White dwarfs that crossed the Chandrasekhar limit
... 100,000 times that of water, while that of Sun’s core is just about 100 times. ...
... 100,000 times that of water, while that of Sun’s core is just about 100 times. ...
UNIT VIII/B: THE EARTH IN SPACE – STARS AND GALAXIES
... c. The various types of galaxies include: * Spiral galaxies, which are typically disk-shaped with a somewhat greater concentration of stars near their centers, often containing arms of stars extending from their central nucleus *Barred spiral galaxies, a type of spiral galaxy that has the stars arra ...
... c. The various types of galaxies include: * Spiral galaxies, which are typically disk-shaped with a somewhat greater concentration of stars near their centers, often containing arms of stars extending from their central nucleus *Barred spiral galaxies, a type of spiral galaxy that has the stars arra ...
Chapter 12
... Analyzing the HR Diagram • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given lumino ...
... Analyzing the HR Diagram • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given lumino ...
Sample Stellar Evolution TEST QUESTIONS
... 7. Nuclear fusion in stars is controlled by the dependence of density on mass. 8. The Sun has a core in which energy travels outward primarily by radiation. 9. Energy flows by radiation or convection inside stars but almost never by conduction. 10. Hydrostatic equilibrium refers to the balance betwe ...
... 7. Nuclear fusion in stars is controlled by the dependence of density on mass. 8. The Sun has a core in which energy travels outward primarily by radiation. 9. Energy flows by radiation or convection inside stars but almost never by conduction. 10. Hydrostatic equilibrium refers to the balance betwe ...
Evolution of High
... star…However, none has been found so far. – The neutron star is there, but it is not pulling in materials. Without materials around it, no X-ray emission can be detected. – Maybe a black hole (Chapter 13), instead of a neutron star, was formed? ...
... star…However, none has been found so far. – The neutron star is there, but it is not pulling in materials. Without materials around it, no X-ray emission can be detected. – Maybe a black hole (Chapter 13), instead of a neutron star, was formed? ...
using a cepheid variable to determine distance
... In this exercise you will use data taken from observations of a Cepheid variable star over a period of 80 days. On each day, the apparent visual magnitude was recorded. Using this data you will be able to plot a light-curve for this Cepheid, and from this light curve, determine the period of the lig ...
... In this exercise you will use data taken from observations of a Cepheid variable star over a period of 80 days. On each day, the apparent visual magnitude was recorded. Using this data you will be able to plot a light-curve for this Cepheid, and from this light curve, determine the period of the lig ...
Kepler 186f - Forum Skylive
... be ‘tidally locked’, which means one side always faces the star and the other side faces the cold open space, much like our moon is tidally locked with the Earth (we only see the “near side of the moon”). Fortunately, Kepler-186f orbits a fairly massive M dwarf star and it orbits at a large enough d ...
... be ‘tidally locked’, which means one side always faces the star and the other side faces the cold open space, much like our moon is tidally locked with the Earth (we only see the “near side of the moon”). Fortunately, Kepler-186f orbits a fairly massive M dwarf star and it orbits at a large enough d ...
July 2014 BRAS Newsletter - The Baton Rouge Astronomical Society
... the constellation Cygnus, monitoring their brightness photometrically every 30 minutes for four years. It was searching for any minute decreases in brightness that might indicate one or more planets transiting (passing in front of) their host star as seen from Earth. (For comparison, if Earth transi ...
... the constellation Cygnus, monitoring their brightness photometrically every 30 minutes for four years. It was searching for any minute decreases in brightness that might indicate one or more planets transiting (passing in front of) their host star as seen from Earth. (For comparison, if Earth transi ...
No Slide Title
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
AST301.Ch21.StellarExpl - University of Texas Astronomy
... 1054 A.D., the Crab Nebula. (Text has great images of what the remains of the explosion look like today, nearly 1000 years later.) A SN produces a billion solar luminosities in just a few hours or less. Until discovery of gamma ray bursts (ch.22), these were, gram for gram, the most luminous objects ...
