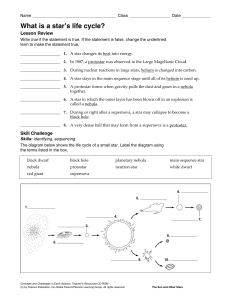
What is a star`s life cycle?
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
December 1, 2011 - Perry Local Schools
... 1. Place the small flashlight on a desk or table near the front of the room. 2. Place the large flashlight on a desk or table near the back of the room. 3. Gather at the front of the room so they can all see both flashlights easily. 4. Turn on both flashlights. 5. Darken the room. 6. Observe and co ...
... 1. Place the small flashlight on a desk or table near the front of the room. 2. Place the large flashlight on a desk or table near the back of the room. 3. Gather at the front of the room so they can all see both flashlights easily. 4. Turn on both flashlights. 5. Darken the room. 6. Observe and co ...
Sun, Star Types and Luminosity
... a. Super giant stars can be up to 1000 times larger than the diameter of the sun b. Late stage of evolution c. Usually explode in a supernova d. Blue super giants are the brightest and exhibit the highest temperature ...
... a. Super giant stars can be up to 1000 times larger than the diameter of the sun b. Late stage of evolution c. Usually explode in a supernova d. Blue super giants are the brightest and exhibit the highest temperature ...
Stars and Galaxies
... from which new stars are born. • Steps for the “birth” of stars: – Large clouds of gas and dust, called nebulae, collapse due to gravity. – The collapsing cloud becomes very dense. – Nuclear reactions involving hydrogen and helium begin. – These nuclear reactions power the star. – A star is born. ...
... from which new stars are born. • Steps for the “birth” of stars: – Large clouds of gas and dust, called nebulae, collapse due to gravity. – The collapsing cloud becomes very dense. – Nuclear reactions involving hydrogen and helium begin. – These nuclear reactions power the star. – A star is born. ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Astronomy Project Purpose: To
... 3.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s radius, and find some way of comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner planets inside it. Something to put it into perspective. 4.) Determin ...
... 3.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s radius, and find some way of comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner planets inside it. Something to put it into perspective. 4.) Determin ...
W > 1 - The Open University
... Broad central glow surrounded by fainter envelope. Stands high magnification well. NGC4559 (10.5) sg. Bright oval smudge. Mottled appearance in large telescopes. NGC4565 (10.5) sg. One of the finest "edge-on" spiral galaxies. Appears as a thin needle of light with the hint of a central bulge. Modera ...
... Broad central glow surrounded by fainter envelope. Stands high magnification well. NGC4559 (10.5) sg. Bright oval smudge. Mottled appearance in large telescopes. NGC4565 (10.5) sg. One of the finest "edge-on" spiral galaxies. Appears as a thin needle of light with the hint of a central bulge. Modera ...
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY
... determined using the newly discovered period-luminosity relation for certain variable stars. The derived distances proved that the Milky Way was an “island universe” of stars, similar to other nebulae seen all around the sky. The MW is classified as a spiral galaxy, containing about 200 billion star ...
... determined using the newly discovered period-luminosity relation for certain variable stars. The derived distances proved that the Milky Way was an “island universe” of stars, similar to other nebulae seen all around the sky. The MW is classified as a spiral galaxy, containing about 200 billion star ...
Stars and Galaxies Misconceptions
... Students who confuse terms like “Galaxy” with “Solar System” or who have no conception of the scale of the Milky Way may think that the stars in the night sky are from other galaxies. All the stars we see with our “naked eyes” are in the Milky Way Galaxy –we cannot see individual stars in other gala ...
... Students who confuse terms like “Galaxy” with “Solar System” or who have no conception of the scale of the Milky Way may think that the stars in the night sky are from other galaxies. All the stars we see with our “naked eyes” are in the Milky Way Galaxy –we cannot see individual stars in other gala ...
Red Dwarfs and Barnard`s star. Their origin and significance to
... Red Dwarfs and Barnard’s star. Their origin and significance to astronomy. What is a Red Dwarf? A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperatur ...
