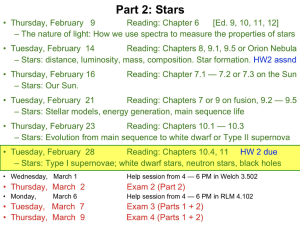
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 3
... used, what kinds of planets have been found, how many planets have been found, what kind of orbits do the planets have? 4. Most of the exoplanets that have been found are “hot Jupiter’s”: large gas giants orbiting very close to their star. Explain why these types of planets are easiest to find with ...
... used, what kinds of planets have been found, how many planets have been found, what kind of orbits do the planets have? 4. Most of the exoplanets that have been found are “hot Jupiter’s”: large gas giants orbiting very close to their star. Explain why these types of planets are easiest to find with ...
Part B
... • Hypernovae - collapse of stars of greater than 30 solar masses which are spinning rapidly. • The black hole forms before star outer layers contract very much. ...
... • Hypernovae - collapse of stars of greater than 30 solar masses which are spinning rapidly. • The black hole forms before star outer layers contract very much. ...
ASTR 1101-001 Spring 2008 - Louisiana State University
... Transient Events (in time) also occur ...
... Transient Events (in time) also occur ...
powerpoint file
... The surface gravity is so high that a 150 pound person would weigh a million tons. You would be squeezed flatter than a piece of paper. The fastest pulsar known has a period of 0.0014 s. The star spins 642 times per second. Dozens of such “millisecond pulsars” are known. More are being discovered. I ...
... The surface gravity is so high that a 150 pound person would weigh a million tons. You would be squeezed flatter than a piece of paper. The fastest pulsar known has a period of 0.0014 s. The star spins 642 times per second. Dozens of such “millisecond pulsars” are known. More are being discovered. I ...
Standard candles
... For distances which are too large to measure using parallax, astronomers use 'standard candles'. Light sources which are further away appear fainter because the light is spread out over a greater area. If we know how luminous a source really is, then we can estimate its distance from how bright it a ...
... For distances which are too large to measure using parallax, astronomers use 'standard candles'. Light sources which are further away appear fainter because the light is spread out over a greater area. If we know how luminous a source really is, then we can estimate its distance from how bright it a ...
Lec12
... squeezed as they move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
... squeezed as they move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
cancer, la constelac..
... Cancer, and this is why the Tropic of Cancer was named so (In the present day the sun now reaches the solstice point near the star eta () Geminorum.) To find Cancer in the sky look between Gemini and Leo, although you may need a dark sky to see all it's stars. According to Greek mythology Cancer wa ...
... Cancer, and this is why the Tropic of Cancer was named so (In the present day the sun now reaches the solstice point near the star eta () Geminorum.) To find Cancer in the sky look between Gemini and Leo, although you may need a dark sky to see all it's stars. According to Greek mythology Cancer wa ...
Summary of the Presentation
... planet. Because stars slowly increase their luminosity during their main sequence phase, they actually are suitable hosts only during about 75% of their main sequence life. Hence F6, and larger, stars are too short-lived. Stars that are too small, however, have CHZs (circumstellar habitable zones) s ...
... planet. Because stars slowly increase their luminosity during their main sequence phase, they actually are suitable hosts only during about 75% of their main sequence life. Hence F6, and larger, stars are too short-lived. Stars that are too small, however, have CHZs (circumstellar habitable zones) s ...
If you wish to a copy of this months Night Sky News
... Denebola the A3 type star at the end of Leo’s tail is about 39 light years away, and, in these times, shines with a magnitude of 2.14. However, up until about 400 years ago, Denebola was recorded as a first magnitude star. The reason for this is still something of a mystery. Were observations inacc ...
... Denebola the A3 type star at the end of Leo’s tail is about 39 light years away, and, in these times, shines with a magnitude of 2.14. However, up until about 400 years ago, Denebola was recorded as a first magnitude star. The reason for this is still something of a mystery. Were observations inacc ...
Distances of the Stars
... Luminosity Distance Relation A star’s luminosity, apparent brightness, and distance from the earth are related through the inverse square law. If any two of these quantities are known, the third can be calculated. ...
... Luminosity Distance Relation A star’s luminosity, apparent brightness, and distance from the earth are related through the inverse square law. If any two of these quantities are known, the third can be calculated. ...
Midterm Study Game
... What was Copernicus’ contribution to Astronomy? Copernicus was the scientist who first believed that the Sun was the center of the solar system, not the Earth AND that all the objects in our solar system revolve around the sun. Galileo also helped confirm this with his trusty telescope! ...
... What was Copernicus’ contribution to Astronomy? Copernicus was the scientist who first believed that the Sun was the center of the solar system, not the Earth AND that all the objects in our solar system revolve around the sun. Galileo also helped confirm this with his trusty telescope! ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... Identify the structure of the Milky Way Galaxy and the location of our solar system within the galaxy. Explain how astronomers measure the distance to stars and galaxies. Identify the scientific evidence that supports the Big Bang theory. ...
