* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Modified True/False - Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
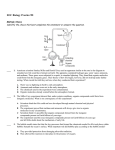
Unit 1 CP Study Guide The Universe and its Stars Modified True/False - Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. 2. 3. 4. HS-ESS1-1 When hydrogen nuclei fuse, they produce helium. HS-ESS1-1 A cloud of dust and gas in which a star forms is called a nebula. HS-ESS1-1 As white dwarfs cool, they often explode as supernovas. HS-ESS1-1 Combining of lightweight nuclei into heavier nuclei, such as four hydrogen nuclei combining to form a helium nucleus is called fission. 5. HS-ESS1-2 A parsec is a greater distance than a light year. 6. HS-ESS1-2 A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year. Multiple Choice - Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 7. HS-ESS1-1 Which stage in stellar evolution is the longest? a. Black hole c. Supergiant b. Neutron star d. Main-sequence ____ 8. HS-ESS1-1 In the last stage of stellar evolution following a supernova, stars too massive to form neutron stars may form a a. Red supergiant. c. White dwarf. b. Black dwarf. d. Black hole. ____ 9. HS-ESS1-1 A main-sequence star maintains a stable size as long as it has an ample supply of hydrogen to fuse into a. Iron. c. Protactinium. b. Magnesium. d. Helium. ____ 10. HS-ESS1-2 The apparent magnitude of a star is a measure of its a. Brightness as it appears from the earth. b. Distance from the earth. c. Surface temperature and composition. d. Position on the H-R diagram. ____ 11. HS-ESS1-2 How far is the sun from the earth? a. 4.3 light-minutes c. 8.3 light-minutes b. 9 light-years d. 680 light-years ____ 12. HS-ESS1-1 The process in which small atomic nuclei are combined into larger ones is known as a. Parallax c. Synthesis b. Fusion d. Fission ____ 13. HS-ESS1-2 Section of the H-R diagram into which about 90 percent of stars fall a. Main Sequence c. Supergiants b. Dwarfs d. Giants Unit 1 CP Study Guide The Universe and its Stars ____ 14. HS-ESS1-1 What stage in the life of a star 10 times more massive than the sun is missing in this chart? a. Supernova c. Black hole b. Red giant d. Neutron star ____ 15. HS-ESS1-1 When a white dwarf star no longer emits energy, it may become a a. Black hole. c. Neutron star. b. Nova. d. Black dwarf. ____ 16. HS-ESS1-1 The process in which smaller atomic nuclei combine into larger atomic nuclei is known as a. Gravitational attraction. c. The Doppler effect. b. Parallax. d. Nuclear fusion. ____ 17. HS-ESS1-2 The apparent shift in a star’s position caused by the motion of the observer is called ____. a. Luminosity c. Apparent magnitude b. Absolute magnitude d. Parallax ____ 18. HS-ESS1-1 Small, massive, dense object that has gravity so immense that nothing—not even light— can escape it a. Black dwarf c. Black hole b. Black hole Black hole d. Giant ____ 19. HS-ESS1-2 A star that is gravitationally bound to another star can either be part of a star cluster or a ____. a. Constellation c. White dwarf b. Binary star d. Red giant ____ 20. HS-ESS1-1 What stage of stellar evolution is the sun experiencing at this time? a. Main-sequence c. Protostar b. White dwarf d. Giant Unit 1 CP Study Guide The Universe and its Stars ____ 21. HS-ESS1-1 Which of the following stages is the earliest in the development of a star? a. Nebula c. Neutron star b. Protostar d. Giant ____ 22. HS-ESS1-1 All stars, including the Sun, have the following identical composition: a. 73 percent hydrogen; 25 percent helium; and 2 percent oxygen b. 73 percent hydrogen; 25 percent helium; and 2 percent other elements c. 25 percent hydrogen; 73 percent helium; and 2 percent oxygen d. 25 percent hydrogen; 73 percent helium; and 2 percent other elements ____ 23. HS-ESS1-2 The ____ of a star determines its temperature, luminosity, and diameter. a. Composition c. Energy output b. Mass d. Density ____ 24. HS-ESS1-1 Cloud of interstellar gas and dust that collapses on itself to form a new star _____. a. Giant c. Protostar b. Supernova d. Nebula ____ 25. HS-ESS1-2 The distance between a star and the earth is measured in ______ a. Parsecs c. Quantum leaps b. Light-years d. Millenniums ____ 26. HS-ESS1-1 An explosion 100 times brighter than a nova is called a (n) a. Main Sequence c. Protostar b. Supernova d. Nebula ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. Critical Thinking and Discussion. Use complete sentences, correct spelling, and the information presented in Chapter 24 to answer the questions below. 37) How do we calculate or determine the distances to stars? What units do we use and what are the limitations (if any) of the method used for such calculations? 38) Label the Giant and Supergiant stars, the Main Sequence stars, and the White dwarf stars on the H-R diagram below. Unit 1 CP Study Guide The Universe and its Stars 39) Briefly explain the sequence of events that are illustrated in Figure 24.11 below. Unit 1 CP Study Guide The Universe and its Stars Answer Section MODIFIED TRUE/FALSE 1. ANS: T 2. ANS: T 3. ANS: F, black dwarfs or dead stars 4. ANS: F, fusion 5. ANS: T 6. ANS: T MULTIPLE CHOICE 7. ANS: D PTS: 1 8. ANS: D PTS: 1 9. ANS: D PTS: 1 10. ANS: A PTS: 1 11. ANS: C PTS: 1 12. ANS: B PTS: 1 13. ANS: A PTS: 1 14. ANS: B PTS: 1 15. ANS: D PTS: 1 16. ANS: D PTS: 1 17. ANS: D PTS: 1 18. ANS: C PTS: 1 19. ANS: B PTS: 1 20. ANS: A PTS: 1 21. ANS: A PTS: 1 22. ANS: B PTS: 1 23. ANS: D PTS: 1 24. ANS: C PTS: 1 25. ANS: A PTS: 1 26. ANS: B PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 NAT: UCP1 | A1 | D4 NAT: UCP3 | A1 | D4 NAT: UCP2 | A1 | D4 NAT: UCP1 | A1 | E1