astrocoursespring2012lec5-1-1
... appear smaller and fainter. When a telescope probes about 5 billion light years into look-back time, it can detect only the brightest galaxies, giant, elliptical galaxies – because spiral galaxies similar to the Milky Way are too dim to be seen at that distance ...
... appear smaller and fainter. When a telescope probes about 5 billion light years into look-back time, it can detect only the brightest galaxies, giant, elliptical galaxies – because spiral galaxies similar to the Milky Way are too dim to be seen at that distance ...
Luminosities and magnitudes of stars
... The solid angle, , that an object subtends at a point is a measure of how big that object appears to an observer at that point. For instance, a small object nearby could subtend the same solid angle as a large object far away. The solid angle is proportional to the surface area, S, of a projection ...
... The solid angle, , that an object subtends at a point is a measure of how big that object appears to an observer at that point. For instance, a small object nearby could subtend the same solid angle as a large object far away. The solid angle is proportional to the surface area, S, of a projection ...
Star Stuff
... - divides the light up into its colors (wavelengths) - use a smaller range of wavelengths than entire EM spectrum because instrumentation is different ...
... - divides the light up into its colors (wavelengths) - use a smaller range of wavelengths than entire EM spectrum because instrumentation is different ...
Astronomy and Space Science
... • The color receptors, called cones, are distributed densely and mainly near the center of vision. • The more sensitive rods can only detect light intensity, and are distributed mainly outside the center of vision. From bright to dark places, it takes 7-10 minutes for saturated rods to become dark a ...
... • The color receptors, called cones, are distributed densely and mainly near the center of vision. • The more sensitive rods can only detect light intensity, and are distributed mainly outside the center of vision. From bright to dark places, it takes 7-10 minutes for saturated rods to become dark a ...
Lecture 9
... Evolution of 4M☉ Stars For stars less than 6M☉ these last slides describe the evolution pretty well. There are some differences in the details that depend on the initial main-sequence mass. For stars that start with 4M☉, it gets hot enough in the cores to (1) avoid the helium flash and (2) to st ...
... Evolution of 4M☉ Stars For stars less than 6M☉ these last slides describe the evolution pretty well. There are some differences in the details that depend on the initial main-sequence mass. For stars that start with 4M☉, it gets hot enough in the cores to (1) avoid the helium flash and (2) to st ...
Red Giants - Faculty Web Pages
... Most blue stars are Main Sequence stars. But whereas some red stars in the list are simply tiny, cool Main Sequence stars, other red stars of the exact same color are huge Red Giants! Telling the difference between the Main Sequence red stars and the Red Giant stars involves some complex measurement ...
... Most blue stars are Main Sequence stars. But whereas some red stars in the list are simply tiny, cool Main Sequence stars, other red stars of the exact same color are huge Red Giants! Telling the difference between the Main Sequence red stars and the Red Giant stars involves some complex measurement ...
Planets
... Sun is 1,000 times more massive than Jupiter So Sun moves 1/1,000 as much as Jupiter Both orbit a Center of Mass which is 1,000x closer to center of Sun than Jupiter ...
... Sun is 1,000 times more massive than Jupiter So Sun moves 1/1,000 as much as Jupiter Both orbit a Center of Mass which is 1,000x closer to center of Sun than Jupiter ...
Lecture 15 Star Formation and Evolution 3/7
... • if Mass(WD) > 1.4 M(Sun) degenerate electrons can not resist gravity called Chandrasekhar limit and no WD has a mass greater than this • If WD can acquire mass from companion star and goes over this limit Supernova and (usually) a Neutron Star ...
... • if Mass(WD) > 1.4 M(Sun) degenerate electrons can not resist gravity called Chandrasekhar limit and no WD has a mass greater than this • If WD can acquire mass from companion star and goes over this limit Supernova and (usually) a Neutron Star ...
Planet formation - problems and future
... For about 300 years, from the middle of the seventeenth century to the middle of the twentieth, there were two fundamentally different, competing scenarios. The nebular hypothesis argued for the formation of planets from residual (or, in earlier versions, spin-ejected) circumstellar material and sug ...
... For about 300 years, from the middle of the seventeenth century to the middle of the twentieth, there were two fundamentally different, competing scenarios. The nebular hypothesis argued for the formation of planets from residual (or, in earlier versions, spin-ejected) circumstellar material and sug ...
here
... Alpha Centauri takes 4.3 years to get to us. Light from our sun only takes 8 minutes. Alpha Centauri are really three stars all orbiting each other. One of these stars Proxima Centauri is the closest star to Earth next to our sun. There are many kinds of stars, big and small, close and far, bright a ...
... Alpha Centauri takes 4.3 years to get to us. Light from our sun only takes 8 minutes. Alpha Centauri are really three stars all orbiting each other. One of these stars Proxima Centauri is the closest star to Earth next to our sun. There are many kinds of stars, big and small, close and far, bright a ...
What is a white dwarf?
... What is a white dwarf? • A white dwarf is the core left over from a low-mass star, supported against the crush of gravity by electron degeneracy pressure. • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? • It can acquire hydrogen from its companion through an accretion disk. As hydrogen ...