... Identify the structure of the Milky Way Galaxy and the location of our solar system within the galaxy. Explain how astronomers measure the distance to stars and galaxies. Identify the scientific evidence that supports the Big Bang theory. ...
DAY AND NIGHT, SEASONS
... any time, however, if it is tilted the northern and southern hemisphere temperatures at any given latitude will still vary. An eccentric orbit may take the exoplanet in and out of the ‘habitable zone’ (where conditions for life are thought to be most favourable) in the course of a year. Life might e ...
... any time, however, if it is tilted the northern and southern hemisphere temperatures at any given latitude will still vary. An eccentric orbit may take the exoplanet in and out of the ‘habitable zone’ (where conditions for life are thought to be most favourable) in the course of a year. Life might e ...
Number of planets - Associazione Astrofili "Crab Nebula"
... How did the Solar System form? The Working Group on Extrasolar Planets (WGESP) of the IAU defines as an extrasolar planet (shortened exoplanet) “…a body whose mass lies below the threshold value for the onset of deuterium thermo-nuclear fusion (which is about 13 Jupiter masses [MJ] for a typical sol ...
... How did the Solar System form? The Working Group on Extrasolar Planets (WGESP) of the IAU defines as an extrasolar planet (shortened exoplanet) “…a body whose mass lies below the threshold value for the onset of deuterium thermo-nuclear fusion (which is about 13 Jupiter masses [MJ] for a typical sol ...
Week 10
... stars. Star A’s luminosity is 5 times higher than star B’s, and star A is 3 times farther away from you than star B. What is the ratio of the brightness of star A to the brightness of star B? (Enter the ratio as a two digit number: if the ratio is 2/3, ...
... stars. Star A’s luminosity is 5 times higher than star B’s, and star A is 3 times farther away from you than star B. What is the ratio of the brightness of star A to the brightness of star B? (Enter the ratio as a two digit number: if the ratio is 2/3, ...
Good Vibrations and Stellar Pulsations - Physics
... Some Results for the Sun • base of convection zone at 0.714 Rsun, where T = 2.18 x 106 K • mass fraction of helium at surface is Y = 0.2437 • helioseismologically measured sound speed and calculated sound speed for standard solar model agree to within 0.1% ...
... Some Results for the Sun • base of convection zone at 0.714 Rsun, where T = 2.18 x 106 K • mass fraction of helium at surface is Y = 0.2437 • helioseismologically measured sound speed and calculated sound speed for standard solar model agree to within 0.1% ...
AyC10 Fall 2007: Midterm 2 Review Sheet
... depends on the observer’s distance from the source. We calculate the luminosity (same as “intrinsic energy output”) of stars by measuring their brightness (counting how many photons hit our camera chip) and their distance (via parallax or other methods we haven’t discussed in detail). Once we know t ...
... depends on the observer’s distance from the source. We calculate the luminosity (same as “intrinsic energy output”) of stars by measuring their brightness (counting how many photons hit our camera chip) and their distance (via parallax or other methods we haven’t discussed in detail). Once we know t ...
the life cycles of stars (5) - U3A Bendigo Courses / Activities
... HEAVY WEIGHT STARS with zero age mass more than 8 M O The main sequence life burning hydrogen lasts only 100 million years instead of 10 billion for the sun. These are O and B type stars. Even before leaving the main sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressu ...
... HEAVY WEIGHT STARS with zero age mass more than 8 M O The main sequence life burning hydrogen lasts only 100 million years instead of 10 billion for the sun. These are O and B type stars. Even before leaving the main sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressu ...
The Spatially-Resolved Scaling Law of Star Formation
... •For example, if the mass of a star is doubled, its luminosity increases by a factor 23.5 ~ 11. •Thus, stars like Sirius that are about twice as massive as the Sun are about 11 times as luminous. •The more massive a Main Sequence star is, the hotter (bluer), and more luminous, the star, and the shor ...
... •For example, if the mass of a star is doubled, its luminosity increases by a factor 23.5 ~ 11. •Thus, stars like Sirius that are about twice as massive as the Sun are about 11 times as luminous. •The more massive a Main Sequence star is, the hotter (bluer), and more luminous, the star, and the shor ...
Planetarium Key Points
... Piero Ranfagni [email protected] 1. Celestial sphere The stars seem numberless and there are actually more than 2 billions of stars in the system we live in (Milky Way), but only 3000 stars are visible at naked eye What we see is NOT what it is actually, the response of our eye is logari ...
... Piero Ranfagni [email protected] 1. Celestial sphere The stars seem numberless and there are actually more than 2 billions of stars in the system we live in (Milky Way), but only 3000 stars are visible at naked eye What we see is NOT what it is actually, the response of our eye is logari ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.