... 1054 A.D., the Crab Nebula. (Text has great images of what the remains of the explosion look like today, nearly 1000 years later.) A SN produces a billion solar luminosities in just a few hours or less. Until discovery of gamma ray bursts (ch.22), these were, gram for gram, the most luminous objects ...
Death of Stars
... fusion of four Hydrogen nuclei to form a He nucleus and conversion of mass to energy The energy appears as K.E of the particles formed, high energy gamma rays and neutrinos The temperature of the star’s core ...
... fusion of four Hydrogen nuclei to form a He nucleus and conversion of mass to energy The energy appears as K.E of the particles formed, high energy gamma rays and neutrinos The temperature of the star’s core ...
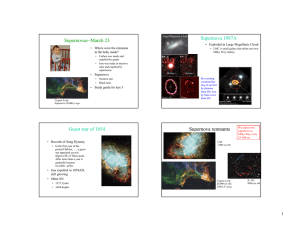
Supernovae March 23 − Supernova 1987A
... Sirius A, a main-sequence star Sirius B, an earth-sized white dwarf ...
... Sirius A, a main-sequence star Sirius B, an earth-sized white dwarf ...
Ch 28 Class Notes
... 2. An important class of pulsating stars are called _____________________________. These are yellow supergiants whose cycles of brightness range from about 1 day to 50 days (5 is average). The absolute magnitude of a Cepheid is related to the length of time between its periods of maximum brightness ...
... 2. An important class of pulsating stars are called _____________________________. These are yellow supergiants whose cycles of brightness range from about 1 day to 50 days (5 is average). The absolute magnitude of a Cepheid is related to the length of time between its periods of maximum brightness ...
Nebular theory
... the web”. Then click on the “Guided Tours” and then click on the Nebula folder. Watch the W5 Star Forming Region video and answer the questions below. Tour #1: The W5 Star Forming Region You may have to watch it a couple of times to get all the answers. 19. What are “O” stars? ...
... the web”. Then click on the “Guided Tours” and then click on the Nebula folder. Watch the W5 Star Forming Region video and answer the questions below. Tour #1: The W5 Star Forming Region You may have to watch it a couple of times to get all the answers. 19. What are “O” stars? ...
Announcements Evolution of High-Mass Stars: Red Supergiants
... • Parallax only works for nearby stars (within about 1000 light years) • For more distant stars, we use Standard Candles Car Headlights are standard candles: We use them to determine the car’s distance ...
... • Parallax only works for nearby stars (within about 1000 light years) • For more distant stars, we use Standard Candles Car Headlights are standard candles: We use them to determine the car’s distance ...
Shocking Truth about Massive Stars Lidia Oskinova Chandra’s First Decade of Discovery
... ’’A very energetic explosion of a massive star is likely to create a ... fireball.... the inner core of a massive, rapidly rotating star collapses into a ~10 M Kerr black hole ... A superstrong ~10 15 G magnetic field is needed to make the object ... a microquasar. Such events must be vary rare...to ...
... ’’A very energetic explosion of a massive star is likely to create a ... fireball.... the inner core of a massive, rapidly rotating star collapses into a ~10 M Kerr black hole ... A superstrong ~10 15 G magnetic field is needed to make the object ... a microquasar. Such events must be vary rare...to ...
Evolution of Stars
... Star is at the tip of the “asymptotic” branch: Core stops contracting; no fusion is occurring. What supports the core? How does the rest of the star support itself? Are gravity and outward pressure balanced? ...
... Star is at the tip of the “asymptotic” branch: Core stops contracting; no fusion is occurring. What supports the core? How does the rest of the star support itself? Are gravity and outward pressure balanced? ...
April 10th
... • Carbon and silicon atoms form grains, which are pushed outward by radiation • Red Giant loses material (as much as 10-4 solar masses per year) ...
... • Carbon and silicon atoms form grains, which are pushed outward by radiation • Red Giant loses material (as much as 10-4 solar masses per year) ...
Chapter 12 - Indiana State University
... Analyzing the HR Diagram • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given lumino ...
... Analyzing the HR Diagram • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given lumino ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.