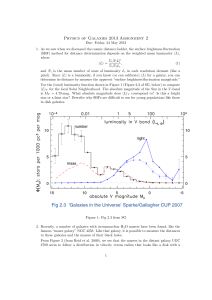
The measure of Cosmological distances
... Found new planet (Uranus)Discover Infra-Red lightFirst map of the sky: Idea: All the stars are the same. Therefore, bright stars are closer. ...
... Found new planet (Uranus)Discover Infra-Red lightFirst map of the sky: Idea: All the stars are the same. Therefore, bright stars are closer. ...
class17
... A. It would be only 1/3 as bright. B. It would be only 1/6 as bright. C. It would be only 1/9 as bright. D. It would be three times brighter. ...
... A. It would be only 1/3 as bright. B. It would be only 1/6 as bright. C. It would be only 1/9 as bright. D. It would be three times brighter. ...
slides - Indico
... Predictions and tests of nuclear physics (mass models, measurements of fundamental properties of nuclei, operation of n-capture processes) can be compared with observations of these rare stars that exhibit the variety of neutron-capture patterns produced in nature ...
... Predictions and tests of nuclear physics (mass models, measurements of fundamental properties of nuclei, operation of n-capture processes) can be compared with observations of these rare stars that exhibit the variety of neutron-capture patterns produced in nature ...
FINAL EXAM Name: ASTRONOMY II - 79202 Spring 1995
... No stars exist with masses greater than 1.5 solar masses. They typically live for many billions of years. Their radiated energy comes from carbon burning. Their density is equivalent to a solar mass packed into the Earth’s radius. ...
... No stars exist with masses greater than 1.5 solar masses. They typically live for many billions of years. Their radiated energy comes from carbon burning. Their density is equivalent to a solar mass packed into the Earth’s radius. ...
EMR, Telescopes, Stars, Solar System study guide `14-15
... • Surface temperature – know that color indicates surface temperature and know the order of colors from hottest to coolest • Sizes of stars – know the size-order of the 5 different star types – you do not need to memorize the actual sizes • Composition – know what stars are mainly made of and that w ...
... • Surface temperature – know that color indicates surface temperature and know the order of colors from hottest to coolest • Sizes of stars – know the size-order of the 5 different star types – you do not need to memorize the actual sizes • Composition – know what stars are mainly made of and that w ...
Homework #4 Astronomy 101 – Fall 2010 Due November 4, 11 a.m.
... planet directly, the light from the star needs to be blocked out - without blocking the orbit of the planet - before it reaches the telescope’s detector, otherwise the detector will be flooded with light from the star alone. Consequently, imaging extrasolar planets directly is quite a challenge, eve ...
... planet directly, the light from the star needs to be blocked out - without blocking the orbit of the planet - before it reaches the telescope’s detector, otherwise the detector will be flooded with light from the star alone. Consequently, imaging extrasolar planets directly is quite a challenge, eve ...
Interpreting the HR diagram of stellar clusters
... In fact, it seems that stars are usually born in big groups, as members of a cluster of stars. All the stars in the cluster form at about the same time. So, if we look at a cluster, we see a bunch of stars which are all roughly the same age. However, the stars do not all have the same mass: most ten ...
... In fact, it seems that stars are usually born in big groups, as members of a cluster of stars. All the stars in the cluster form at about the same time. So, if we look at a cluster, we see a bunch of stars which are all roughly the same age. However, the stars do not all have the same mass: most ten ...
1 WHY DO THE STARS IN ORION LOOK SO DIFFERENT FROM
... magnitude. In Table 1, apparent magnitude of a star, symbolized as mv, is represented by a numerical value. The smaller the number, the brighter the star. The brightest star in Table 1 is Rigel, with an mv of 0.12, which happens to also be the brightest star in the Orion constellation. The apparent ...
... magnitude. In Table 1, apparent magnitude of a star, symbolized as mv, is represented by a numerical value. The smaller the number, the brighter the star. The brightest star in Table 1 is Rigel, with an mv of 0.12, which happens to also be the brightest star in the Orion constellation. The apparent ...
