Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies
... larger star would be more luminous If the same size, hotter one would be brighter Types of magnitude Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth Apparent – as they appear in the nighttime sky ...
... larger star would be more luminous If the same size, hotter one would be brighter Types of magnitude Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth Apparent – as they appear in the nighttime sky ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Stars and Galaxies
... 24. Astronomers use spectrographs to study the ___________________ of stars to identify properties of stars. 25. Spectrographs break ______________________ into its component colors. 26. Dark lines are in the spectrum of a star. 27. The dark lines are caused by _____________________ in the star’s at ...
... 24. Astronomers use spectrographs to study the ___________________ of stars to identify properties of stars. 25. Spectrographs break ______________________ into its component colors. 26. Dark lines are in the spectrum of a star. 27. The dark lines are caused by _____________________ in the star’s at ...
3.1e Finding Polaris and Sirius
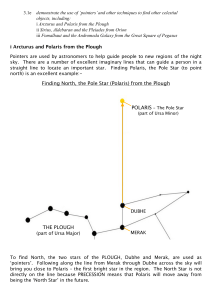
... have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Square of Pegasus, you need to find the top left hand star of the square (the star d ...
... have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Square of Pegasus, you need to find the top left hand star of the square (the star d ...
OTA System Report For June 4, 2009 8:30 AM
... magnitude determined is 14.004 . The star is 0.45 magnitudes dimmer, although close to the GSC2 1 sigma error, this value is approximately 1.5 1 sigma. The star has been matched to a single star. One can only assume it is dimmer than suspected and I recommend not using this star in the future. Natur ...
... magnitude determined is 14.004 . The star is 0.45 magnitudes dimmer, although close to the GSC2 1 sigma error, this value is approximately 1.5 1 sigma. The star has been matched to a single star. One can only assume it is dimmer than suspected and I recommend not using this star in the future. Natur ...
Planisphere Exercise
... progresses? Do these directions ever change? Turn the star wheel to find out. ...
... progresses? Do these directions ever change? Turn the star wheel to find out. ...
Stars - Trimble County Schools
... Distance to Stars • Distance to stars from Earth is measured in Light-years – Light-year = distance light travels in one year – Light-year = 9.461 x 1015 m ...
... Distance to Stars • Distance to stars from Earth is measured in Light-years – Light-year = distance light travels in one year – Light-year = 9.461 x 1015 m ...
Tour the sky`s reddest stars
... know it as Herschel’s Garnet Star. As the prototype of a class of variable stars called Mu Cephei variables, this star swings between magnitudes 3.6 and 5 during a period of roughly 2 years. These numbers, however, give only its apparent brightness. In reality, Mu ranks as one of the brightest and l ...
... know it as Herschel’s Garnet Star. As the prototype of a class of variable stars called Mu Cephei variables, this star swings between magnitudes 3.6 and 5 during a period of roughly 2 years. These numbers, however, give only its apparent brightness. In reality, Mu ranks as one of the brightest and l ...
File - SMIC Physics
... • ~ 1 trillion stars • Stars (including Sun) orbit around the core. It takes 225 million years for the Sun to make 1 round around the core. • Has a supermassive black hole at its center. It is about 2.5 million times as massive as the Sun. ...
... • ~ 1 trillion stars • Stars (including Sun) orbit around the core. It takes 225 million years for the Sun to make 1 round around the core. • Has a supermassive black hole at its center. It is about 2.5 million times as massive as the Sun. ...
Unit 2-1 Life Cycle of the Sun
... The purpose of this activity is to have you observe the changes in the temperature, absolute magnitude, and other observable characteristics of two different types of stars as they go through their life cycles. The absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would appear if it was approxima ...
... The purpose of this activity is to have you observe the changes in the temperature, absolute magnitude, and other observable characteristics of two different types of stars as they go through their life cycles. The absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would appear if it was approxima ...
Study Guide for the 4TH Astronomy Exam
... Study Guide for the 4TH Astronomy Exam Stellar Evolution The successful student will be able to… 1. Star Formation a. Describe the physical characteristics of a giant molecular cloud b. Identify the source of heating (energy production) in protostars c. Explain why more low-mass K & M main sequence ...
... Study Guide for the 4TH Astronomy Exam Stellar Evolution The successful student will be able to… 1. Star Formation a. Describe the physical characteristics of a giant molecular cloud b. Identify the source of heating (energy production) in protostars c. Explain why more low-mass K & M main sequence ...
Astronomy 2 Relativity and Gravitation
... - Since classification is based on the flux in different parts of the spectrum, one must beware of the effects of wavelength-dependent absorption (i.e. interstellar reddening) which would change the position of a star in the colour magnitude diagram depending on its distance as well as spectral type ...
... - Since classification is based on the flux in different parts of the spectrum, one must beware of the effects of wavelength-dependent absorption (i.e. interstellar reddening) which would change the position of a star in the colour magnitude diagram depending on its distance as well as spectral type ...
