Cepheid Variables and the Faulkes Telescope
... Astronomers believe that the intrinsic brightness of this process is nearly constant. This allows the distance to the supernova to be calculated. Supernovae are relatively rare but important events for astronomers. The chance to observe the process is eagerly sought after. However, research telescop ...
... Astronomers believe that the intrinsic brightness of this process is nearly constant. This allows the distance to the supernova to be calculated. Supernovae are relatively rare but important events for astronomers. The chance to observe the process is eagerly sought after. However, research telescop ...
Chapter 12
... 1. Binary stars are important because they allow us to measure stellar masses using Kepler’s third law as modified by Newton. 2. Knowledge of the size of one of the star’s ellipses, along with knowledge of the period of its motion, permits calculation of the total mass of the two stars. 3. To determ ...
... 1. Binary stars are important because they allow us to measure stellar masses using Kepler’s third law as modified by Newton. 2. Knowledge of the size of one of the star’s ellipses, along with knowledge of the period of its motion, permits calculation of the total mass of the two stars. 3. To determ ...
An Archive of Chandra Observations of Regions of Star Formation...
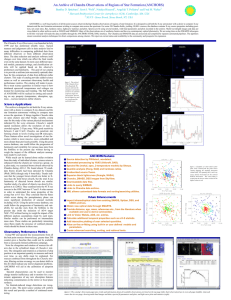
... different observers or from different observation dates. The data reduction and analysis software itself changes over time which can affect the final results even on the same dataset. In most cases different spectral models, parameter settings, and classification criteria will be applied based on th ...
... different observers or from different observation dates. The data reduction and analysis software itself changes over time which can affect the final results even on the same dataset. In most cases different spectral models, parameter settings, and classification criteria will be applied based on th ...
Characteristics of Stars - Laconia School District
... earth the star is. This method is only accurate for stars within a few hundred light-years of Earth. When the stars are very far away, the parallax shift is too small to measure. ...
... earth the star is. This method is only accurate for stars within a few hundred light-years of Earth. When the stars are very far away, the parallax shift is too small to measure. ...
Nebulae
... • They are found near hot, luminous stars of spectral types O and B • They are powered by ultraviolet light that they absorb from nearby hot stars • They are composed of ionized hydrogen atoms; the so called H II region. • They emit light through a ...
... • They are found near hot, luminous stars of spectral types O and B • They are powered by ultraviolet light that they absorb from nearby hot stars • They are composed of ionized hydrogen atoms; the so called H II region. • They emit light through a ...
Blowing Bubbles in Space: The Birth and Death of Practically
... The Quick, the Slow, and the Dead • All stars go through a protostar phase. It’s a short phase relative to the star’s total lifetime. That makes it harder to observe. • All stars go through a longer-lived MS phase • All stars above 0.3 M go through a red giant ...
... The Quick, the Slow, and the Dead • All stars go through a protostar phase. It’s a short phase relative to the star’s total lifetime. That makes it harder to observe. • All stars go through a longer-lived MS phase • All stars above 0.3 M go through a red giant ...
Star Formation
... burning (fusion) begins in the core and its properties settle down to stable values (i.e., it’s in equilibrium) ...
... burning (fusion) begins in the core and its properties settle down to stable values (i.e., it’s in equilibrium) ...
Watch - ggg999.org
... The four panels show the power density spectrum of the WIRE 2000 time series along with different simulations. Each simulation is the mean of five simulations with different seed numbers. The hatched regions show the 1-σ variation for selected simulations. ...
... The four panels show the power density spectrum of the WIRE 2000 time series along with different simulations. Each simulation is the mean of five simulations with different seed numbers. The hatched regions show the 1-σ variation for selected simulations. ...
Powerpoint for today
... Measuring the Stars How big are stars? How far away are they? How bright are they? How hot? How old, and how long do they live? What is their chemical composition? How are they moving? Are they isolated or in clusters? By answering these questions, we not only learn about stars, but about the struc ...
