Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System
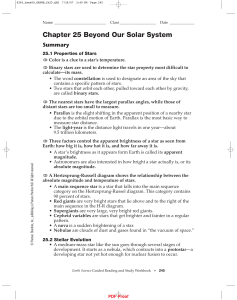
... absolute magnitude and temperature of stars. • A main sequence star is a star that falls into the main sequence category on the Hertzsprung-Russel diagram. This category contains 90 percent of stars. • Red giants are very bright stars that lie above and to the right of the main sequence in the H-R d ...
... absolute magnitude and temperature of stars. • A main sequence star is a star that falls into the main sequence category on the Hertzsprung-Russel diagram. This category contains 90 percent of stars. • Red giants are very bright stars that lie above and to the right of the main sequence in the H-R d ...
The Hertzsprung – Russell Diagram
... For astronomers, a graph that displays a star’s luminosity on the y-axis and its surface temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell, or H-R Diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when all of the known stars were put ...
... For astronomers, a graph that displays a star’s luminosity on the y-axis and its surface temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell, or H-R Diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when all of the known stars were put ...
August 2013 - Joliet Junior College
... scorpion. The Big Dipper has moved around and is now in the western sky after sunset. In the northeastern sky is the “W’ that marks the constellation of Cassiopeia. To the right of Vega is Hercules and the Hercules globular cluster. The globular cluster is hundreds of thousands of stars in a tight g ...
... scorpion. The Big Dipper has moved around and is now in the western sky after sunset. In the northeastern sky is the “W’ that marks the constellation of Cassiopeia. To the right of Vega is Hercules and the Hercules globular cluster. The globular cluster is hundreds of thousands of stars in a tight g ...
File
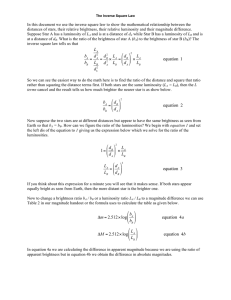
... If we know how large an object really is, and we know what angle it takes up in the sky, then we can calculate how far it must be. Pro: Can be used for even distant galaxies and quasars Con: Requires an assumption about the actual size of the object. (Sometimes this is not a problem, but other times ...
... If we know how large an object really is, and we know what angle it takes up in the sky, then we can calculate how far it must be. Pro: Can be used for even distant galaxies and quasars Con: Requires an assumption about the actual size of the object. (Sometimes this is not a problem, but other times ...
PDF version (two pages, including the full text)
... Southern Cross and the Pointers (Alpha and Beta Centauri). Alpha Centauri is a triple system, with two sun like stars orbiting each other every 80 years and a dim red dwarf tagging along at a much larger distance. This star was discovered by Robert Innes at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg in 1 ...
... Southern Cross and the Pointers (Alpha and Beta Centauri). Alpha Centauri is a triple system, with two sun like stars orbiting each other every 80 years and a dim red dwarf tagging along at a much larger distance. This star was discovered by Robert Innes at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg in 1 ...
Stars
... • DISTANCE – Measured in light-years • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • SPEED of LIGHT is ...
... • DISTANCE – Measured in light-years • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • SPEED of LIGHT is ...
File - SMIC Physics
... A: large, massive, hot ball of gas held together by gravity and gives off light. • Q: What is a Constellation? A : a number of stars that appear to form a pattern. ...
... A: large, massive, hot ball of gas held together by gravity and gives off light. • Q: What is a Constellation? A : a number of stars that appear to form a pattern. ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
Support worksheet – Topic 3 Questions
... Suggest why the stellar parallax method is limited to distances of about 300 pc for Earth-based telescopes but can be extended to 1000 pc for satellite-based telescopes. ...
... Suggest why the stellar parallax method is limited to distances of about 300 pc for Earth-based telescopes but can be extended to 1000 pc for satellite-based telescopes. ...
Mountain Skies - Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute
... in particular at the middle star and you will notice it is a bit fuzzy;; it is called the “smoking star” in some Native American traditions. A pair of binoculars or a telescope reveals this to be the beautiful “Great Nebula of Orion,” an immense cloud ...
... in particular at the middle star and you will notice it is a bit fuzzy;; it is called the “smoking star” in some Native American traditions. A pair of binoculars or a telescope reveals this to be the beautiful “Great Nebula of Orion,” an immense cloud ...
