The Great Nebula in Orion
... temperature and luminosity. From these measurements, we can determine the radius, mass, age, and even the mass accretion rate of each star. This catalog of stellar properties will be the largest uniform survey of young stars ever achieved. The Hubble images reveal dozens of candidates for brown dwar ...
... temperature and luminosity. From these measurements, we can determine the radius, mass, age, and even the mass accretion rate of each star. This catalog of stellar properties will be the largest uniform survey of young stars ever achieved. The Hubble images reveal dozens of candidates for brown dwar ...
document
... stone by flashing the face of Medusa right before the monster’s eyes. Perseus was carried away just in time by the winged horse Pegasus. All of these have constellations and are located in the same region of the sky as the others. ...
... stone by flashing the face of Medusa right before the monster’s eyes. Perseus was carried away just in time by the winged horse Pegasus. All of these have constellations and are located in the same region of the sky as the others. ...
Killer Skies
... When modern astronomers turned their telescopes to the location of the guest star, they found a peculiar nebula—now known as the Crab Nebula. The Crab Nebula is called so for its many-legged shape. The ‘legs’ are filaments of gas that are moving away from the site of the explosion at about 1,400 km/ ...
... When modern astronomers turned their telescopes to the location of the guest star, they found a peculiar nebula—now known as the Crab Nebula. The Crab Nebula is called so for its many-legged shape. The ‘legs’ are filaments of gas that are moving away from the site of the explosion at about 1,400 km/ ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1
... Polaris is almost exactly above the pole of Earth’s rotational axis, so Polaris moves only slightly around the pole during one rotation of Earth. ...
... Polaris is almost exactly above the pole of Earth’s rotational axis, so Polaris moves only slightly around the pole during one rotation of Earth. ...
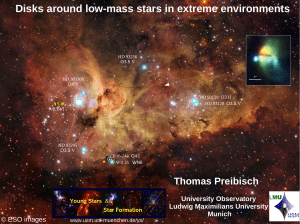
Disks around low-mass stars in extreme environments
... Implications on the formation environment of our planetary system The oldest Meteorites in our Solar System contain excesses in the daughter products of short-lived radionuclides: ...
... Implications on the formation environment of our planetary system The oldest Meteorites in our Solar System contain excesses in the daughter products of short-lived radionuclides: ...
black holes activity
... 6. Our sun has a temperature of 6000 K and an absolute magnitude of +4.7. Use an asterisk I * I to show the location of the sun on your diagram. To what group does the sun ...
... 6. Our sun has a temperature of 6000 K and an absolute magnitude of +4.7. Use an asterisk I * I to show the location of the sun on your diagram. To what group does the sun ...
INTERSTELLAR MedLab
... 26. Figure 7 shows the Helix Nebula. Ever since its discovery in the 18th century, this type of nebula is traditionally called a planetary nebula. Why do you think it earned that name? ...
... 26. Figure 7 shows the Helix Nebula. Ever since its discovery in the 18th century, this type of nebula is traditionally called a planetary nebula. Why do you think it earned that name? ...
Lecture 12
... • What star do we know the mass of very precisely? • Why is it so unlikely that binaries are in eclipsing systems? • Most binaries are seen as spectroscopic. Why? • How can we know the sizes of more stars than masses? ASTR111 Lecture 12 ...
... • What star do we know the mass of very precisely? • Why is it so unlikely that binaries are in eclipsing systems? • Most binaries are seen as spectroscopic. Why? • How can we know the sizes of more stars than masses? ASTR111 Lecture 12 ...
OSP2016Level 3 Map - Oregon Star Party
... What is it? V404 Cyg is a black hole (12+/- 3 solar masses) with late K or early G type stellar companion that’s slightly smaller than the Sun, orbiting each other in less than 6.5 days. They are approximately 7800 light years away. Why you want to see it: The stellar companion is distorted into a ...
... What is it? V404 Cyg is a black hole (12+/- 3 solar masses) with late K or early G type stellar companion that’s slightly smaller than the Sun, orbiting each other in less than 6.5 days. They are approximately 7800 light years away. Why you want to see it: The stellar companion is distorted into a ...
