D1 Stellar quantities (PPT)
... overdensity in the cloud caused the contraction to begin and the overdensity to grow, thus producing a faster contraction ▪ Initially, most of the motions of the cloud particles were random, yet the nebula had a net rotation. As collapse proceeded, the rotation speed of the cloud gradually increased ...
... overdensity in the cloud caused the contraction to begin and the overdensity to grow, thus producing a faster contraction ▪ Initially, most of the motions of the cloud particles were random, yet the nebula had a net rotation. As collapse proceeded, the rotation speed of the cloud gradually increased ...
Astronomy 114 – Summary of Important Concepts #2 1 Stars: key
... Q: A star has an absolute magnitude of 4 and lies 1 parsec from the Earth. Suppose that star is moved to a distance of 10 parsecs from the Sun. What is its absolute magnitude? A: The absolute magnitude is still 4. Absolute magnitude does not depend on distance. It measures the luminosity of the star ...
... Q: A star has an absolute magnitude of 4 and lies 1 parsec from the Earth. Suppose that star is moved to a distance of 10 parsecs from the Sun. What is its absolute magnitude? A: The absolute magnitude is still 4. Absolute magnitude does not depend on distance. It measures the luminosity of the star ...
Project 4: The HR diagram. Open clusters
... This site has collected almost all the available data on open clusters and you can call up a plot showing the cluster you have measured. You can scale this plot to show the stars you see in your image, and then, by just clicking on a particular star, get its published values of V and (B-V) – provide ...
... This site has collected almost all the available data on open clusters and you can call up a plot showing the cluster you have measured. You can scale this plot to show the stars you see in your image, and then, by just clicking on a particular star, get its published values of V and (B-V) – provide ...
1.3 Lifecycle of stars
... the same age, but different masses, appear as the whole cluster ages. After 10 million years, the most massive stars have already left the Main Sequence, while many of the least massive have not even reached it yet. ...
... the same age, but different masses, appear as the whole cluster ages. After 10 million years, the most massive stars have already left the Main Sequence, while many of the least massive have not even reached it yet. ...
No Slide Title
... • Cen X-2 brighter and softer than Sco X-1. Tau X-1 also detected. (Cen X-3 not seen) • SL 723 (July 1968) and 724 (April 1969) with largest PCS to date, 2 x 1380 cm2 • spectra of brightest sources ...
... • Cen X-2 brighter and softer than Sco X-1. Tau X-1 also detected. (Cen X-3 not seen) • SL 723 (July 1968) and 724 (April 1969) with largest PCS to date, 2 x 1380 cm2 • spectra of brightest sources ...
The Northern Winter Constellations - Science
... rough hexagon of very bright stars. This is called the Winter Hexagon. Starting at Rigel, if you go counterclockwise by one, you end up at Aldebaran in Taurus. Go counterclockwise once more and you end up at Capella in Auriga. Go counterclockwise once more and you end up at the pair of stars Pollux ...
... rough hexagon of very bright stars. This is called the Winter Hexagon. Starting at Rigel, if you go counterclockwise by one, you end up at Aldebaran in Taurus. Go counterclockwise once more and you end up at Capella in Auriga. Go counterclockwise once more and you end up at the pair of stars Pollux ...
NGC 3370 Spiral Galaxy
... • Stars form in clusters, with all types of stars forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the ...
... • Stars form in clusters, with all types of stars forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the ...
death_low_mass
... • Stars form in clusters, with all types of stars forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the ...
... • Stars form in clusters, with all types of stars forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the ...
The Temperature of Stars
... – The apparent motion of stars is the motion visible to the unaided eye. – Apparent motion is caused by the movement of Earth. – The rotation of Earth causes the apparent motion of stars sees as though the stars are moving counter-clockwise around the North Star. – Earth’s revolution around the sun ...
... – The apparent motion of stars is the motion visible to the unaided eye. – Apparent motion is caused by the movement of Earth. – The rotation of Earth causes the apparent motion of stars sees as though the stars are moving counter-clockwise around the North Star. – Earth’s revolution around the sun ...
society journal - Auckland Astronomical Society
... When people think of astrophotography, they usually think of impressive photos of the Milky Way or Deep Space. This image captures neither of those, but what it does capture is the true sense of a New Zealand starry sky as seen from many of the towns throughout the country. It’s a beautifully compos ...
... When people think of astrophotography, they usually think of impressive photos of the Milky Way or Deep Space. This image captures neither of those, but what it does capture is the true sense of a New Zealand starry sky as seen from many of the towns throughout the country. It’s a beautifully compos ...
Chapter 13 (Properties of Stars)
... 24. The largest known stars. 25. Most low mass, red stars in our neighborhood. 26. Sirius B, the hot white dwarf only 1/1000th as luminous as the sun. 27. The vast majority of bright blue naked eye stars. 28. Most naked eye stars that appear red or orange in color. 29. The most massive young stars. ...
... 24. The largest known stars. 25. Most low mass, red stars in our neighborhood. 26. Sirius B, the hot white dwarf only 1/1000th as luminous as the sun. 27. The vast majority of bright blue naked eye stars. 28. Most naked eye stars that appear red or orange in color. 29. The most massive young stars. ...