... Measuring the Stars How big are stars? How far away are they? How bright are they? How hot? How old, and how long do they live? What is their chemical composition? How are they moving? Are they isolated or in clusters? By answering these questions, we not only learn about stars, but about the struc ...
Ch. 15 Notes
... • The existence of black holes was first proposed by Albert Einstein as a result of his Theory of General Relativity. He called them “dark stars”, but suggested these monsters could not possibly exist for real. • They have been observed due to the effect of their massive amounts of gravity on ...
... • The existence of black holes was first proposed by Albert Einstein as a result of his Theory of General Relativity. He called them “dark stars”, but suggested these monsters could not possibly exist for real. • They have been observed due to the effect of their massive amounts of gravity on ...
The Universe - UNC Charlotte Pages
... Outline of the History of the Universe • The universe began about 15 billion years ago - the big bang. The early universe was very hot and dense. The amount of space in the universe increased rapidly with time. • The expansion of space cooled the universe and made it less dense. As a result, about ...
... Outline of the History of the Universe • The universe began about 15 billion years ago - the big bang. The early universe was very hot and dense. The amount of space in the universe increased rapidly with time. • The expansion of space cooled the universe and made it less dense. As a result, about ...
Scientists classify stars by
... 1. Stars are also classified by their brightness. 2. The brightness of a star as seen from Earth is called apparent magnitude. 3. The actual brightness of a star is called absolute magnitude. Example: The SUN has an absolute magnitude of 4.8 when compared to the other stars. The SUN has an apparent ...
... 1. Stars are also classified by their brightness. 2. The brightness of a star as seen from Earth is called apparent magnitude. 3. The actual brightness of a star is called absolute magnitude. Example: The SUN has an absolute magnitude of 4.8 when compared to the other stars. The SUN has an apparent ...
Galaxy1
... • M 82 is smaller than M 81 yet it is producing stars at an enormous rate. Ten times faster than the Milky Way is producing stars. • Most of the erupted gas is coming from supernova explosions. This is star formation on steroids. • Why do you think this little galaxy is producing stars so rapidly? ...
... • M 82 is smaller than M 81 yet it is producing stars at an enormous rate. Ten times faster than the Milky Way is producing stars. • Most of the erupted gas is coming from supernova explosions. This is star formation on steroids. • Why do you think this little galaxy is producing stars so rapidly? ...
Charcteristic of Stars Powerpoint C
... approximately 695,000 km, or about 109 times the radius of Earth. So the sun would equal 1 solar radius. • In comparison white dwarfs are about the same size as Earth and would equal 0.01 solar radius. Supergiants can have sizes up to 1,000 solar radii. ...
... approximately 695,000 km, or about 109 times the radius of Earth. So the sun would equal 1 solar radius. • In comparison white dwarfs are about the same size as Earth and would equal 0.01 solar radius. Supergiants can have sizes up to 1,000 solar radii. ...
Earth`s Motion and Seasons
... The Hubble Telescope is a reflecting telescope with a mirror 2.4 meters in diameter. Because it orbits Earth above the atmosphere, it can produce very detailed images. Hubble images have changed how astronomers view the universe. The most recent addition to NASA’s lineup of telescopes in space is th ...
... The Hubble Telescope is a reflecting telescope with a mirror 2.4 meters in diameter. Because it orbits Earth above the atmosphere, it can produce very detailed images. Hubble images have changed how astronomers view the universe. The most recent addition to NASA’s lineup of telescopes in space is th ...
Which object is a meteor?
... • Not Option A (Nebular Star? What the heck is that?) • Not Option C (A Binary Star isn’t formed as a result of a star dying) • Not Option D (A supernova can be created when a star dies, but nothing is left -like with a the other options listed) • CORRECT ANSWER: Option B must be correct. A Black H ...
... • Not Option A (Nebular Star? What the heck is that?) • Not Option C (A Binary Star isn’t formed as a result of a star dying) • Not Option D (A supernova can be created when a star dies, but nothing is left -like with a the other options listed) • CORRECT ANSWER: Option B must be correct. A Black H ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.