DTU 8e Chap 11 Characterizing Stars
... the background of distant stars. The star’s parallax angle (p) is equal to the angle between the Sun and Earth, as seen from the star. ...
... the background of distant stars. The star’s parallax angle (p) is equal to the angle between the Sun and Earth, as seen from the star. ...
14 The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation
... completely empty, but filled with a very dilute gas and dust. It produces some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested in the interstellar medium because a) dense interstellar clouds are the birth place of stars b) clouds alter and absorb the light from stars behind them ...
... completely empty, but filled with a very dilute gas and dust. It produces some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested in the interstellar medium because a) dense interstellar clouds are the birth place of stars b) clouds alter and absorb the light from stars behind them ...
Advances in Environmental Biology Approach Mahin Shahrivar and
... is changed to the energy publishing as the light and heat [16]. Our sun is about 5 milliard years old and about 4.5 milliard years later it will be ended up by consumption its hydrogen; in this case the Helium begins to melt producing carbon and oxygen and the temperature of the sun reaches to 100 m ...
... is changed to the energy publishing as the light and heat [16]. Our sun is about 5 milliard years old and about 4.5 milliard years later it will be ended up by consumption its hydrogen; in this case the Helium begins to melt producing carbon and oxygen and the temperature of the sun reaches to 100 m ...
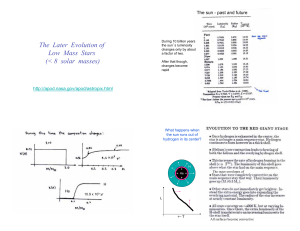
The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses)
... The C-O core is degenerate and transports its radiation by conduction. ...
... The C-O core is degenerate and transports its radiation by conduction. ...
chapter15SurveyStars..
... frequencies. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stefan-Boltzmann_law 2. Hotter objects emit photons with a higher average energy.http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wien%27s_displacement_law ...
... frequencies. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stefan-Boltzmann_law 2. Hotter objects emit photons with a higher average energy.http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wien%27s_displacement_law ...
The universe is faster, colder, and wackier than anything we can
... that any object in the universe exerts, and yet is still able to force another body to orbit it? Many small galaxies have correspondingly weak gravity. But if two low-mass galaxies can somehow come together in an isolated region of space such that they can move without being affected by larger galaxi ...
... that any object in the universe exerts, and yet is still able to force another body to orbit it? Many small galaxies have correspondingly weak gravity. But if two low-mass galaxies can somehow come together in an isolated region of space such that they can move without being affected by larger galaxi ...
ph507-16-1exo2
... Direct imaging of planets is difficult because of the enormous difference in brightness between the star and the planet, and the small angular separation between them. Direct detection: must be large and distant from star Circumstellar dust discs. (Circumstantial evidence.) Disc of material around t ...
... Direct imaging of planets is difficult because of the enormous difference in brightness between the star and the planet, and the small angular separation between them. Direct detection: must be large and distant from star Circumstellar dust discs. (Circumstantial evidence.) Disc of material around t ...
Model of Stars—6 Oct Test 1: Average 17 (75%) •
... The luminosity of a star (the energy produced every second) depends on temperature and size. What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? (Without modifying the sun, what can I do to make the sun brighter or fainter?) A. B. ...
... The luminosity of a star (the energy produced every second) depends on temperature and size. What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? (Without modifying the sun, what can I do to make the sun brighter or fainter?) A. B. ...
Topic 3: The Spectroscope - Danielle`s science9 weebly
... Spectroscopy: The Science of Colour The significance of the spectral lines was discovered about 50 years later when Kirschoff and Bunsen, two chemists used a spectroscope to observe various chemicals when they were heated. They found some of the lines missing in some of the chemicals. Each particula ...
... Spectroscopy: The Science of Colour The significance of the spectral lines was discovered about 50 years later when Kirschoff and Bunsen, two chemists used a spectroscope to observe various chemicals when they were heated. They found some of the lines missing in some of the chemicals. Each particula ...