Homework #7 (Ch. 19)
... 9. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.17 What do star clusters and associations have to do with star formation? 10. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.18 Compare and contrast the observed properties of open star clusters and globular star clusters. 11. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.19 How can we ...
... 9. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.17 What do star clusters and associations have to do with star formation? 10. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.18 Compare and contrast the observed properties of open star clusters and globular star clusters. 11. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.19 How can we ...
night watch - Warren Astronomical Society
... would pass near a 15th magnitude star in 1965, and so the passage was observed very closely by several observatories to see if the star would be occulted. We knew the orbital path of Pluto in the sky very accurately, but since a planet’s gravity acts as though it were concentrated at the center of t ...
... would pass near a 15th magnitude star in 1965, and so the passage was observed very closely by several observatories to see if the star would be occulted. We knew the orbital path of Pluto in the sky very accurately, but since a planet’s gravity acts as though it were concentrated at the center of t ...
Chapter 1 Seeing the Light: The Art and Science of Astronomy
... Chapter 1: Seeing the Light: The Art and Science of Astronomy When you look at a star atlas, you discover that the individual stars in a constellation aren’t marked α Canis Majoris, β Canis Majoris, and so on. Usually, the creator of the atlas marks the area of the whole constellation as Canis Majo ...
... Chapter 1: Seeing the Light: The Art and Science of Astronomy When you look at a star atlas, you discover that the individual stars in a constellation aren’t marked α Canis Majoris, β Canis Majoris, and so on. Usually, the creator of the atlas marks the area of the whole constellation as Canis Majo ...
URAT-1 - Gaia Portal
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
Extragalactic Astrophysics 1 AA 2011-2012 Prof. LA Antonelli
... need to select distant quasars and galaxies in order to define a non-moving reference frame radial velocities easily measurable subtracting solar motion, it is found that Milky Way and M31 approach each other at V~120 km/s most other galaxies have velocities within ~60 km/s from MilkyWay+M31 center ...
... need to select distant quasars and galaxies in order to define a non-moving reference frame radial velocities easily measurable subtracting solar motion, it is found that Milky Way and M31 approach each other at V~120 km/s most other galaxies have velocities within ~60 km/s from MilkyWay+M31 center ...
SGHS Faulkes ASISTM Star Cluster Photometry
... The colour of a star is due to the temperature of its outer atmosphere. Relatively cool stars are orange or red and hot stars are white or blue. The temperature of a star’s outer layers is determined by how much energy a star is giving out and how far the star’s outer layers are from the centre of t ...
... The colour of a star is due to the temperature of its outer atmosphere. Relatively cool stars are orange or red and hot stars are white or blue. The temperature of a star’s outer layers is determined by how much energy a star is giving out and how far the star’s outer layers are from the centre of t ...
Glossary Topics - Home - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... Stars with initial masses between eight and 50 times that of the Sun do NOT evolve to the Wolf-Rayet stage: they never completely lose the hydrogen in their outer layers. Such stars also become blue and red supergiants. As they build up an iron core, they too explode as supernovae. The remaining cor ...
... Stars with initial masses between eight and 50 times that of the Sun do NOT evolve to the Wolf-Rayet stage: they never completely lose the hydrogen in their outer layers. Such stars also become blue and red supergiants. As they build up an iron core, they too explode as supernovae. The remaining cor ...
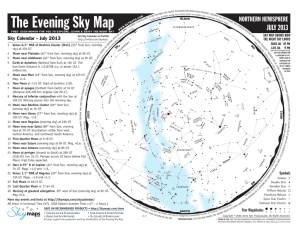
The Evening Sky Map
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
The Evening Sky Map
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
Lecture 15 Star Formation and Evolution 3/7
... • test out model of stellar evolution using Star Clusters • HR diagram of a cluster gives “snapshot” of stars with the same age but different masses • Birth Main Sequence Red Giant “live+die” faster if higher mass • tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...
... • test out model of stellar evolution using Star Clusters • HR diagram of a cluster gives “snapshot” of stars with the same age but different masses • Birth Main Sequence Red Giant “live+die” faster if higher mass • tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.