Earth in Space and Time: SC.5.E.5.1
... 5) Latoya is studying the stars and she learns that Barnard's star is the third closest star to Earth, although it cannot be seen without a telescope. She also knows that the brightest star in the night sky, Sirius, is much farther away but can be seen by the naked eye. Which of the following expla ...
... 5) Latoya is studying the stars and she learns that Barnard's star is the third closest star to Earth, although it cannot be seen without a telescope. She also knows that the brightest star in the night sky, Sirius, is much farther away but can be seen by the naked eye. Which of the following expla ...
- National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... Figure 1: (X=color index (b-v), Y=Brightness (v)) According to the graph, the tip of the main sequence appears to lie around NGC 1496-1. This star’s color index is approximately 0.062, classifying it as a spectral type A star. Based on this observation, the age of the cluster is estimated to be no ...
... Figure 1: (X=color index (b-v), Y=Brightness (v)) According to the graph, the tip of the main sequence appears to lie around NGC 1496-1. This star’s color index is approximately 0.062, classifying it as a spectral type A star. Based on this observation, the age of the cluster is estimated to be no ...
Life cycle of a star
... between 1.4 and 3 times as much mass as the Sun, but are compressed into a ball with a radius of about 10 km. A thimbleful of a neutron star would weigh more than 100 million tons on earth ...
... between 1.4 and 3 times as much mass as the Sun, but are compressed into a ball with a radius of about 10 km. A thimbleful of a neutron star would weigh more than 100 million tons on earth ...
PARTS OF THE UNIVERSE
... once packed into a tiny particle smaller than a speck of dust. v The particle began to expand and matter and energy moved rapidly outward in all directions. v The matter cooled and collected to form stars, galaxies, nebulae, and planets. v Most scientists believe the universe is about 13.7 bil ...
... once packed into a tiny particle smaller than a speck of dust. v The particle began to expand and matter and energy moved rapidly outward in all directions. v The matter cooled and collected to form stars, galaxies, nebulae, and planets. v Most scientists believe the universe is about 13.7 bil ...
Stars - Academic Computer Center
... • Since stars are so far away they almost always appear just as points of light. • But as we already know we can learn a lot from light! • Light can tell us about a star’s: ...
... • Since stars are so far away they almost always appear just as points of light. • But as we already know we can learn a lot from light! • Light can tell us about a star’s: ...
Announcements Evolution of High-Mass Stars: Red Supergiants
... • To map the Milky Way Galaxy, we need to measure distances to stars. • Parallax only works for nearby stars (within about 1000 light years) • For more distant stars, we use Standard Candles Car Headlights are standard candles: We use them to determine the car’s distance ...
... • To map the Milky Way Galaxy, we need to measure distances to stars. • Parallax only works for nearby stars (within about 1000 light years) • For more distant stars, we use Standard Candles Car Headlights are standard candles: We use them to determine the car’s distance ...
Powerpoint file
... means that the nearest life-bearing planet might only be 10-100 light years away, close enough that in the future we may be able to detect such planets and obtain their spectra (that is the primary goal of astrobiology space missions for the next decade). This result is a major reason for exerting m ...
... means that the nearest life-bearing planet might only be 10-100 light years away, close enough that in the future we may be able to detect such planets and obtain their spectra (that is the primary goal of astrobiology space missions for the next decade). This result is a major reason for exerting m ...
What is a Red Shift?
... What did the telescope find after viewing a black sky for 10 days? What was one difference with the telescope the second time they pointed it at a black area in space? Technology is defined as the use of knowledge gained through science to make new products or tools people can use. What role does te ...
... What did the telescope find after viewing a black sky for 10 days? What was one difference with the telescope the second time they pointed it at a black area in space? Technology is defined as the use of knowledge gained through science to make new products or tools people can use. What role does te ...
PPTX
... • Associations are arbitrary, man-made, culture-specific. • Not natural groupings: stars are not necessarily close in 3D space. Shapes are specific to Earth's present location in galaxy. • Fainter stars don't participate in pattern • Constellations are transient because stars are all moving with res ...
... • Associations are arbitrary, man-made, culture-specific. • Not natural groupings: stars are not necessarily close in 3D space. Shapes are specific to Earth's present location in galaxy. • Fainter stars don't participate in pattern • Constellations are transient because stars are all moving with res ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.