... What is a white dwarf? • A white dwarf is the core left over from a low-mass star, supported against the crush of gravity by electron degeneracy pressure. • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? • It can acquire hydrogen from its companion through an accretion disk. As hydrogen ...
Free Referat Word Dimensiune: 63.5KB
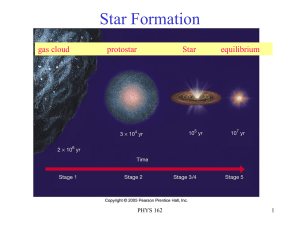
... 2. Pre-Main Sequence Once near-equilibrium has been established, the contraction slows down, but the star continues to radiate energy (light) and thus must continue to contract to provide gravitational energy to supply the necessary luminosity. The star must continue to contract until the temperatur ...
... 2. Pre-Main Sequence Once near-equilibrium has been established, the contraction slows down, but the star continues to radiate energy (light) and thus must continue to contract to provide gravitational energy to supply the necessary luminosity. The star must continue to contract until the temperatur ...
description
... to season as the Earth orbits the Sun. The stars will be in a different location (west of) as it was the previous night at the same exact time. Which stars & constellations you see depends on your latitude on Earth. People in the Southern hemisphere see different constellations at different times of ...
... to season as the Earth orbits the Sun. The stars will be in a different location (west of) as it was the previous night at the same exact time. Which stars & constellations you see depends on your latitude on Earth. People in the Southern hemisphere see different constellations at different times of ...
Review: How does a star*s mass determine its life story?
... Tidal forces would be gentler near a supermassive black hole because its radius is much bigger. ...
... Tidal forces would be gentler near a supermassive black hole because its radius is much bigger. ...
Nature of Stars 2
... back and forth between eyes, they use the biggest possible difference in observing position without leaving Earth - our planet’s orbit around the Sun. To do that, they observe a star, and they note where the star appears to be relative to more distant stars. Then, they wait 6 months; during this tim ...
... back and forth between eyes, they use the biggest possible difference in observing position without leaving Earth - our planet’s orbit around the Sun. To do that, they observe a star, and they note where the star appears to be relative to more distant stars. Then, they wait 6 months; during this tim ...
Stars (Ch. 13)
... Luminosity Classes • Another method was discovered to measure the luminosity of a star (other than using a star’s apparent magnitude and the inverse square law) – It was noticed that some stars had very narrow absorption lines compared to other stars of the same temperature – It was also noticed th ...
... Luminosity Classes • Another method was discovered to measure the luminosity of a star (other than using a star’s apparent magnitude and the inverse square law) – It was noticed that some stars had very narrow absorption lines compared to other stars of the same temperature – It was also noticed th ...
Variable Star Spectroscopy 2008
... Raw images of spectra are processed to generate useful scientific data. This is the raw image of the spectrum of 9th magnitude Be star IL Cep (HD216629) Taken using a Star Analyser (The grating was rotated so that the fainter close companion could be separated out). The image was corrected for darks ...
... Raw images of spectra are processed to generate useful scientific data. This is the raw image of the spectrum of 9th magnitude Be star IL Cep (HD216629) Taken using a Star Analyser (The grating was rotated so that the fainter close companion could be separated out). The image was corrected for darks ...
The Kepler spacecraft has found thousands of likely extrasolar
... habitable zone. In our solar system, Earth sits within this orbit, while Venus doesn’t. (Mars actually does too, which is a major reason why scientists continue to study it with hopes of finding signs of past life. They have confirmed that the Red Planet once had flowing water.) A smaller and cooler ...
... habitable zone. In our solar system, Earth sits within this orbit, while Venus doesn’t. (Mars actually does too, which is a major reason why scientists continue to study it with hopes of finding signs of past life. They have confirmed that the Red Planet once had flowing water.) A smaller and cooler ...
New light on our Sun`s fate - Space Telescope Science Institute
... of white-dwarf matter can be a million times higher than the Sun’s average. Because white dwarf densities are so high, we call these stellar remnants natural condensed-matter laboratories. The pressure at a white dwarf’s surface is extreme because of that density, and that makes its characteristic l ...
... of white-dwarf matter can be a million times higher than the Sun’s average. Because white dwarf densities are so high, we call these stellar remnants natural condensed-matter laboratories. The pressure at a white dwarf’s surface is extreme because of that density, and that makes its characteristic l ...
Plotting Variable Stars on the H
... north celestial pole and referred to as the North Star or Pole Star. Polaris is a multiple star system, consisting of Polaris A, a six solar mass Cepheid variable star, and two main sequence stars Polaris B and Polaris C. RR Lyrae variables are older pulsating white giants with low metallicity. They ...
... north celestial pole and referred to as the North Star or Pole Star. Polaris is a multiple star system, consisting of Polaris A, a six solar mass Cepheid variable star, and two main sequence stars Polaris B and Polaris C. RR Lyrae variables are older pulsating white giants with low metallicity. They ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.