File
... Little dipper – they are actually asterisms - prominent patterns or groups of stars, typically having a popular name but smaller than a constellation 12. Explain precession and what it means in the future - slow movement of the axis of a spinning body around another axis due to a torque (such as gra ...
... Little dipper – they are actually asterisms - prominent patterns or groups of stars, typically having a popular name but smaller than a constellation 12. Explain precession and what it means in the future - slow movement of the axis of a spinning body around another axis due to a torque (such as gra ...
Space Science Unit
... • These clusters are grouped together into the various stages of a stars life cycle. • Let’s look at those briefly. ...
... • These clusters are grouped together into the various stages of a stars life cycle. • Let’s look at those briefly. ...
Science Assessment Stage H--Performance Standard 12F-H
... themselves by the constellations in which their selected star is found. Ask students to focus on the individual star on their card. Ask students to propose additional arrangements for the stars they represent (other than by constellation). Color is among the most obvious of the properties, so when i ...
... themselves by the constellations in which their selected star is found. Ask students to focus on the individual star on their card. Ask students to propose additional arrangements for the stars they represent (other than by constellation). Color is among the most obvious of the properties, so when i ...
Eagle Nebula - Amazing Space
... that make stars, including our Sun, shine. Photoevaporation in the Eagle Nebula has cut newly forming stars off from the cloud feeding them. While some of the EGGs are large enough to eventually become stars, others may never make it. ...
... that make stars, including our Sun, shine. Photoevaporation in the Eagle Nebula has cut newly forming stars off from the cloud feeding them. While some of the EGGs are large enough to eventually become stars, others may never make it. ...
Create a HR Diagram - EarthSpaceScience
... Use that Table of stars and plot them on the Empty H-R diagram based on Luminosity and Spectral Class. Use circles or shading to correctly label the Main Sequence, Giants, and Dwarfs. Then use your diagram to answer the questions. Stars: Star Name ...
... Use that Table of stars and plot them on the Empty H-R diagram based on Luminosity and Spectral Class. Use circles or shading to correctly label the Main Sequence, Giants, and Dwarfs. Then use your diagram to answer the questions. Stars: Star Name ...
Stars Notes
... Sirius is the brightest star in our sky. It is about 9 light-years away from Earth and has a magnitude of 1.4 ...
... Sirius is the brightest star in our sky. It is about 9 light-years away from Earth and has a magnitude of 1.4 ...
Friday, August 29
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
Constellations
... from those seen by the ancient Greeks, the Babylonians, and the people of other cultures, even though they were all looking at the same stars in the night sky. Interestingly, though, different cultures often made the same basic groupings of stars, despite widely varying interpretations of what they ...
... from those seen by the ancient Greeks, the Babylonians, and the people of other cultures, even though they were all looking at the same stars in the night sky. Interestingly, though, different cultures often made the same basic groupings of stars, despite widely varying interpretations of what they ...
Lesson #5: Constellations - Center for Learning in Action
... Ask the students what they know about stars. Try to lead them towards the definition: Stars are massive shining spheres of hot gas. The stars you can see with your naked eye in the night sky are part of the Milky Way Galaxy, a huge system of stars that contains our solar system. Use pictures or over ...
... Ask the students what they know about stars. Try to lead them towards the definition: Stars are massive shining spheres of hot gas. The stars you can see with your naked eye in the night sky are part of the Milky Way Galaxy, a huge system of stars that contains our solar system. Use pictures or over ...
Review Guide
... 5. What type of galaxy contains both young and old stars? 6. What type of galaxy contains only old stars? 7. What type of galaxy contains only young stars? 8. Besides their shape what other characteristic distinguishes the different types of galaxies from each other? 9. Why do distant galaxies appea ...
... 5. What type of galaxy contains both young and old stars? 6. What type of galaxy contains only old stars? 7. What type of galaxy contains only young stars? 8. Besides their shape what other characteristic distinguishes the different types of galaxies from each other? 9. Why do distant galaxies appea ...
Luminosity
... • Distance =63 light years • Close approach in 1.5 million years • Close enough to disrupt Oort cloud? • Comet showers?? ...
... • Distance =63 light years • Close approach in 1.5 million years • Close enough to disrupt Oort cloud? • Comet showers?? ...
Lecture 12
... – Allows for easy comparison of sources with immense ranges in flux density. – The magnitude system, let’s be honest, is not readily intuitive. ...
... – Allows for easy comparison of sources with immense ranges in flux density. – The magnitude system, let’s be honest, is not readily intuitive. ...
your star chart here - Australasian Science Magazine
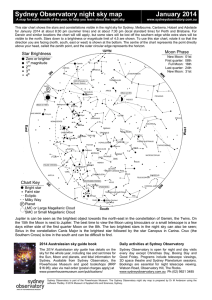
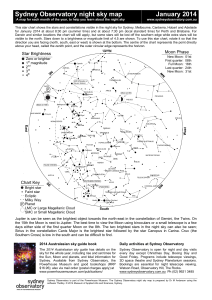
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
Star names and magnitudes
... By grouping stars into constellations, our ancestors developed the first system for unambiguously identifying celestial sources. Now, we use co-ordinate systems based on angular distance scales. Astronomical co-ordinates ...
... By grouping stars into constellations, our ancestors developed the first system for unambiguously identifying celestial sources. Now, we use co-ordinate systems based on angular distance scales. Astronomical co-ordinates ...
Society News - Bristol Astronomical Society
... (Algieba), this is a great double for small telescopes. The primary is a magnitude +2.2 K-class yellow-orange giant, it’s companion is a magnitude +2.5 yellow Gclass star. The pair are separated by 4.4 arcseconds. Just to the west of Leo lies the faint constellation of Cancer, which is home to one o ...
... (Algieba), this is a great double for small telescopes. The primary is a magnitude +2.2 K-class yellow-orange giant, it’s companion is a magnitude +2.5 yellow Gclass star. The pair are separated by 4.4 arcseconds. Just to the west of Leo lies the faint constellation of Cancer, which is home to one o ...
SSG Coordinators will be at the Cronan Ranch observing site at 5
... distant, M31 is one of the most distant objects visible to the unaided eye. The galaxy is tilted about 30 to our line of sight. With about 300 billion stars spread across a 130,000 light year disk, this is an object worth spending some time with. Of interest is that M31 is approaching us at about 1 ...
... distant, M31 is one of the most distant objects visible to the unaided eye. The galaxy is tilted about 30 to our line of sight. With about 300 billion stars spread across a 130,000 light year disk, this is an object worth spending some time with. Of interest is that M31 is approaching us at about 1 ...
less than 1 million years
... 3. This (depletion of star’s hydrogen) can take less than 1 million years for the _________ stars to many billions of years for the _________ stars. 4. The Sun has a main sequence life span of about ___ ________ years. (2 words/numbers) 5. Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called a ______ ...
... 3. This (depletion of star’s hydrogen) can take less than 1 million years for the _________ stars to many billions of years for the _________ stars. 4. The Sun has a main sequence life span of about ___ ________ years. (2 words/numbers) 5. Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called a ______ ...
The Night Sky 12-07
... evening twilight. During the first few days of April, before it disappears from view, Mercury can be glimpsed along the horizon well below Mars. Jupiter reaches opposition this month, which means that it will be up all night long and high in the south at local midnight. For us in the U.P. on Eastern ...
... evening twilight. During the first few days of April, before it disappears from view, Mercury can be glimpsed along the horizon well below Mars. Jupiter reaches opposition this month, which means that it will be up all night long and high in the south at local midnight. For us in the U.P. on Eastern ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.