Brightness and Temperature of Stars
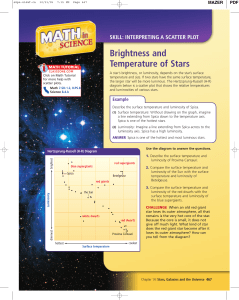
... A star’s brightness, or luminosity, depends on the star’s surface temperature and size. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star will be more luminous. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram below is a scatter plot that shows the relative temperatures and luminosities of variou ...
... A star’s brightness, or luminosity, depends on the star’s surface temperature and size. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star will be more luminous. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram below is a scatter plot that shows the relative temperatures and luminosities of variou ...
Surveying the Stars
... hydrogen into helium in their cores like the Sun Luminous mainsequence stars are hot (blue) Less luminous ones are cooler (yellow or red) ...
... hydrogen into helium in their cores like the Sun Luminous mainsequence stars are hot (blue) Less luminous ones are cooler (yellow or red) ...
Name - MIT
... 24) Which is not a reason why all large modern telescopes tend to be reflectors? A) It is much easier to make a high-quality mirror than the same quality lens B) Large mirrors are much lighter than large lenses C) Lenses focus different wavelengths of light slightly differently. Mirrors do not have ...
... 24) Which is not a reason why all large modern telescopes tend to be reflectors? A) It is much easier to make a high-quality mirror than the same quality lens B) Large mirrors are much lighter than large lenses C) Lenses focus different wavelengths of light slightly differently. Mirrors do not have ...
Spectral analysis for the RV Tau star R Sct: In this section, we will
... have luminosity classes of III, II, or I (where class II has properties in between III and I). Luminosity class V stars, like the sun, are main sequence stars and are generally used for reference as they do not vary and their intrinsic properties are well known. “By eye” we can see that the blue spe ...
... have luminosity classes of III, II, or I (where class II has properties in between III and I). Luminosity class V stars, like the sun, are main sequence stars and are generally used for reference as they do not vary and their intrinsic properties are well known. “By eye” we can see that the blue spe ...
Part A
... Different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum have different wavelengths and different energies. You can see only a small part of the energy in these wavelengths. ...
... Different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum have different wavelengths and different energies. You can see only a small part of the energy in these wavelengths. ...
The Stars of Namaqualand
... generations. Aristoteles (384 – 322 B.C.), a Greek mathematician, was the first man who proof scientifically that the earth is round and not flat. He pointed out that you could see stars in Alexandria who are not visible from Athens. And he wrote down that you could see the shadow of the earth on th ...
... generations. Aristoteles (384 – 322 B.C.), a Greek mathematician, was the first man who proof scientifically that the earth is round and not flat. He pointed out that you could see stars in Alexandria who are not visible from Athens. And he wrote down that you could see the shadow of the earth on th ...
Stellar Evolution Guiding Questions Stars Evolve
... • Red giant becomes less luminous and smaller, but hotter. The core is in a steady state: – Temperature increases, core expands – Core expands, temperature decreases • Shell hydrogen fusion rate drops that lead to a lower ...
... • Red giant becomes less luminous and smaller, but hotter. The core is in a steady state: – Temperature increases, core expands – Core expands, temperature decreases • Shell hydrogen fusion rate drops that lead to a lower ...
General Introduction 1. Luminosity, Flux and Magnitude The
... The evolution of the Sun is shown schematically in Fig. 7.3. The red giant phase occurs after the interior of the Sun is exhausted of hydrogen and helium burning initiates. The Sun is not massive enough to burn elements beyond He, so after shedding roughly half its mass in a violent wind leading to ...
... The evolution of the Sun is shown schematically in Fig. 7.3. The red giant phase occurs after the interior of the Sun is exhausted of hydrogen and helium burning initiates. The Sun is not massive enough to burn elements beyond He, so after shedding roughly half its mass in a violent wind leading to ...
Stars - CBSD.org
... night sky were “first order magnitude” stars. • As they got dimmer, he classified them as “second magnitude,” “third magnitude,” and so on… • He got up to magnitude 6, after which stars are too dim to be seen without a telescope. • So, a star’s apparent magnitude is essentially its brightness. – The ...
... night sky were “first order magnitude” stars. • As they got dimmer, he classified them as “second magnitude,” “third magnitude,” and so on… • He got up to magnitude 6, after which stars are too dim to be seen without a telescope. • So, a star’s apparent magnitude is essentially its brightness. – The ...
Death of Stars • Models of Star behavior can give estimates of how
... • Crab Nebula in 1057 (Chinese observed it) • Tycho’s star in 1527 • Kepler’s star in 1604 • SN1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud. The neutrino flux from this event was seen before the visible light was observed. The star was known as Sanduleak 69-202, a blue supergiant 25 times more massive than t ...
... • Crab Nebula in 1057 (Chinese observed it) • Tycho’s star in 1527 • Kepler’s star in 1604 • SN1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud. The neutrino flux from this event was seen before the visible light was observed. The star was known as Sanduleak 69-202, a blue supergiant 25 times more massive than t ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... 1. During May the constellation Cancer is visible near the Western Horizon. However in June the Cancer is no longer visible in the night sky. The reason for that is that (a) the Earth is spinning about North-South axis. (b) the Earth is revolving around the Sun. (c) the Earth has rotational axis tip ...