Friday, Oct. 10
... How do astronomers use parallax to measure the distances to stars? Why does parallax vary inversely with distance? Describe and explain the relationship between a star’s apparent brightness (or flux), its absolute brightness (or luminosity), and its distance from us. Describe and explain the relatio ...
... How do astronomers use parallax to measure the distances to stars? Why does parallax vary inversely with distance? Describe and explain the relationship between a star’s apparent brightness (or flux), its absolute brightness (or luminosity), and its distance from us. Describe and explain the relatio ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...
... When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...
changing constellations
... n 2.5 million the Earth moves more tha the Sun (or und aro kilometres as it orbits stars The it). orb full a about 1/365th of dually gra ht nig mid at ds hea above our g a full cycle in change each night, makin one year. kes an extra The Earth therefore ma tion to the stars rotation each year in rel ...
... n 2.5 million the Earth moves more tha the Sun (or und aro kilometres as it orbits stars The it). orb full a about 1/365th of dually gra ht nig mid at ds hea above our g a full cycle in change each night, makin one year. kes an extra The Earth therefore ma tion to the stars rotation each year in rel ...
Night Sky Checklist October–November
... Square is high in the south, Alpheratz is the upper left star. Its name comes from an Arabic phrase meaning “navel of the horse,” and reflects a time when Alpheratz was considered as part of Pegasus. Markab is the brightest star in Pegasus and the second brightest star of the Great Square. When the ...
... Square is high in the south, Alpheratz is the upper left star. Its name comes from an Arabic phrase meaning “navel of the horse,” and reflects a time when Alpheratz was considered as part of Pegasus. Markab is the brightest star in Pegasus and the second brightest star of the Great Square. When the ...
OUSNMAY06 - The George Abell Observatory
... NGC4258 (M106) (8.3) sg. Large inclined galaxy located about 5o east of UMa on the borders of Canes Venatici and Ursa Major. NGC4395 (11.0) sg. Bright core with a low surface brightness circular halo. NGC4449 (10.5) ir. Appears almost rectangular making it an unusual object to view. NGC4485 (12.5) ...
... NGC4258 (M106) (8.3) sg. Large inclined galaxy located about 5o east of UMa on the borders of Canes Venatici and Ursa Major. NGC4395 (11.0) sg. Bright core with a low surface brightness circular halo. NGC4449 (10.5) ir. Appears almost rectangular making it an unusual object to view. NGC4485 (12.5) ...
Stellar evolution, I
... If interstellar gas is cold enough and dense enough, it will collapse under its own gravitational power to form stars. The “free fall” time of a spherical cloud is given by: Tff = [3/(32 G )]1/2 , where G is Newton's gravitational constant and is the initial density of the cloud. If the densi ...
... If interstellar gas is cold enough and dense enough, it will collapse under its own gravitational power to form stars. The “free fall” time of a spherical cloud is given by: Tff = [3/(32 G )]1/2 , where G is Newton's gravitational constant and is the initial density of the cloud. If the densi ...
- hoganshomepage
... chemical composition of the stars. (also temperature and direction the star is moving in relation to the Earth.) How? Set up a spectroscope with different tubes; each gas has different spectras – light patterns. ...
... chemical composition of the stars. (also temperature and direction the star is moving in relation to the Earth.) How? Set up a spectroscope with different tubes; each gas has different spectras – light patterns. ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... • all stars fuse hydrogen into helium • 90% of all stars, including our Sun, are main sequence stars • range from high luminosity (brightness) and high surface temperature to low luminosity and low surface temperature ...
... • all stars fuse hydrogen into helium • 90% of all stars, including our Sun, are main sequence stars • range from high luminosity (brightness) and high surface temperature to low luminosity and low surface temperature ...
Summer Triangle (Winter in the south hemisphere) Lyra
... which Zeus transformed himself to seduce Leda, the Queen of Sparta. Leda laid the eggs which hatched Helen of Troy and the twins, Castor and Pollux. Cygnus is sometimes made out to be Orpheus 奧菲斯, the Greek tragic hero who was murdered for refusing to honor Dionysus. In death, Orpheus was transforme ...
... which Zeus transformed himself to seduce Leda, the Queen of Sparta. Leda laid the eggs which hatched Helen of Troy and the twins, Castor and Pollux. Cygnus is sometimes made out to be Orpheus 奧菲斯, the Greek tragic hero who was murdered for refusing to honor Dionysus. In death, Orpheus was transforme ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.