Things to know: This meant as a guide to what you should know. I
... Know the HR diagram!!!!!! What is the sequence of spectral types with decreasing mass and temperature (OBAFGKM)? Which stars are the most common? What is a brown dwarf? Where do star form? What are protostars and pre-main sequence stars? How long does each phase last? What is the source energy for ...
... Know the HR diagram!!!!!! What is the sequence of spectral types with decreasing mass and temperature (OBAFGKM)? Which stars are the most common? What is a brown dwarf? Where do star form? What are protostars and pre-main sequence stars? How long does each phase last? What is the source energy for ...
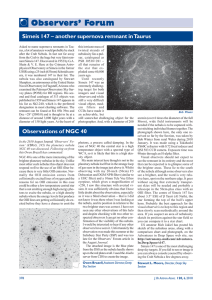
Betelgeuse
... and the narrow bandwidth avoids any spectral lines, and so we see the star relatively undistorted," said Townes. "We have also had the good fortune to have an instrument that has operated in a very similar manner for some 15 years, providing a long and consistent series of measurements that no one e ...
... and the narrow bandwidth avoids any spectral lines, and so we see the star relatively undistorted," said Townes. "We have also had the good fortune to have an instrument that has operated in a very similar manner for some 15 years, providing a long and consistent series of measurements that no one e ...
Lecture18
... luminosity of the star Using the luminosity and the apparent brightness, the astronomer can calculate the distance to the star The relationship between period and luminosity was discovered by Henrietta Leavit in 1908 Leavit found that the brighter cepheids always had longer periods These cepheids we ...
... luminosity of the star Using the luminosity and the apparent brightness, the astronomer can calculate the distance to the star The relationship between period and luminosity was discovered by Henrietta Leavit in 1908 Leavit found that the brighter cepheids always had longer periods These cepheids we ...
Exam 3 Study Guide
... The theoretical upper limit for the mass of a super massive black hole is 50 billion solar masses. A quasar is a type of active galactic nucleus (AGN). Blazars are AGN which are oriented such that its radio jet is directed toward our line of sight. The luminosity of an AGN is >1012 LSun. The size of ...
... The theoretical upper limit for the mass of a super massive black hole is 50 billion solar masses. A quasar is a type of active galactic nucleus (AGN). Blazars are AGN which are oriented such that its radio jet is directed toward our line of sight. The luminosity of an AGN is >1012 LSun. The size of ...
Ch.11 Massive star death
... Neutron Stars & Supernova Remnants • Energy released by collapse of core drives outer layers into space • The Crab Nebula is the remnant of the supernova seen in A.D. 1054 ...
... Neutron Stars & Supernova Remnants • Energy released by collapse of core drives outer layers into space • The Crab Nebula is the remnant of the supernova seen in A.D. 1054 ...
A Triple Conjunction
... an object seen for two and a half months. Such doubts do not stop many “stars” from being depicted as comets – this practice is particularly widespread in Spain where stylised comets which show a large star with a flowing curved tail (thus getting the best of both worlds), adorn Christmas trees and ...
... an object seen for two and a half months. Such doubts do not stop many “stars” from being depicted as comets – this practice is particularly widespread in Spain where stylised comets which show a large star with a flowing curved tail (thus getting the best of both worlds), adorn Christmas trees and ...
The Ancient Heavens: Exploring the History of Astronomy
... these activities help participants appreciate not only what we know, but how we know it. ...
... these activities help participants appreciate not only what we know, but how we know it. ...
Stars - Mike Brotherton
... The Fate of our Sun and the End of Earth • Sun will expand to a red giant in ~ 5 billion years • Expands to ~ Earth’s orbit • Earth will then be ...
... The Fate of our Sun and the End of Earth • Sun will expand to a red giant in ~ 5 billion years • Expands to ~ Earth’s orbit • Earth will then be ...
Here
... This region of a molecular cloud shows several dense clumps of gas which over the next 100,000 years may collapse to form more stars. The properties of these clumps such as their size, density, temperature, chemistry and angular momentum tell us the initial conditions for star formation. We measure ...
... This region of a molecular cloud shows several dense clumps of gas which over the next 100,000 years may collapse to form more stars. The properties of these clumps such as their size, density, temperature, chemistry and angular momentum tell us the initial conditions for star formation. We measure ...
Target Stars for Earth-like Planet Searches with the Terrestrial
... basic parameters for an Earth-like planet near each of the stars, including the diameter of the Habitable Zone (HZ). For these purposes, the HZ is defined as the distance from the star at which an Earth-like planet would have the same equilibrium temperature as Earth. (3) Select those stars for whic ...
... basic parameters for an Earth-like planet near each of the stars, including the diameter of the Habitable Zone (HZ). For these purposes, the HZ is defined as the distance from the star at which an Earth-like planet would have the same equilibrium temperature as Earth. (3) Select those stars for whic ...
Lecture 1
... Size and Time Scales of the Universe Physical scale: What does the solar system look like? How far away are the stars? How big is our Milky Way? How does it compare to other galaxies? How far away are galaxies? Time scale: How much time do we live? how much time do stars live? how old is the univers ...
