Globular Clusters Dynamic Lives The
... the more mass a star loses, the bluer it will appear. These astronomers have found that among the clusters of a given intermediate metallicity, the morphology of the horizontal branch depends on the cluster density and concentration, in the sense that denser and more concentrated clusters tend to ha ...
... the more mass a star loses, the bluer it will appear. These astronomers have found that among the clusters of a given intermediate metallicity, the morphology of the horizontal branch depends on the cluster density and concentration, in the sense that denser and more concentrated clusters tend to ha ...
PPT
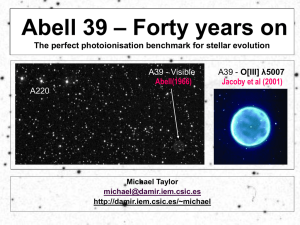
... 4) Stellar atmosphere theory and the mass loss stage of PNs It is relatively unstudied (only 1 dedicated publication!) Ideal case to assess our progress in astrophysics after 40 years ...
... 4) Stellar atmosphere theory and the mass loss stage of PNs It is relatively unstudied (only 1 dedicated publication!) Ideal case to assess our progress in astrophysics after 40 years ...
The Stars education kit - Student activities 5-10
... blue flame from a Bunsen burner is hotter and more dangerous than a red/yellow flame. The metal rod and the gas in the Bunsen burner have no colour of their own but change colour depending on their temperature. This is the same with stars. Cooler stars (with temperatures around 3,000K) glow red, whi ...
... blue flame from a Bunsen burner is hotter and more dangerous than a red/yellow flame. The metal rod and the gas in the Bunsen burner have no colour of their own but change colour depending on their temperature. This is the same with stars. Cooler stars (with temperatures around 3,000K) glow red, whi ...
Stars PowerPoint
... – Although stars may appear to be close to each other, very few are gravitationally bound to one other. – By measuring distances to stars and observing how they interact with each other, scientists can determine which stars are gravitationally bound to each other. – A group of stars that are gravita ...
... – Although stars may appear to be close to each other, very few are gravitationally bound to one other. – By measuring distances to stars and observing how they interact with each other, scientists can determine which stars are gravitationally bound to each other. – A group of stars that are gravita ...
Understanding the H-R Diagram
... In other words, how hot, how luminous and which stages a star will go through and eventually become (its life span) is dependent upon the star's original mass at the time of formation. "The Hertzsprung -Russell (H-R) Diagram is a graph that plots stars color (spectral type or surface temperature) vs ...
... In other words, how hot, how luminous and which stages a star will go through and eventually become (its life span) is dependent upon the star's original mass at the time of formation. "The Hertzsprung -Russell (H-R) Diagram is a graph that plots stars color (spectral type or surface temperature) vs ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... the Visual part of the electromagnetic spectrum instead of the normal magnutide M which is based on the flux integrated over all wavelengths λ. Before describing in detail the difference between M and MV , we will end our discussion on the Cepheid stars. When pulsating stars were first used to measu ...
... the Visual part of the electromagnetic spectrum instead of the normal magnutide M which is based on the flux integrated over all wavelengths λ. Before describing in detail the difference between M and MV , we will end our discussion on the Cepheid stars. When pulsating stars were first used to measu ...
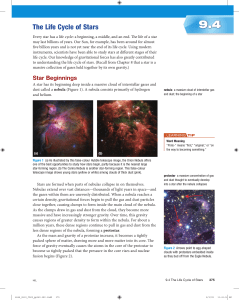
The Life Cycle of Stars
... Stars Like the Sun: Red Giant to White Dwarf After spending approximately 10 billion years as a main sequence star, a star’s available hydrogen will have been converted to helium by nuclear fusion. This results in the formation of a helium-rich core, surrounded by an outer layer of hydrogen. With le ...
... Stars Like the Sun: Red Giant to White Dwarf After spending approximately 10 billion years as a main sequence star, a star’s available hydrogen will have been converted to helium by nuclear fusion. This results in the formation of a helium-rich core, surrounded by an outer layer of hydrogen. With le ...
The star Epsilon UMa, or more commonly known as Alioth
... Alpha-CV type stars are divided into three main groups depending on which spectral lines are most dominant. These three types of spectral lines are silicon, manganese, or as in Alioth’s case, chromium-strontium lines.8 These stars usually lack the more common elements that are found in stars and hav ...
