* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Constellations
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Orion Nebula wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
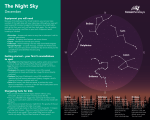
Name:___________________ Date:____________________ Class:___________________ Constellations 1. If you live in the Northern Hemisphere, at what time of year can you see Polaris, the north star? Choose the best answer. A. The winter B. The spring and fall C. The summer D. All year round 2. The number of constellations in the Zodiac is equivalent to: A. The number of months in a year B. The number of days in a month C. The number of weeks in a year D. The number of years in a decade 3. Astronomers recognize the Orion Nebula as a large celestial body. What can you infer about the Orion Nebula from its name? A. It is a star in the constellation Orion B. It plays an important role in the myth of Orion C. It is located near the constellation Orion D. It is made up of stars from the constellation Orion 6. What phenomenon is responsible for the fact that some constellations are only visible at certain times during the year? A. The rotation of the earth on its axis B. The revolution of the moon around the earth C. The revolution of the earth around the sun D. The revolution of the sun around the Milky Way galaxy 7. Most of the constellations we're familiar with were first charted by: A. The International Astronomical Union B. Ancient Europeans and Middle Easterners C. Astronomers in ancient China D. Ancient Mayan astronomers 8. Which of the following can be found in the ecliptic? A. The Big Dipper B. Orion, the mighty hunter C. Ursa Minor, the little bear D. Taurus, the bull 9. Modern astronomers' definition of a constellation is most similar to: 4. Astrology, or the study of horoscopes, is not based on the scientific method. Therefore, it's considered pseudoscience. What can you infer about the prefix "pseudo-?" A. A specific area on a map B. A large sphere with the earth at its center C. A pattern of stars that forms a picture D. A range of dates on a calendar A. It means "ancient" B. It means "false" C. It means "popular" D. It means "heavenly" 10. If you wanted to see certain constellations appear upside-down, to which country could you travel? 5. If you wanted to watch a constellation rise one evening, in which direction would you look? A. North B. South C. East D. West A. Mexico B. Australia C. Russia D. Japan