... 1. During May the constellation Cancer is visible near the Western Horizon. However in June the Cancer is no longer visible in the night sky. The reason for that is that (a) the Earth is spinning about North-South axis. (b) the Earth is revolving around the Sun. (c) the Earth has rotational axis tip ...
Student Handout - Mr. vallee`s Class Site
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
Wednesday, April 17 - Otterbein University
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
Lecture (Powerpoint)
... the mass of the Sun, or ~80 Jupiter masses) never ``turn on'' Central temperatures never get hot enough for nuclear burning to begin in earnest Nuclear burning is what powers the star through its life Star sits around as a brown dwarf – too big and hot to be a planet, too small and cold to be a real ...
... the mass of the Sun, or ~80 Jupiter masses) never ``turn on'' Central temperatures never get hot enough for nuclear burning to begin in earnest Nuclear burning is what powers the star through its life Star sits around as a brown dwarf – too big and hot to be a planet, too small and cold to be a real ...
Star Constellations
... some stars are smaller than our Sun, and some are larger. Except for our own Sun, all stars are so far away that they only look like single points—even through a telescope. Constellations ...
... some stars are smaller than our Sun, and some are larger. Except for our own Sun, all stars are so far away that they only look like single points—even through a telescope. Constellations ...
mass of star
... (as Main Sequence Stars)? A star on Main Sequence has fusion of H to He in its core. How fast depends on mass of H available and rate of fusion. Mass of H in core depends on mass of star. Fusion rate is related to luminosity (fusion reactions make the radiation energy). ...
... (as Main Sequence Stars)? A star on Main Sequence has fusion of H to He in its core. How fast depends on mass of H available and rate of fusion. Mass of H in core depends on mass of star. Fusion rate is related to luminosity (fusion reactions make the radiation energy). ...
The magnitude scale, parallax, the parsec, and Cepheid distances
... Typical range of Abs. mag: stars -‐1 to +10, galaxies -‐24 to -‐6 Typical range of app. mag: stars/galaxies, -‐27 (Sun) to +30 (faintest detectable star or galaxy) – Objects with app mag < ...
... Typical range of Abs. mag: stars -‐1 to +10, galaxies -‐24 to -‐6 Typical range of app. mag: stars/galaxies, -‐27 (Sun) to +30 (faintest detectable star or galaxy) – Objects with app mag < ...
Constellations and the Galactic Plane
... Constellations are simply patterns of the brightest stars in the heavens that inspired the ancients to attribute names and stories to. Orion the hunter, Cygnus the swan, Leo the lion are all familiar names to northern hemisphere night sky watchers. There are 88 named constellations, each having nume ...
... Constellations are simply patterns of the brightest stars in the heavens that inspired the ancients to attribute names and stories to. Orion the hunter, Cygnus the swan, Leo the lion are all familiar names to northern hemisphere night sky watchers. There are 88 named constellations, each having nume ...
chapter 7 review questions
... GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: How do atoms interact with light? F 5. An absorption spectrum is also called a bright line spectrum. GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: What kind of spectra do you see when you look at celestial objects? T. 6. Hydrogen alpha is the longest wavelength Balmer line. F ...
... GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: How do atoms interact with light? F 5. An absorption spectrum is also called a bright line spectrum. GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: What kind of spectra do you see when you look at celestial objects? T. 6. Hydrogen alpha is the longest wavelength Balmer line. F ...
What is a white dwarf?
... What is a white dwarf? • A white dwarf is the core left over from a lowmass star, supported against the crush of gravity by electron degeneracy pressure. • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? • It can acquire hydrogen from its companion through an accretion disk. As hy ...
... What is a white dwarf? • A white dwarf is the core left over from a lowmass star, supported against the crush of gravity by electron degeneracy pressure. • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? • It can acquire hydrogen from its companion through an accretion disk. As hy ...
Earth in Space and Time (SC.5.E.5.1)
... actually larger than the Sun. If this is true, why do these stars appear like points of light in the sky? A. These stars are hotter than the Sun. B. These stars have less mass than the Sun. C. These stars are farther away from Earth than the Sun is. D. These stars are made of different chemicals tha ...
... actually larger than the Sun. If this is true, why do these stars appear like points of light in the sky? A. These stars are hotter than the Sun. B. These stars have less mass than the Sun. C. These stars are farther away from Earth than the Sun is. D. These stars are made of different chemicals tha ...
29-4 - Fremont Peak Observatory
... been Secretary, Treasurer and President before retiring from the FPOA Board at the end of 2012. Rick has also been the principal liaison between State Parks and the FPOA during his tenure as resident ranger at the Peak and as a member of the board. No one could hope to equal the decades of service a ...
... been Secretary, Treasurer and President before retiring from the FPOA Board at the end of 2012. Rick has also been the principal liaison between State Parks and the FPOA during his tenure as resident ranger at the Peak and as a member of the board. No one could hope to equal the decades of service a ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.























