* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NAME:______ANSWER KEY_______________________Period
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
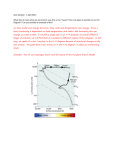
NAME:___________ANSWER KEY_______________________Period:__________ Unit 10-11 Review Sheet ANSWER KEY 1. What is the universe made up of? matter, energy, and space 2. What does light year measure? distance 3. Why do we use light year instead of kilometers? Kilometers would be way to big of a number 4. Change the following number 78,000,000 to scientific notation. 7.8 x 107 5. Write 1.90 x 108 in standard number form. 190,000,000 6. Define Nebula: a large cloud of gas and dust from which a star begins 7. Main Sequence Star turns into a giant when it loses all its hydrogen. 8. What type of star is our Sun on the H-R diagram? Main Sequence Star 9. Which group of stars on the H-R diagram is the brightest? Main Sequence Star 10. After a star dies what happens to the remains? It turns back into gas and dust and the CYCLE starts over again. 11. Our Sun is at what stage of it’s life cycle? Our Sun is a Main Sequence star and it is halfway through it’s life cycle. Our Sun is 4.5 billion years old and it has 5.5 billion years left. 12. The brightness of the star is most dependent on the star’s mass. 13. Which group of stars on the H-R diagram do most stars start out as? Main Sequence Stars Fill in the following stars life cycles: 14. Sun-Like Star--->Red Giant--->Nebula--->White Dwarf--->Black Dwarf 15. Huge Star--->Red Supergiant--->Supernova--->Neutron Star 16. Giant Star--->Red Supergiant--->Supernova--->Black Hole 17. Define Absolute magnitude: the actual brightness of the star 18. Define Apparent magnitude: how bright the star looks from earth 19. The black hole is a region in space where the gravitational pull is so great that light cannot escape. 20. A region in space that is so dense that nothing, even light energy, can’t escape its gravitational field is know as a black hole. 21. What are the three type of galaxies? spiral, elliptical, and irregular 22. The galaxy that has spiral arms with a bulge it the center is the spiral galaxy. 23. The galaxy that has an elongated shape is the elliptical galaxy. 24. The galaxy with no shape is the irregular galaxy. 25. The Milky Way is an example of a galaxy with a spiral shape. 26. Earth is in which kind of galaxy? Spiral 27. Define Quasar: a galaxy that has a black hole in it’s center 28. What did Copernicus think? he thought the first to suggest that the Earth was not the center of the Universe 29. Define Theory: a logical explanation of events that occur in nature 30. Which theory of the universe is the most accepted by all the scientists? THE BIG BANG NAME:_____________________________________________Period:__________ Unit 10-11 Review Sheet 1. What is the universe made up of? 2. What does light year measure? 3. Why do we use light year instead of kilometers? 4. Change the following number 78,000,000 to scientific notation. 5. Write 1.90 x 108 in standard number form. 6. Define Nebula: 7. Main Sequence Star turns into a _________when it loses all its hydrogen. 8. What type of star is our Sun on the H-R diagram? 9. Which group of stars on the H-R diagram is the brightest? 10. After a star dies what happens to the remains? I 11. Our Sun is at what stage of it’s life cycle? 12. The ___________________ of the star is most dependent on the star’s mass. 13. Which group of stars on the H-R diagram do most stars start out as? Label the Star’s Life Cycles below: 14. Sun-Like Star--->___________--->___________--->___________--->___________ 15. Huge Star--->___________--->___________--->___________ 16. Giant Star --->___________--->___________--->___________ 17. Define Absolute magnitude: 18. Define Apparent magnitude: 19. The __________________ is a region in space where the gravitational pull is so great that light cannot escape. 20. A region in space that is so dense that nothing, even light energy, can escape its gravitational field is know as a ___________________. 21. What are the three type of galaxies? 22. The galaxy that has spiral arms with a bulge it the center is the ________________. 23. The galaxy that has an elongated shape is the __________________. 24. The galaxy with no shape is the _______________________. 25. The ________________ is an example of a galaxy with a spiral shape. 26. Earth is in which kind of galaxy? 27. Define Quasar: 28. What did Copernicus think? 29. Define Theory: 30. Which theory of the universe is the most accepted by all the scientists?