... Alpha-CV type stars are divided into three main groups depending on which spectral lines are most dominant. These three types of spectral lines are silicon, manganese, or as in Alioth’s case, chromium-strontium lines.8 These stars usually lack the more common elements that are found in stars and hav ...
color magnitude diagrams - AST 114, Astronomy Lab II for Spring
... The final piece we use to calibrate the system, and so the whole H-R diagram, is the application of the inverse-square law for nearby stars. If a star is close enough to us we see it move relative to distant stars as we orbit the Sun through Parallax. By measuring how much it appears to move we can ...
... The final piece we use to calibrate the system, and so the whole H-R diagram, is the application of the inverse-square law for nearby stars. If a star is close enough to us we see it move relative to distant stars as we orbit the Sun through Parallax. By measuring how much it appears to move we can ...
Section 4
... There are two major types of star clusters: open clusters and globular clusters. Open clusters have a loose, disorganized appearance and contain no more than a few thousand stars. They often contain many bright supergiants and much gas and dust. In contrast, globular clusters are large groupings of ...
... There are two major types of star clusters: open clusters and globular clusters. Open clusters have a loose, disorganized appearance and contain no more than a few thousand stars. They often contain many bright supergiants and much gas and dust. In contrast, globular clusters are large groupings of ...
Stars - gilbertmath.com
... The "Life Cycle" of a Star Low Mass Stars 1. Use their ______________ much more ____________ than more massive stars 2. Can last for ______ ______________ years 3. With ________ gravity and __________ pressures than other stars, the ______________ reactions in the core happen at a relatively _____ ...
... The "Life Cycle" of a Star Low Mass Stars 1. Use their ______________ much more ____________ than more massive stars 2. Can last for ______ ______________ years 3. With ________ gravity and __________ pressures than other stars, the ______________ reactions in the core happen at a relatively _____ ...
description
... Little Dipper = shaped like a small ladle or spoon. The end star of the Little Dipper’s handle is Polaris. The Little Dipper is part of a bigger constellation called “Ursa Minor” which means Little Bear. Orion = constellation represented by the figure of a great hunter in Greek mythology. The be ...
... Little Dipper = shaped like a small ladle or spoon. The end star of the Little Dipper’s handle is Polaris. The Little Dipper is part of a bigger constellation called “Ursa Minor” which means Little Bear. Orion = constellation represented by the figure of a great hunter in Greek mythology. The be ...
Neutron stars and quark stars - Goethe
... • first order phase transition to exotic matter in dense QCD likely! • → generates a new, stable solution for compact stars! (besides white dwarfs and neutron stars) • not constraint by mass-radius data yet! • impacts on supernovae, proto-neutron star evolution, neutron star properties, pulsars, . . ...
... • first order phase transition to exotic matter in dense QCD likely! • → generates a new, stable solution for compact stars! (besides white dwarfs and neutron stars) • not constraint by mass-radius data yet! • impacts on supernovae, proto-neutron star evolution, neutron star properties, pulsars, . . ...
March 2016 BRAS Addendum Newsletter
... star that is a spectroscopic binary. There is a 5 th component, a mag. 10.0 star at a separation of 13,000 AU (0.21 light year). Tau CMa is the brightest star of the open cluster NGC 2362 (Caldwell 64), which is why the cluster is sometimes called the Tau Canis Major Cluster. HD B47536, mag. 5.25, 0 ...
... star that is a spectroscopic binary. There is a 5 th component, a mag. 10.0 star at a separation of 13,000 AU (0.21 light year). Tau CMa is the brightest star of the open cluster NGC 2362 (Caldwell 64), which is why the cluster is sometimes called the Tau Canis Major Cluster. HD B47536, mag. 5.25, 0 ...
WSN 42 (2016) 132-142
... the outside in the center of the star and the star-shaped particle Roentgen rays, ultraviolet light and radio waves emitted heat. Some of the stars at the end of his life destroyed by huge explosions. Then it's just small balls of material remains quite congested in astronomy, white dwarfs, neutron ...
... the outside in the center of the star and the star-shaped particle Roentgen rays, ultraviolet light and radio waves emitted heat. Some of the stars at the end of his life destroyed by huge explosions. Then it's just small balls of material remains quite congested in astronomy, white dwarfs, neutron ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.