AJAstroProject
... million ly away. • It is in the same group as M95 (Previous) and M96 not photographed. • In this exposure you can see two other galaxies, NGC3384 and NGC3379. • NGC3384 is in the Leo Group I and NGC3379 is a more distant galaxy. This was a 90sec exposure through the V-filter. ...
... million ly away. • It is in the same group as M95 (Previous) and M96 not photographed. • In this exposure you can see two other galaxies, NGC3384 and NGC3379. • NGC3384 is in the Leo Group I and NGC3379 is a more distant galaxy. This was a 90sec exposure through the V-filter. ...
Interstellar medium, birth and life of stars
... occurs at a point where the shortlived stars enter their red giant phases, leaving only the smaller, longer-lived stars ...
... occurs at a point where the shortlived stars enter their red giant phases, leaving only the smaller, longer-lived stars ...
Chapter 6 Stars
... from the life cycle of a low-mass or medium-mass star. High-mass stars quickly evolve into brilliant supergiants. When a supergiant runs out of fuel, it can explode suddenly. Within hours, the star blazes millions of times brighter. The explosion is called a supernova. After a supernova, some of th ...
... from the life cycle of a low-mass or medium-mass star. High-mass stars quickly evolve into brilliant supergiants. When a supergiant runs out of fuel, it can explode suddenly. Within hours, the star blazes millions of times brighter. The explosion is called a supernova. After a supernova, some of th ...
Devika kamath Institute of Astronomy, KU. Leuven, Belgium
... The Post-RGB stars (old) have [Fe/H] peaking at about -1.0 dex ...
... The Post-RGB stars (old) have [Fe/H] peaking at about -1.0 dex ...
Lecture 10-11 - OSU Astronomy
... Which of the following spectral classifications represents the hottest stellar surface temperature? ...
... Which of the following spectral classifications represents the hottest stellar surface temperature? ...
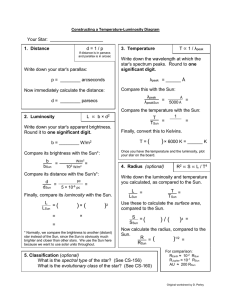
Your Star: _____________________ Write down the wavelength at which the one
... but please help each other out and check each other's answers. To help speed the calculations along, you are highly encouraged to round all numbers to one significant digit – for example, to round the Sun's apparent brightness of 1.37×10 +3 W/m2 to simply 1×10+3 W/m2. You can go for more careful pre ...
... but please help each other out and check each other's answers. To help speed the calculations along, you are highly encouraged to round all numbers to one significant digit – for example, to round the Sun's apparent brightness of 1.37×10 +3 W/m2 to simply 1×10+3 W/m2. You can go for more careful pre ...
Stars III The Hertzsprung
... through interstellar clouds (explaining the reddened stars at the edge of the cloud) • If there is enough dust, everything can be blocked, causing dark patches • It is not a coincidence that there are young, blue stars near this dark cloud • Stars are forming in these dense clouds of dust and gas ...
... through interstellar clouds (explaining the reddened stars at the edge of the cloud) • If there is enough dust, everything can be blocked, causing dark patches • It is not a coincidence that there are young, blue stars near this dark cloud • Stars are forming in these dense clouds of dust and gas ...
The Mighty Hunter in the Winter Sky By Shannon Jackson
... Five constellations are always in our northern sky. Other groupings appear seasonally, and then disappear as they fall below the horizon. There are five constellations, however, which seem to circle Polaris (po LAR us), also known as the North Star. The North Star always stays put while the other st ...
... Five constellations are always in our northern sky. Other groupings appear seasonally, and then disappear as they fall below the horizon. There are five constellations, however, which seem to circle Polaris (po LAR us), also known as the North Star. The North Star always stays put while the other st ...
ASTROPHYSICS UNIVERSE - Physics
... masses (or their combined mass) by measuring how long they take to complete one orbit around their centre of mass (the orbital period) Their orbital period (T) is related to their masses by: ...
... masses (or their combined mass) by measuring how long they take to complete one orbit around their centre of mass (the orbital period) Their orbital period (T) is related to their masses by: ...
Stars
... Sequence stars go through is a result of its temperature increasing ________________________ • Our Sun is a Main Sequence star of yellow ____________ color ...
... Sequence stars go through is a result of its temperature increasing ________________________ • Our Sun is a Main Sequence star of yellow ____________ color ...
2014 State Test
... B11. While a star is on the main sequence, the vast majority of its energy comes from burning what element as fuel? A. Hydrogen C. Carbon B. Helium D. Neon B12. The electron capture required for turning a proton into a neutron (needed to burn hydrogen into helium) releases a very light particle that ...
... B11. While a star is on the main sequence, the vast majority of its energy comes from burning what element as fuel? A. Hydrogen C. Carbon B. Helium D. Neon B12. The electron capture required for turning a proton into a neutron (needed to burn hydrogen into helium) releases a very light particle that ...
10.1 Introduction
... Figure 10.6). At a distance of only 2.4 pc, Wolf 359 is the fifth closest star to the Sun, after the three stars that make up the α Centauri system and Barnard’s star. Its spectral type is M6.0 V and its luminosity is 0.001L ; ...
... Figure 10.6). At a distance of only 2.4 pc, Wolf 359 is the fifth closest star to the Sun, after the three stars that make up the α Centauri system and Barnard’s star. Its spectral type is M6.0 V and its luminosity is 0.001L ; ...
Stellar Evolution
... • all the stars are at about the same distance from the Earth • all the stars formed at about the same time Determining the distance and age to a globular cluster is much easier than trying to find the distances and ages of a million random stars! Laboratories for understanding how stars of differen ...
... • all the stars are at about the same distance from the Earth • all the stars formed at about the same time Determining the distance and age to a globular cluster is much easier than trying to find the distances and ages of a million random stars! Laboratories for understanding how stars of differen ...
PEGASUS, THE FLYING HORSE Pegasus is a constellation in the
... constellation boundaries, as set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined as a polygon of 35 segments. In the equatorial coordinate system, the right ascension coordinates of these borders lie between 21h 12.6m and 00h. Its position in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere means that the whole constellat ...
... constellation boundaries, as set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined as a polygon of 35 segments. In the equatorial coordinate system, the right ascension coordinates of these borders lie between 21h 12.6m and 00h. Its position in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere means that the whole constellat ...
CS3_Ch 3 - Leon County Schools
... Life Cycle of a Star (cont.) • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. • Massive stars eventually become red ...
... Life Cycle of a Star (cont.) • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. • Massive stars eventually become red ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.