The Life Cycle of a Star Webquest:
... 3. How long can a star stay a protostar? ____________________________ 4. Explain nuclear fusion. ____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. How long does a star live before it begins to die? _ ...
... 3. How long can a star stay a protostar? ____________________________ 4. Explain nuclear fusion. ____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. How long does a star live before it begins to die? _ ...
wk09noQ
... • The Zero Age Main Sequence (ZAMS) represents the onset or start of nuclear burning (fusion) • The properties of a star on the ZAMS are primarily determined by its mass, somewhat dependent on chemical composition (fraction of He and heavier elements) • The classification of stars in an HR diagram b ...
... • The Zero Age Main Sequence (ZAMS) represents the onset or start of nuclear burning (fusion) • The properties of a star on the ZAMS are primarily determined by its mass, somewhat dependent on chemical composition (fraction of He and heavier elements) • The classification of stars in an HR diagram b ...
lecture23
... More luminous variable stars have large Period Variability is EXTREMELY USEFUL, because it is an absolute distance indicator ...
... More luminous variable stars have large Period Variability is EXTREMELY USEFUL, because it is an absolute distance indicator ...
FRIENDS OF THE PLANETARIUM NEWSLETTER April2002
... the southeastern part of the sky with a reminder that winter is approaching and that it is time for another newsletter. Having just mentioned the constellation Orion, no doubt you have had no trouble recognising the usually ruby red star in the shoulder of Orion. This is the red super giant star Bet ...
... the southeastern part of the sky with a reminder that winter is approaching and that it is time for another newsletter. Having just mentioned the constellation Orion, no doubt you have had no trouble recognising the usually ruby red star in the shoulder of Orion. This is the red super giant star Bet ...
constellations are not real!
... per day. This apparent rotation of the celestial sphere presents us with an obvious means of defining a coordinate system for the surface of the celestial sphere - the extensions of the north pole (NP) and south pole (SP) of the Earth intersect with the north celestial pole (NCP) and the south celes ...
... per day. This apparent rotation of the celestial sphere presents us with an obvious means of defining a coordinate system for the surface of the celestial sphere - the extensions of the north pole (NP) and south pole (SP) of the Earth intersect with the north celestial pole (NCP) and the south celes ...
Constellations - Jolie McLaine`s Senior Project
... only the sacrifice of Andromeda to the monster could appease the wrath of the sea god. The king chained Andromeda to a sea cliff. Fortunately, at this same moment, Perseus, was traveling along the coast. Perseus noticed the beautiful woman and fell in love with her. Learning of Andromeda's story, he ...
... only the sacrifice of Andromeda to the monster could appease the wrath of the sea god. The king chained Andromeda to a sea cliff. Fortunately, at this same moment, Perseus, was traveling along the coast. Perseus noticed the beautiful woman and fell in love with her. Learning of Andromeda's story, he ...
SOLUTIONS ASTROPHYSICS – OPTION D 2015-17
... b) State and explain the change in the luminosity of the Sun that occurs between positions S and I. ...
... b) State and explain the change in the luminosity of the Sun that occurs between positions S and I. ...
For stars
... • Rigel (m = 0.12) • Spica (m = +1.0) • Which looks brighter? Rigel BUT... It turns out that Spica actually gives off 1000 times more light than Rigel!! SO..If Spica is giving off more light, why would it appear dimmer in the sky here at Earth? ...
... • Rigel (m = 0.12) • Spica (m = +1.0) • Which looks brighter? Rigel BUT... It turns out that Spica actually gives off 1000 times more light than Rigel!! SO..If Spica is giving off more light, why would it appear dimmer in the sky here at Earth? ...
The Sun and Other Stars - Tuslaw Local School District
... • Light year - the distance light travels in 1 year - light travels at a speed of 186,000 mps (300,000km/s) - light travels about 6 trillion miles in 1 year - ( 9.5 million million kilometers) Parallax - the apparent motion of an object when viewed from 2 different points in space; can only measure ...