... Red Dwarfs and Barnard’s star. Their origin and significance to astronomy. What is a Red Dwarf? A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperatur ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... Eagle Nebula and other nebulae (stars in formation) on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while? Realize that once our Sun starts to run o ...
... Eagle Nebula and other nebulae (stars in formation) on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while? Realize that once our Sun starts to run o ...
Kinds of Stars
... Both Centauri stars can only be seen at locations within 30 degrees of the south pole. ...
... Both Centauri stars can only be seen at locations within 30 degrees of the south pole. ...
Big bang and Stars
... the shorter wavelength blue end of the spectrum or to the longer wavelength red end of the spectrum ...
... the shorter wavelength blue end of the spectrum or to the longer wavelength red end of the spectrum ...
NAME:______ANSWER KEY_______________________Period
... 1. What is the universe made up of? matter, energy, and space 2. What does light year measure? distance 3. Why do we use light year instead of kilometers? Kilometers would be way to big of a number 4. Change the following number 78,000,000 to scientific notation. 7.8 x 107 5. Write 1.90 x 108 in sta ...
... 1. What is the universe made up of? matter, energy, and space 2. What does light year measure? distance 3. Why do we use light year instead of kilometers? Kilometers would be way to big of a number 4. Change the following number 78,000,000 to scientific notation. 7.8 x 107 5. Write 1.90 x 108 in sta ...
The Milky Way – A Classic Galaxy
... • Pick off the Luminosity from the Cepheid P-L Relation • Calculate how far away the star must be to have that luminosity look like the apparent brightness we see here from Earth ...
... • Pick off the Luminosity from the Cepheid P-L Relation • Calculate how far away the star must be to have that luminosity look like the apparent brightness we see here from Earth ...
Proxima
... Centaurus is known as a “myth” constellation. It’s the 9th largest constellation in the sky Proxima is the 3rd star in Centaurus Contains 2 of the brightest stars (Alpha Centauri and Beta Centauri) It contains 11 stars ...
... Centaurus is known as a “myth” constellation. It’s the 9th largest constellation in the sky Proxima is the 3rd star in Centaurus Contains 2 of the brightest stars (Alpha Centauri and Beta Centauri) It contains 11 stars ...
Space Science Unit - World of Teaching
... • These clusters are grouped together into the various stages of a stars life cycle. • Let’s look at those briefly. ...
... • These clusters are grouped together into the various stages of a stars life cycle. • Let’s look at those briefly. ...
Measuring the Stars
... Space is Big. “Space is big. Really big. You just won't believe how vastly hugely mind-bogglingly big it is. I mean, you may think it's a long way down the road to the chemist, but that's just peanuts to space…” To be fair though, when confronted by the sheer enormity of the distances between the s ...
... Space is Big. “Space is big. Really big. You just won't believe how vastly hugely mind-bogglingly big it is. I mean, you may think it's a long way down the road to the chemist, but that's just peanuts to space…” To be fair though, when confronted by the sheer enormity of the distances between the s ...
Space Science Unit
... • These clusters are grouped together into the various stages of a stars life cycle. • Let’s look at those briefly. ...
... • These clusters are grouped together into the various stages of a stars life cycle. • Let’s look at those briefly. ...
Cosmology 2 - schoolphysics
... 11. Star A has an apparent magnitude of +0.5 and an intensity of 1000 units. Star B has an apparent magnitude of –1.0. What is the intensity of star B? 12. Explain carefully what is meant by the absolute magnitude of a star. 13. Derive the connection between the absolute magnitude and the apparent m ...
... 11. Star A has an apparent magnitude of +0.5 and an intensity of 1000 units. Star B has an apparent magnitude of –1.0. What is the intensity of star B? 12. Explain carefully what is meant by the absolute magnitude of a star. 13. Derive the connection between the absolute magnitude and the apparent m ...
PHY299B Poster-Justin Hudson-v2
... when the brighter star blocks out the light from the other star when passing in front of it. • From these curves, we can tell if stars follow the characteristics of an eclipsing binary or other types of variable stars. ...
... when the brighter star blocks out the light from the other star when passing in front of it. • From these curves, we can tell if stars follow the characteristics of an eclipsing binary or other types of variable stars. ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.