Using Star Charts Introduction A Digression on Star Names
... Star charts are literally maps of the sky. We use them for a number of purposes, such as telling us what time of night certain stars and constellations will be visible, plotting the positions of the Sun, Moon, and planets against the background stars, and locating nonstellar objects such as nebulae ...
... Star charts are literally maps of the sky. We use them for a number of purposes, such as telling us what time of night certain stars and constellations will be visible, plotting the positions of the Sun, Moon, and planets against the background stars, and locating nonstellar objects such as nebulae ...
April - Bristol Astronomical Society
... "Asterion". But with the brighter of the stars that make the southern dog called "Cor Caroli,” Beta CVn got the name to itself. Chara is very similar to the Sun, at a distance of 27 light years it gives us a good indication of what the Sun would look like from a planet orbiting one of our near neigh ...
... "Asterion". But with the brighter of the stars that make the southern dog called "Cor Caroli,” Beta CVn got the name to itself. Chara is very similar to the Sun, at a distance of 27 light years it gives us a good indication of what the Sun would look like from a planet orbiting one of our near neigh ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... black holes -- once they grow to a critical size - stifle the formation of new stars in elliptical galaxies. Black holes are thought to do this by heating up and blasting away the gas that fuels star formation. • The blue color here represents radiation pouring out from material very close to the bl ...
... black holes -- once they grow to a critical size - stifle the formation of new stars in elliptical galaxies. Black holes are thought to do this by heating up and blasting away the gas that fuels star formation. • The blue color here represents radiation pouring out from material very close to the bl ...
Constellation Part II readingConstellation Part II reading(es)
... Northern Hemisphere, and for a few in the Southern Hemisphere that they could sometimes see, close to the horizon. Other societies had their own mythologies for the stars. The stories were part of their religions, helping them to explain everyday events, such as the seasons. These stories usually ha ...
... Northern Hemisphere, and for a few in the Southern Hemisphere that they could sometimes see, close to the horizon. Other societies had their own mythologies for the stars. The stories were part of their religions, helping them to explain everyday events, such as the seasons. These stories usually ha ...
Friday, Oct. 10
... Describe and explain the relationship between a star’s apparent brightness (or flux), its absolute brightness (or luminosity), and its distance from us. Describe and explain the relationship between a star’s luminosity, its radius, and its temperature, and how this relationship is used to measure ra ...
... Describe and explain the relationship between a star’s apparent brightness (or flux), its absolute brightness (or luminosity), and its distance from us. Describe and explain the relationship between a star’s luminosity, its radius, and its temperature, and how this relationship is used to measure ra ...
122final10
... There is no evidence of their existence They only form when two stars collide with one another none of the above are characteristics. ...
... There is no evidence of their existence They only form when two stars collide with one another none of the above are characteristics. ...
Hertzsprung2 - courses.psu.edu
... What is the luminosity (relative to the sun) of a star 3 times more massive than the sun? ...
... What is the luminosity (relative to the sun) of a star 3 times more massive than the sun? ...
and Concept Self-test (1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9)
... II. Stellar Motion – Stars move in two directions that we observe from Earth: Transverse component is the star’s motion across (V) the sky. Radial component is the star’s motion along our sight – directly towards or away, from us. Proper Motion – Annual movement of a star across the sky (transv ...
... II. Stellar Motion – Stars move in two directions that we observe from Earth: Transverse component is the star’s motion across (V) the sky. Radial component is the star’s motion along our sight – directly towards or away, from us. Proper Motion – Annual movement of a star across the sky (transv ...
TAURUS ZODIAC CONSTELLATION In Greek mythology, Taurus
... local spiral arm to which the Sun belongs. The belt contains bright stars in many constellations including (in order going more or less eastward) Cepheus, Lacerta, Perseus, Orion, Canis Major, Puppis, Vela, Carina, Crux, Centaurus, Lupus, and Scorpius The Milky Way also passes through most of these ...
... local spiral arm to which the Sun belongs. The belt contains bright stars in many constellations including (in order going more or less eastward) Cepheus, Lacerta, Perseus, Orion, Canis Major, Puppis, Vela, Carina, Crux, Centaurus, Lupus, and Scorpius The Milky Way also passes through most of these ...
Photometry
... Now you are ready to find the apparent B and V magnitudes. Move to one of the stars indicated on the data sheet on the following page. You may use the monitor / change view button to navigate the area in finder mode. Switch back to photometer / instrument mode before taking your readings. Make sure ...
... Now you are ready to find the apparent B and V magnitudes. Move to one of the stars indicated on the data sheet on the following page. You may use the monitor / change view button to navigate the area in finder mode. Switch back to photometer / instrument mode before taking your readings. Make sure ...
The Life Cycle of a star
... • A supernova can light up the sky for weeks. • The temperature in one can reach 1,000,000,000 °C. • The supernova then either becomes a neutron star or a black hole. ...
... • A supernova can light up the sky for weeks. • The temperature in one can reach 1,000,000,000 °C. • The supernova then either becomes a neutron star or a black hole. ...
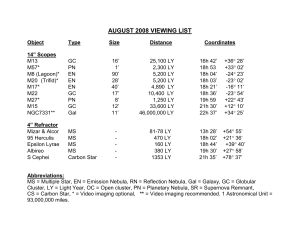
August
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
Star Classification
... Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to ...
... Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to ...
www.NewYorkScienceTeacher.org/review
... a. the emission of specific elements b. different chemical elements which absorb light at specific wavelengths c. highly compressed, glowing gas d. warmer gas in front of a source that emits a continuous spectrum The apparent shift in a star’s position caused by the motion of the observer is called ...
... a. the emission of specific elements b. different chemical elements which absorb light at specific wavelengths c. highly compressed, glowing gas d. warmer gas in front of a source that emits a continuous spectrum The apparent shift in a star’s position caused by the motion of the observer is called ...
Night Sky Checklist April–May–June Unaided Eye Astronomy
... Corvus, the Crow, is a challenging lozenge-shaped constellation not far from Spica, the brightest star in Virgo. Crater, the Cup, represents the goblet of Apollo in Greek mythology. It has been accepted as a constellation for at least 18 centuries! It’s faint, but with some imagination it really do ...
... Corvus, the Crow, is a challenging lozenge-shaped constellation not far from Spica, the brightest star in Virgo. Crater, the Cup, represents the goblet of Apollo in Greek mythology. It has been accepted as a constellation for at least 18 centuries! It’s faint, but with some imagination it really do ...
Constellations
... The first on the list of Heracles' jobs was the task of killing the Nemean Lion, a giant beast that roamed the hills and the streets of the Peloponnesian villages, devouring whomever it met. The animal's skin was immune to iron, bronze, and stone and Heracles' arrows bounced off the lion. So Heracle ...
... The first on the list of Heracles' jobs was the task of killing the Nemean Lion, a giant beast that roamed the hills and the streets of the Peloponnesian villages, devouring whomever it met. The animal's skin was immune to iron, bronze, and stone and Heracles' arrows bounced off the lion. So Heracle ...
PH109 Exploring the Universe, Test 3, Fall 2001 Please indicate the
... 32. About how old do astronomers think the sun is a) 10 billion years, b) 5 billion years, c) 10 million years, d) 5 millions years 33. A measurement of the parallax of a star allows us directly to determine the star's a) rotation rate, b) temperature, c) distance, d) age 34. The stars located in th ...
... 32. About how old do astronomers think the sun is a) 10 billion years, b) 5 billion years, c) 10 million years, d) 5 millions years 33. A measurement of the parallax of a star allows us directly to determine the star's a) rotation rate, b) temperature, c) distance, d) age 34. The stars located in th ...
1 WHY DO THE STARS IN ORION LOOK SO DIFFERENT FROM
... Luminosity shows the relationship of stars’ radii and surface temperature. Each of the stars in Table 1 is many times more luminous than our sun, and emits enormous amounts of energy. Luminosity is related to a stars surface area and temperature. Two stars having the same temperature and size will b ...
... Luminosity shows the relationship of stars’ radii and surface temperature. Each of the stars in Table 1 is many times more luminous than our sun, and emits enormous amounts of energy. Luminosity is related to a stars surface area and temperature. Two stars having the same temperature and size will b ...
What is the Zodiac? The Zodiac is defined by 12 constellations
... from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constellations that are recognized as the Zodiac. The IAU (International Astronomical Union) established in 1919 has identified 88 constellations. These are called the modern constellations. They have mapped the entire sky and have there are no ...
... from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constellations that are recognized as the Zodiac. The IAU (International Astronomical Union) established in 1919 has identified 88 constellations. These are called the modern constellations. They have mapped the entire sky and have there are no ...
Sermon Notes
... from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constellations that are recognized as the Zodiac. The IAU (International Astronomical Union) established in 1919 has identified 88 constellations. These are called the modern constellations. They have mapped the entire sky and have there are no ...
... from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constellations that are recognized as the Zodiac. The IAU (International Astronomical Union) established in 1919 has identified 88 constellations. These are called the modern constellations. They have mapped the entire sky and have there are no ...
Night Sky Checklist July–August–September Unaided Eye Astronomy
... just outside the Summer Triangle between Cygnus and Aquila. Stars (The stars on the checklist are easily visible to the unaided eye except in the most light polluted parts of cities.) Antares is a red supergiant star estimated to be some 800 times bigger than the sun. It’s bigger than the orbits of ...
... just outside the Summer Triangle between Cygnus and Aquila. Stars (The stars on the checklist are easily visible to the unaided eye except in the most light polluted parts of cities.) Antares is a red supergiant star estimated to be some 800 times bigger than the sun. It’s bigger than the orbits of ...
Option_E_Astrophysics_
... to figure out luminosity… It is often helpful to put luminosity on the magnitude scale… ...
... to figure out luminosity… It is often helpful to put luminosity on the magnitude scale… ...
P2_5 The Apparent Magnitude of α Orionis Supernova
... It has been found that when α Orionis becomes a supernova, it will be visible during the day. However, it will appear as a bright star rather than illuminating the Earth in the same way as the sun or moon. The moon has a mean apparent magnitude of -12.74 [6], and gives just enough light to help see ...
... It has been found that when α Orionis becomes a supernova, it will be visible during the day. However, it will appear as a bright star rather than illuminating the Earth in the same way as the sun or moon. The moon has a mean apparent magnitude of -12.74 [6], and gives just enough light to help see ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.