... • Light year - the distance light travels in 1 year - light travels at a speed of 186,000 mps (300,000km/s) - light travels about 6 trillion miles in 1 year - ( 9.5 million million kilometers) Parallax - the apparent motion of an object when viewed from 2 different points in space; can only measure ...
Stellar Properties
... 17-1 How we can measure the 17-9 How we can use binary stars to distances to the stars measure the masses of stars 17-2 How we measure a star’s 17-10 How we can learn about binary brightness and luminosity stars in very close orbits 17-3 The magnitude scale for 17-11 What eclipsing binaries are and ...
... 17-1 How we can measure the 17-9 How we can use binary stars to distances to the stars measure the masses of stars 17-2 How we measure a star’s 17-10 How we can learn about binary brightness and luminosity stars in very close orbits 17-3 The magnitude scale for 17-11 What eclipsing binaries are and ...
Mr - White Plains Public Schools
... diagram, a star like Earth’s Sun will eventually (1) explode in a supernova (2) become a black hole (3) change to a white dwarf (4) become a neutron star 2. Stars like Earth’s Sun ...
... diagram, a star like Earth’s Sun will eventually (1) explode in a supernova (2) become a black hole (3) change to a white dwarf (4) become a neutron star 2. Stars like Earth’s Sun ...
05spectralclasses
... • Some are very luminous compared to main sequence stars of their spectral class (implied large radius) giants • Some are very underluminous for their class white dwarfs ...
... • Some are very luminous compared to main sequence stars of their spectral class (implied large radius) giants • Some are very underluminous for their class white dwarfs ...
Stars
... • As Earth rotates, Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, and other constellations in the northern sky circle around Polaris • Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. • It appears that the constellations complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 hr. as Earth rotates on its axis. ...
... • As Earth rotates, Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, and other constellations in the northern sky circle around Polaris • Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. • It appears that the constellations complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 hr. as Earth rotates on its axis. ...
SNC1PL The Life Cycle of Stars
... quickly. This spinning creates highfrequency radio waves, which have been detected by astronomers on Earth. ...
... quickly. This spinning creates highfrequency radio waves, which have been detected by astronomers on Earth. ...
P10263v1.2 Lab 5 Text
... sky during the spring, there is a small asterism known as “The Pleiades”, which marks the location of a cluster of stars. In legend, the Pleiades are the seven sisters, daughters of Atlas, the titan who holds up the sky, and the Oceanid named Pleione. The sisters are Alcyone, Maia, Electra, Taygeta, ...
... sky during the spring, there is a small asterism known as “The Pleiades”, which marks the location of a cluster of stars. In legend, the Pleiades are the seven sisters, daughters of Atlas, the titan who holds up the sky, and the Oceanid named Pleione. The sisters are Alcyone, Maia, Electra, Taygeta, ...
Stellar Spectral Classes
... Using these data, describe and explain one similarity and one difference in the appearance of the two stars as seen with the unaided eye by an observer on the Earth. similarity................................................................................................. ...
... Using these data, describe and explain one similarity and one difference in the appearance of the two stars as seen with the unaided eye by an observer on the Earth. similarity................................................................................................. ...
here - Lund Observatory
... A star has been observed to have the apparent visual magnitude V. Later observations show that the star in fact is a binary with two identical components. What is apparent visual magnitude of one of these components? ...
... A star has been observed to have the apparent visual magnitude V. Later observations show that the star in fact is a binary with two identical components. What is apparent visual magnitude of one of these components? ...
H-R Diagram Student
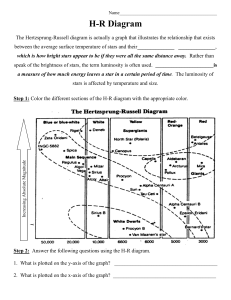
... H-R Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of ...
... H-R Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of ...
HR Diagram (Temperature Versus Absolute Magnitude)
... single ray of light can travel in space in one year (9.5 trillion kilometers) • A single ray of light travels at about 300,000 kilometers per second in space ...
... single ray of light can travel in space in one year (9.5 trillion kilometers) • A single ray of light travels at about 300,000 kilometers per second in space ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.