QDSpaperFred1.tex
... and other high-density stars with eq. 4. Eq. 5 eliminates most normal and all giant stars. Eq. 3 eliminates hot stars, even on the main sequence, because we do not expect them to live long enough for intelligest life to develop. Eq. 1 limits the sample to stars with accurately measured distances. Th ...
... and other high-density stars with eq. 4. Eq. 5 eliminates most normal and all giant stars. Eq. 3 eliminates hot stars, even on the main sequence, because we do not expect them to live long enough for intelligest life to develop. Eq. 1 limits the sample to stars with accurately measured distances. Th ...
HW7-3
... enough in their cores to run fusion. These are brown dwarfs. (b) Very massive stars have so much fusion that the outward forces overwhelm gravity and they are unstable. Stars greater than 100M☉ cannot even form. Stars more than 25 or 30M☉ engage in mass loss and lose weight down to 25 or 30M☉. ...
... enough in their cores to run fusion. These are brown dwarfs. (b) Very massive stars have so much fusion that the outward forces overwhelm gravity and they are unstable. Stars greater than 100M☉ cannot even form. Stars more than 25 or 30M☉ engage in mass loss and lose weight down to 25 or 30M☉. ...
Two new transiting extra-solar planets discovered with SuperWASP
... discovered with SuperWASP and SOPHIE A team of British, French and Swiss astronomers has just discovered two new transiting extra-solar planets. This double discovery was made using the British SuperWASP cameras at La Palma, Spain, and the new SOPHIE spectrograph at Haute-Provence, France. These two ...
... discovered with SuperWASP and SOPHIE A team of British, French and Swiss astronomers has just discovered two new transiting extra-solar planets. This double discovery was made using the British SuperWASP cameras at La Palma, Spain, and the new SOPHIE spectrograph at Haute-Provence, France. These two ...
pdf file with complementary illustrations / animations
... our understanding of how planetary systems form and evolve. Embargoed until 20 June 2016 at 1600 London time / 1100 US Eastern time For this discovery, the team monitored a 2 million-year-old infant star called V830 Tau, located in the Taurus stellar nursery, some 430 light-years away. Over the 1.5 ...
... our understanding of how planetary systems form and evolve. Embargoed until 20 June 2016 at 1600 London time / 1100 US Eastern time For this discovery, the team monitored a 2 million-year-old infant star called V830 Tau, located in the Taurus stellar nursery, some 430 light-years away. Over the 1.5 ...
Astronomy_Stellar_Evolution_and_Type_II_Supernovae_Exam
... 5) This object was the first of its kind to have its diameter measured with “Michelson's Beam Interferometer” ...
... 5) This object was the first of its kind to have its diameter measured with “Michelson's Beam Interferometer” ...
How Bright is that star?
... Luminosity is the amount of energy a star gives off as light. Measured in Watts or Solar Units or “Sols” However for all practical purposes Absolute magnitude and Luminosity of a star measure the same thing. Absolute Magnitude Approximate Luminosity ...
... Luminosity is the amount of energy a star gives off as light. Measured in Watts or Solar Units or “Sols” However for all practical purposes Absolute magnitude and Luminosity of a star measure the same thing. Absolute Magnitude Approximate Luminosity ...
h-r_diagram_online_lab
... Step 4: Now add a series. Name it “Nearby Stars” and again make sure the cells within the “Type” column for “Table 2: Nearby Stars” are set as your X values, and cells within the “log (L/Lsun)” column for “Table 2: Nearby Stars” are set as your Y values. (Define the x values by clicking on the litt ...
... Step 4: Now add a series. Name it “Nearby Stars” and again make sure the cells within the “Type” column for “Table 2: Nearby Stars” are set as your X values, and cells within the “log (L/Lsun)” column for “Table 2: Nearby Stars” are set as your Y values. (Define the x values by clicking on the litt ...
PHYS 390 Lecture 29 - White dwarfs and neutron stars 29
... Sirius was observed (by a new 18-inch refractor) to be a binary system in 1862, almost 20 years after it was proposed to be such as system by Friedrich Bessel. The smaller of the binary pair has a mass now quoted at 1.05±0.03 solar masses, and a surface temperature (determined half a century later) ...
... Sirius was observed (by a new 18-inch refractor) to be a binary system in 1862, almost 20 years after it was proposed to be such as system by Friedrich Bessel. The smaller of the binary pair has a mass now quoted at 1.05±0.03 solar masses, and a surface temperature (determined half a century later) ...
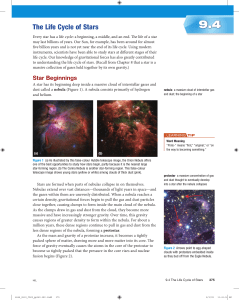
The Life Cycle of Stars
... cool. These stars are located on the H–R diagram off the main sequence, in the upper right corner and lower left corner. How could cooler stars, which likely produce less energy per unit area, be more luminous than hotter stars? It was reasoned that these cooler stars have a greater surface area tha ...
... cool. These stars are located on the H–R diagram off the main sequence, in the upper right corner and lower left corner. How could cooler stars, which likely produce less energy per unit area, be more luminous than hotter stars? It was reasoned that these cooler stars have a greater surface area tha ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.