Wednesday, April 2 - Otterbein University
... observed to have the same apparent brightness. Which one is more distant? • Star A • Star B • Same distance ...
... observed to have the same apparent brightness. Which one is more distant? • Star A • Star B • Same distance ...
Study Guide: Unit 1, The Universe and its Stars, HS
... 12) HS-ESS1-1 The name applied to concentrations of interstellar matter that glow when it is close to very hot stars is ________. A) granules B) prominences C) nebulas D) quasars E) plages 13) HS-ESS1-1 As _____________ shrinks, gravitational energy is converted into energy of motion, or heat energy ...
... 12) HS-ESS1-1 The name applied to concentrations of interstellar matter that glow when it is close to very hot stars is ________. A) granules B) prominences C) nebulas D) quasars E) plages 13) HS-ESS1-1 As _____________ shrinks, gravitational energy is converted into energy of motion, or heat energy ...
Name: pd: ______ Date: Constellation Scavenger Hunt! Google Sky
... Cassini Overlay (as pictured). - How is Draco pictured in the Cassini Overlay? __________________________________ 10. Explore the night sky with the Cassini Overlay activated. Name three constellations and describe the pictures that go with them. a) Constellation: ______________________ Description: ...
... Cassini Overlay (as pictured). - How is Draco pictured in the Cassini Overlay? __________________________________ 10. Explore the night sky with the Cassini Overlay activated. Name three constellations and describe the pictures that go with them. a) Constellation: ______________________ Description: ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 1
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
Phys133-Sample MT2
... 10) Compared to the star it evolved from, a red giant is A) cooler and brighter. B) hotter and brighter. C) hotter and dimmer. D) the same temperature and brightness. E) cooler and dimmer. ...
... 10) Compared to the star it evolved from, a red giant is A) cooler and brighter. B) hotter and brighter. C) hotter and dimmer. D) the same temperature and brightness. E) cooler and dimmer. ...
Stars: flux, luminosity, color, and temperature
... `magnitude’ groups according to how bright they looked to his eye. • Herschel (1800s) first measured the brightness of stars quantitatively and matched his measurements onto Ptolemy’s magnitude groups and assigned a number for the magnitude of each star. ...
... `magnitude’ groups according to how bright they looked to his eye. • Herschel (1800s) first measured the brightness of stars quantitatively and matched his measurements onto Ptolemy’s magnitude groups and assigned a number for the magnitude of each star. ...
Lives of stars
... 7. When the sun starts to die, the sun will start to expand. The sun will be larger, hence brighter, but it till be lower temperature. Which letter represents this state of the sun? What do call this type of star? 8. After the dieing process the sun starts, sun will be variable star for short period ...
... 7. When the sun starts to die, the sun will start to expand. The sun will be larger, hence brighter, but it till be lower temperature. Which letter represents this state of the sun? What do call this type of star? 8. After the dieing process the sun starts, sun will be variable star for short period ...
Star Questions 2008 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... What does it mean for a star to have a life cycle? Explain what it means for a star to be on the main sequence. Which two pressures act upon any star on the main sequence? Why a star remains roughly the same diameter when on the main sequence. Explain the following relationships: a. Surface temperat ...
... What does it mean for a star to have a life cycle? Explain what it means for a star to be on the main sequence. Which two pressures act upon any star on the main sequence? Why a star remains roughly the same diameter when on the main sequence. Explain the following relationships: a. Surface temperat ...
Starry Night¨ Times - October 2008
... (40x) to find the object, and then try 100x and 200x. The name "planetary" is misleading, as these objects are not planets at all but stars at the end of their life cycle. However, they do look something like cloudy planets, and this fact confused earlier observers whose incorrect naming convention ...
... (40x) to find the object, and then try 100x and 200x. The name "planetary" is misleading, as these objects are not planets at all but stars at the end of their life cycle. However, they do look something like cloudy planets, and this fact confused earlier observers whose incorrect naming convention ...
Astro 2 - Red Hook Central School District
... • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jjmjEDY qbCk • From 4:48 ...
... • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jjmjEDY qbCk • From 4:48 ...
Test #3
... 13. What will be the last element that the Sun will be able to "burn" a. Hydrogen, b. Helium, c. Carbon, d. Oxygen 14. The total mass of a binary system can be calculated from a. the ratio of the angular separation from the center of mass of each of the stars. b. the distance to the binary and its ...
... 13. What will be the last element that the Sun will be able to "burn" a. Hydrogen, b. Helium, c. Carbon, d. Oxygen 14. The total mass of a binary system can be calculated from a. the ratio of the angular separation from the center of mass of each of the stars. b. the distance to the binary and its ...
15 - Edmodo
... 1. Where did the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram come from? Why is it significant? (2 Marks) ...
... 1. Where did the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram come from? Why is it significant? (2 Marks) ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.