SAMPLE TEST: Stars and Galaxies Multiple Choice Identify the letter
... 48. A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. 49. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ____________________ as it appears from ____________________. 50. Some stars, called ____________________, get brighter and fainter in a regular pattern. 51. A(n) ____________________ i ...
... 48. A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. 49. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ____________________ as it appears from ____________________. 50. Some stars, called ____________________, get brighter and fainter in a regular pattern. 51. A(n) ____________________ i ...
Everything Under and Over The Stars
... Neutron Stars? Neutron stars spin very fast and are only 10-15 km in radius. Neutron stars are made when super giants break down and together comes a neutron star. A few neutron stars emit radio waves and are known as pulsars. ...
... Neutron Stars? Neutron stars spin very fast and are only 10-15 km in radius. Neutron stars are made when super giants break down and together comes a neutron star. A few neutron stars emit radio waves and are known as pulsars. ...
Ch.1, Sec.3 - Mapping the Stars
... planets and we use the lightyear to measure their distance from us - one light-year represents the distance light travels in 365 days (6 trillion miles @ 186,000 miles per second) ...
... planets and we use the lightyear to measure their distance from us - one light-year represents the distance light travels in 365 days (6 trillion miles @ 186,000 miles per second) ...
Life Cycle of a Star worksheet
... space, forming a cloud of gas called a planetary nebula. The blue-white hot core of the star that is left behind cools and becomes a ____________________________________. The white dwarf eventually runs out of fuel and dies as a ___________________________________. ...
... space, forming a cloud of gas called a planetary nebula. The blue-white hot core of the star that is left behind cools and becomes a ____________________________________. The white dwarf eventually runs out of fuel and dies as a ___________________________________. ...
Stars_Galaxies_Introduction - Etiwanda E
... What is the source of light in a galaxy? – How is energy produced by the sun? – How are sunspots, prominences, and solar flares related? – Why is our sun considered to be an average star? – How does our sun differ from stars in binary systems? ...
... What is the source of light in a galaxy? – How is energy produced by the sun? – How are sunspots, prominences, and solar flares related? – Why is our sun considered to be an average star? – How does our sun differ from stars in binary systems? ...
ASTR101 Unit 10 Assessment Answer Key 1. Mass, luminosity, size
... from about 60 solar masses to about 1/12 solar mass, in luminosity from about 1,000,000 to 1/10,000 solar luminosities, in radius from about 1,000 to 1/10 solar radii, in surface temperature from about 35,000 to 3,000 K, and in age, from about 13 billion years to stars that are just now being born. ...
... from about 60 solar masses to about 1/12 solar mass, in luminosity from about 1,000,000 to 1/10,000 solar luminosities, in radius from about 1,000 to 1/10 solar radii, in surface temperature from about 35,000 to 3,000 K, and in age, from about 13 billion years to stars that are just now being born. ...
Astronomy Part 2 - Malvern Troop 7
... runs a distinctive line of three stars comprising Orion’s Belt. To the top right of Orion lies another prominent star, Alderbaran, which represents the eye of Taurus. Continue the line from Orion through Aldebaran brings you to the Pleiades, a star cluster. ...
... runs a distinctive line of three stars comprising Orion’s Belt. To the top right of Orion lies another prominent star, Alderbaran, which represents the eye of Taurus. Continue the line from Orion through Aldebaran brings you to the Pleiades, a star cluster. ...
Stars - Moodle
... ____________ or ________________ from a viewer Which way is the color shifted if the object is moving toward the viewer? Which way is the color shifted if the object is moving away from the viewer? ...
... ____________ or ________________ from a viewer Which way is the color shifted if the object is moving toward the viewer? Which way is the color shifted if the object is moving away from the viewer? ...
III. Contents of The Universe
... B. Stars – balls of hot gas that emit light The Sun is the closest star to us 1. Multiple Star System most stars that we see in the sky are parts of multiple star systems revolve around each other. two stars = binary star system. ex. Algol, eclipsing binary ...
... B. Stars – balls of hot gas that emit light The Sun is the closest star to us 1. Multiple Star System most stars that we see in the sky are parts of multiple star systems revolve around each other. two stars = binary star system. ex. Algol, eclipsing binary ...
Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star
... gas and dust in my Solar Nursery and begins to Shine! When the cool masses of dust and gas combine, a star has a temperature of 1,800,000 degrees F! http://www.virginmedia.com/images/ ...
... gas and dust in my Solar Nursery and begins to Shine! When the cool masses of dust and gas combine, a star has a temperature of 1,800,000 degrees F! http://www.virginmedia.com/images/ ...
The Milky Way
... • How many trips of Sun around Milky Way? R = 8.5 kpc V = 220km/s P = 2.5x108 yrs ...
... • How many trips of Sun around Milky Way? R = 8.5 kpc V = 220km/s P = 2.5x108 yrs ...
Skywatch Astro Ed Dec13
... Even our nearest star system to the Sun, Alpha Centauri, is more than four light-years away; a reminder of the vast gulf that separates us from even our closest stellar neighbours. Between Sirius and Aldebaran, another bright star beckons us. This is Rigel, which at 900 light years away, is more tha ...
... Even our nearest star system to the Sun, Alpha Centauri, is more than four light-years away; a reminder of the vast gulf that separates us from even our closest stellar neighbours. Between Sirius and Aldebaran, another bright star beckons us. This is Rigel, which at 900 light years away, is more tha ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500 K are red. Shade a vertical band from 2000 K to 3500 K a light red. 4. Shade other color bands as follows: Stars up to 5000 K are orange-red, up to 6000 K yellow-white, up to 7500 K blue-white, and up to 40,000 K blue. 5. Look for patterns in your graph ...
... 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500 K are red. Shade a vertical band from 2000 K to 3500 K a light red. 4. Shade other color bands as follows: Stars up to 5000 K are orange-red, up to 6000 K yellow-white, up to 7500 K blue-white, and up to 40,000 K blue. 5. Look for patterns in your graph ...
Photometry
... this is the case, we can use special filters so that the only photons we see are of a particular wavelength. This wavelength is identified with a color. The number of photons observed can be converted into an apparent magnitude (m), which is simply a measure of how bright the stars look from Earth. ...
... this is the case, we can use special filters so that the only photons we see are of a particular wavelength. This wavelength is identified with a color. The number of photons observed can be converted into an apparent magnitude (m), which is simply a measure of how bright the stars look from Earth. ...
The magnitude scale, parallax, the parsec, and Cepheid distances
... • But not convenient when comparing sources of very different brightness – e.g. if f ranges from 101 to 1030 units ...
... • But not convenient when comparing sources of very different brightness – e.g. if f ranges from 101 to 1030 units ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Which star has strong lines of ionized helium in its spectrum? Which star is the white dwarf? Which star has spectrum lines due to molecules? ...
... Which star has strong lines of ionized helium in its spectrum? Which star is the white dwarf? Which star has spectrum lines due to molecules? ...
Death of Low Mass Stars 8 Solar Masses or less
... it further. Called Electron Degeneracy • The black dwarf will continue to exist at temps close to absolute zero forever…. ...
... it further. Called Electron Degeneracy • The black dwarf will continue to exist at temps close to absolute zero forever…. ...
THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM (H
... NOTE: Absolute Magnitude IS THE SAME THING AS LUMINOSITY ON THE GRAPH DEFINE: absolute magnitude (Pg. 372 if you don’t know) ...
... NOTE: Absolute Magnitude IS THE SAME THING AS LUMINOSITY ON THE GRAPH DEFINE: absolute magnitude (Pg. 372 if you don’t know) ...
lifedeath - University of Glasgow
... Hydrogen fusion – fuelling a star’s nuclear furnace H = Hydrogen He = Helium ...
... Hydrogen fusion – fuelling a star’s nuclear furnace H = Hydrogen He = Helium ...
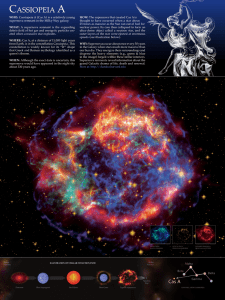
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.