in so doing will release a huge amount of energy. This will cause a blast wave that ejects the star's envelope into interstellar space. ...
... supported by the release of nuclear energy. If the star is particularly massive, then its core will collapse and in so doing will release a huge amount of energy. This will cause a blast wave that ejects the star's envelope into interstellar space. ...
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1
... 1. What is the Julian date at midnight CST on 2-3 September 2013? 2. What is the CST of local midnight? 3. At midnight CST: Compute the hour angles of the 5 brightest stars. Which, if any, are observable (zenith distance <60o )? Which, if any, are above the horizon? 4. Which of these 5 stars can be ...
... 1. What is the Julian date at midnight CST on 2-3 September 2013? 2. What is the CST of local midnight? 3. At midnight CST: Compute the hour angles of the 5 brightest stars. Which, if any, are observable (zenith distance <60o )? Which, if any, are above the horizon? 4. Which of these 5 stars can be ...
Nucleus hydrogen helium Relative Mass 1.007825 4.0037 Helium
... star may eventually form a black hole. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. ...
... star may eventually form a black hole. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. ...
Chapter 30 Notes
... • Giant stars called Cepheid variables brighten and fade in a regular pattern. Most Cepheids have regular cycles. The longer the cycle, the brighter the star’s absolute magnitude. • Scientists compare the Cepheid’s absolute magnitude and the Cepheid’s apparent magnitude to calculate the distance to ...
... • Giant stars called Cepheid variables brighten and fade in a regular pattern. Most Cepheids have regular cycles. The longer the cycle, the brighter the star’s absolute magnitude. • Scientists compare the Cepheid’s absolute magnitude and the Cepheid’s apparent magnitude to calculate the distance to ...
Topic Outline - Physics Rocks!
... Solve problems involving stellar parallax. Absolute and apparent magnitudes E.3.5 Describe the apparent magnitude scale E.3.4 ...
... Solve problems involving stellar parallax. Absolute and apparent magnitudes E.3.5 Describe the apparent magnitude scale E.3.4 ...
Using the Southern Cross to find south
... 1. Find the Southern Cross. 2. Draw an imaginary line through the long axis of the Southern Cross beginning with the star that marks the top of the cross. (Note: during summer, the Southern Cross is low in the sky and therefore upside-down). 3. Extend the line four and a half times the length of the ...
... 1. Find the Southern Cross. 2. Draw an imaginary line through the long axis of the Southern Cross beginning with the star that marks the top of the cross. (Note: during summer, the Southern Cross is low in the sky and therefore upside-down). 3. Extend the line four and a half times the length of the ...
February 2013 - astronomy for beginners
... brightest stars are called Pollux (β) and Castor (α) and are known as the Gemini Twins. The twins originated in a Greek myth which told that they had one mother but two fathers. Castor was the mortal son of King Tyndareus but Pollux was the immortal son of the God Zeus who had disguised himself as C ...
... brightest stars are called Pollux (β) and Castor (α) and are known as the Gemini Twins. The twins originated in a Greek myth which told that they had one mother but two fathers. Castor was the mortal son of King Tyndareus but Pollux was the immortal son of the God Zeus who had disguised himself as C ...
Slide 1
... observational proof is still lacking. We do know, however, that many or most of the elements beyond iron had to have been created very rapidly, so supernovae are still the best bet. ...
... observational proof is still lacking. We do know, however, that many or most of the elements beyond iron had to have been created very rapidly, so supernovae are still the best bet. ...
Day-26
... We can take images and directly see the planets. We can detect radio signals from life on the planets. A star’s light could be affected by its planet. ...
... We can take images and directly see the planets. We can detect radio signals from life on the planets. A star’s light could be affected by its planet. ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.