Introduction to Basic Stargazing Part II - Naples Free-Net
... astronomical unit (au) – one au is defined as the average distance from Earth to the Sun. There are two reasons for this; 1. It greatly improves computational ease of raw data. 2. It improves comprehension of relative distances. For example, the astronomical unit is measured at 92,956,000 miles. If ...
... astronomical unit (au) – one au is defined as the average distance from Earth to the Sun. There are two reasons for this; 1. It greatly improves computational ease of raw data. 2. It improves comprehension of relative distances. For example, the astronomical unit is measured at 92,956,000 miles. If ...
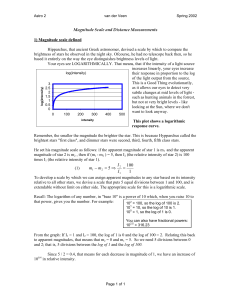
Magnitude Scale and Distance Measurements
... and this give us a way to find the relative intensities of any two stars, based on their apparent magnitudes. Try a few examples: 1. The apparent magnitude of Spica is +0.98, and the apparent magnitude of Sirius A is -1.44. How many times brighter is Sirius A than Spica? 2. The apparent magnitude of ...
... and this give us a way to find the relative intensities of any two stars, based on their apparent magnitudes. Try a few examples: 1. The apparent magnitude of Spica is +0.98, and the apparent magnitude of Sirius A is -1.44. How many times brighter is Sirius A than Spica? 2. The apparent magnitude of ...
Stars: from Adolescence to Old Age
... terms of star lifetimes!) create conditions where the pressure and gravity are out of sync and the pulsations continue for a time • Larger, more luminous stars will pulsate with longer periods than the smaller, fainter stars – because gravity takes longer to pull the more extended outer layers of th ...
... terms of star lifetimes!) create conditions where the pressure and gravity are out of sync and the pulsations continue for a time • Larger, more luminous stars will pulsate with longer periods than the smaller, fainter stars – because gravity takes longer to pull the more extended outer layers of th ...
EXOPLANETS The search for planets beyond our solar system
... The first exoplanets were discovered through the gravitational tug they exert on their parent stars, which causes the stars to wobble. This motion is revealed in the spectrum of a star’s emitted light. Elements present in the star absorb particular wavelengths of light to produce a characteristic se ...
... The first exoplanets were discovered through the gravitational tug they exert on their parent stars, which causes the stars to wobble. This motion is revealed in the spectrum of a star’s emitted light. Elements present in the star absorb particular wavelengths of light to produce a characteristic se ...
Milky Way
... Further observations show that there are two classes: • Long gamma-ray bursts (> 2 sec): Found in young, star forming regions. Some are clearly massive supernovae (hypernovae?) because spectra are seen. • Short gamma-ray bursts (< 2 sec): Found in young and old regions. Thought to be two merging neu ...
... Further observations show that there are two classes: • Long gamma-ray bursts (> 2 sec): Found in young, star forming regions. Some are clearly massive supernovae (hypernovae?) because spectra are seen. • Short gamma-ray bursts (< 2 sec): Found in young and old regions. Thought to be two merging neu ...
star guide 2013
... clouds in the atmosphere and dark regions of exposed rock on the surface. Beyond Mars lies the gas giant Jupiter, the largest planet in the Solar System. Viewed through a telescope the planet’s disc appears crossed by dark belts. A huge storm known as the Great Red Spot can also be seen. This is two ...
... clouds in the atmosphere and dark regions of exposed rock on the surface. Beyond Mars lies the gas giant Jupiter, the largest planet in the Solar System. Viewed through a telescope the planet’s disc appears crossed by dark belts. A huge storm known as the Great Red Spot can also be seen. This is two ...
Daynightseasonsstars-1
... 1. What is changing at the same (annual) timescale that we are observing the changing zodiac? 2. Do the constellations appear to change positions in the night sky as Earth travels around our Sun throughout the year? 3. Are the constellations themselves moving? 4. What causes this apparent change in ...
... 1. What is changing at the same (annual) timescale that we are observing the changing zodiac? 2. Do the constellations appear to change positions in the night sky as Earth travels around our Sun throughout the year? 3. Are the constellations themselves moving? 4. What causes this apparent change in ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.