... Size and Time Scales of the Universe Physical scale: What does the solar system look like? How far away are the stars? How big is our Milky Way? How does it compare to other galaxies? How far away are galaxies? Time scale: How much time do we live? how much time do stars live? how old is the univers ...
about Stars
... • Astronomers quantify the “color” of a star by using the difference in brightness between the brightness in the B and V spectral regions • The B-V color is related to the slope of the ...
... • Astronomers quantify the “color” of a star by using the difference in brightness between the brightness in the B and V spectral regions • The B-V color is related to the slope of the ...
Properties of Stars - Indiana State University
... Analyzing the HR Diagram • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given lumino ...
... Analyzing the HR Diagram • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given lumino ...
The Marathon
... The Marathon As soon as it is possible to see the guide stars for the first objects, begin looking for the first objects. As darkness begins to prevail over twilight, the first objects must be hunted quickly. Do not linger over them, as they will be difficult to find and see at best. The first hour ...
... The Marathon As soon as it is possible to see the guide stars for the first objects, begin looking for the first objects. As darkness begins to prevail over twilight, the first objects must be hunted quickly. Do not linger over them, as they will be difficult to find and see at best. The first hour ...
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
The H-R Diagram
... • Parallax, the only direct method of finding distances to stars, except for rare eclipsing binaries • Spectral types are a Temperature sequence: OBAFGKM hot to cool. • 90% of all stars are on Main Sequence= hydrogen burning stars • Main Sequence is a mass sequence, lower right to upper left is risi ...
... • Parallax, the only direct method of finding distances to stars, except for rare eclipsing binaries • Spectral types are a Temperature sequence: OBAFGKM hot to cool. • 90% of all stars are on Main Sequence= hydrogen burning stars • Main Sequence is a mass sequence, lower right to upper left is risi ...
slides
... It is the densest form of matter in the observable universe: 1017 kg/m3 – a teaspoon of neutron star matter would be 100 million tons Due to conservation of angular momentum, it is spinning very fast, up to thousands times a second – angular momentum of the star now carried by a small object, hundre ...
... It is the densest form of matter in the observable universe: 1017 kg/m3 – a teaspoon of neutron star matter would be 100 million tons Due to conservation of angular momentum, it is spinning very fast, up to thousands times a second – angular momentum of the star now carried by a small object, hundre ...
stargazing - davis.k12.ut.us
... Groups of stars are called constellations, patterns of stars in the sky that have been identified and named. Some constellations can be seen all year. These are stars that are close to the North Star. The North Star is directly above the North Pole and does not appear to move. The other stars seem t ...
... Groups of stars are called constellations, patterns of stars in the sky that have been identified and named. Some constellations can be seen all year. These are stars that are close to the North Star. The North Star is directly above the North Pole and does not appear to move. The other stars seem t ...
Other Solar Systems Around Other Stars
... How to Discover and Characterize Atmospheres, and Climate of Exoplanets? • During a transit, some of the light of the parent star is filtering through the atmosphere of the planet and making it into our telescopes. • Measuring the depth of the transit light loss in narrow wavelength bands results i ...
... How to Discover and Characterize Atmospheres, and Climate of Exoplanets? • During a transit, some of the light of the parent star is filtering through the atmosphere of the planet and making it into our telescopes. • Measuring the depth of the transit light loss in narrow wavelength bands results i ...
Presentation
... have such alignment, and the fraction decreases for planets with larger orbits. For a planet orbiting a sun-sized star at 1AU, the probability of a random alignment producing a transit is ...
... have such alignment, and the fraction decreases for planets with larger orbits. For a planet orbiting a sun-sized star at 1AU, the probability of a random alignment producing a transit is ...
AST101 Lecture 13 The Lives of the Stars
... • Stars generate luminosity through fusion of H into He • The lifetime of a star is proportional to the amount of fuel it has (mass) divided by the rate at which it expends the fuel (luminosity) • The lifetime τ ~ M/L ~ M-2 (because L ~ M3) • τ ranges from 4x106 years for O stars to ~1012 years ...
... • Stars generate luminosity through fusion of H into He • The lifetime of a star is proportional to the amount of fuel it has (mass) divided by the rate at which it expends the fuel (luminosity) • The lifetime τ ~ M/L ~ M-2 (because L ~ M3) • τ ranges from 4x106 years for O stars to ~1012 years ...
AST101_lect_13
... • Stars generate luminosity through fusion of H into He • The lifetime of a star is proportional to the amount of fuel it has (mass) divided by the rate at which it expends the fuel (luminosity) • The lifetime τ ~ M/L ~ M-2 (because L ~ M3) ...
... • Stars generate luminosity through fusion of H into He • The lifetime of a star is proportional to the amount of fuel it has (mass) divided by the rate at which it expends the fuel (luminosity) • The lifetime τ ~ M/L ~ M-2 (because L ~ M3) ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.