Parallaxes are very small The position of Ursa Major
... arcseconds. A star near the center of our Galaxy has a parallax of about 0.0001 arcseconds. In order to measure such small angles we need an instrument like Gaia. ...
... arcseconds. A star near the center of our Galaxy has a parallax of about 0.0001 arcseconds. In order to measure such small angles we need an instrument like Gaia. ...
Star Properties and Stellar Evolution
... 1. Pulsating stars – expand and contract 2. Cepheid Variables – used to find distances to galaxies that contain them 3. Eclipsing Binaries – 2 stars revolve around each other ...
... 1. Pulsating stars – expand and contract 2. Cepheid Variables – used to find distances to galaxies that contain them 3. Eclipsing Binaries – 2 stars revolve around each other ...
galaxies and stars - Valhalla High School
... groups of two or more stars • Binary systems have two stars • A system where one star blocks the other is an eclipsing binary • A system with three stars is a triple star system ...
... groups of two or more stars • Binary systems have two stars • A system where one star blocks the other is an eclipsing binary • A system with three stars is a triple star system ...
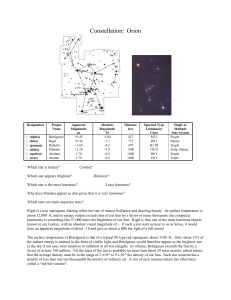
Orion
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
How is a Star`s Color Related to Its temperature?
... How is a Star’s Color Related to Its temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than cthers. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue. and Betelgense is red. Capella and ore" Sun are yellow, in this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russel ...
... How is a Star’s Color Related to Its temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than cthers. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue. and Betelgense is red. Capella and ore" Sun are yellow, in this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russel ...
Support worksheet – Topic 3 Questions
... Suggest why the stellar parallax method is limited to distances of about 300 pc for Earth-based telescopes but can be extended to 1000 pc for satellite-based telescopes. ...
... Suggest why the stellar parallax method is limited to distances of about 300 pc for Earth-based telescopes but can be extended to 1000 pc for satellite-based telescopes. ...
Galaxies - Where Science Meets Life
... light from distant galaxies. The red shift indicates that the stars are moving away from a central point in the universe at a certain speed. This supports the theory of the Big Bang in that the universe started from a ...
... light from distant galaxies. The red shift indicates that the stars are moving away from a central point in the universe at a certain speed. This supports the theory of the Big Bang in that the universe started from a ...
STARS AND CONSTELLATIONS
... - Used to find North Star. The North Star is about six times the distance between bowl stars (pointer stars) - Two galaxies and one planetary nebula are found in the Big Dipper. The planetary nebula is the Owl Nebula, (a star explodes shedding it’s outer layer of gases). - In Greek mythology the Big ...
... - Used to find North Star. The North Star is about six times the distance between bowl stars (pointer stars) - Two galaxies and one planetary nebula are found in the Big Dipper. The planetary nebula is the Owl Nebula, (a star explodes shedding it’s outer layer of gases). - In Greek mythology the Big ...
Astronomy Study Guide #2
... 23. What is the ``Doppler Effect" and how does it apply to light? And to stars? 24. Why are the Balmer lines of hydrogen important? What are they and how are they formed? (Hint: We saw these in the spectral tube demonstrations.) 25. How will stars less massive than 1.5 M_0 end their Post-Main Seque ...
... 23. What is the ``Doppler Effect" and how does it apply to light? And to stars? 24. Why are the Balmer lines of hydrogen important? What are they and how are they formed? (Hint: We saw these in the spectral tube demonstrations.) 25. How will stars less massive than 1.5 M_0 end their Post-Main Seque ...
OTA System Report For June 4, 2009 8:30 AM
... Previous 24 hours: 1) All hardware nominal, but FGS Thermal E442 – Aft F/G Panel is hitting YLW Hi 2) The 4 previous Acquisitions that were pending ETR telemetry were successful 3) There were 5 successful Acquisitions, and 1 TRANS Mode Observation with FGS 2 to support the AMA move. 4) 1 GSACQ was a ...
... Previous 24 hours: 1) All hardware nominal, but FGS Thermal E442 – Aft F/G Panel is hitting YLW Hi 2) The 4 previous Acquisitions that were pending ETR telemetry were successful 3) There were 5 successful Acquisitions, and 1 TRANS Mode Observation with FGS 2 to support the AMA move. 4) 1 GSACQ was a ...
Stars - Weebly
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
a. Recognize the physical attributes of stars in the night sky such as
... Yvonne looks at the stars in the night sky through a telescope. She sees four stars that have different colors. One star is blue, one is white, one looks yellow, and the fourth looks red. Which star is the coolest? a. the red star b. the blue star c. the white star d. the yellow star Answer: b How a ...
... Yvonne looks at the stars in the night sky through a telescope. She sees four stars that have different colors. One star is blue, one is white, one looks yellow, and the fourth looks red. Which star is the coolest? a. the red star b. the blue star c. the white star d. the yellow star Answer: b How a ...
Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 17 Nature of Stars
... On the H-R diagram, giant and supergiant stars lie above the main sequence, while white dwarfs are below the main sequence. By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a mainsequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf. Using the H-R diagram and ...
... On the H-R diagram, giant and supergiant stars lie above the main sequence, while white dwarfs are below the main sequence. By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a mainsequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf. Using the H-R diagram and ...
Comet Lulin - indstate.edu
... distance of about 61 million kilometers. By now, Comet Lulin is predicted to be 5th magnitude, which means it could be visible to the naked eye in rural locations. The most interesting thing about closest approach, however, is the comet's ridiculously high apparent velocity. Comet Lulin will be spee ...
... distance of about 61 million kilometers. By now, Comet Lulin is predicted to be 5th magnitude, which means it could be visible to the naked eye in rural locations. The most interesting thing about closest approach, however, is the comet's ridiculously high apparent velocity. Comet Lulin will be spee ...
Stars
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
20081 Study Guide_77-120
... Similarly, astronomers detect black holes by their gravitational effects on nearby stars, gas, or dust. ...
... Similarly, astronomers detect black holes by their gravitational effects on nearby stars, gas, or dust. ...
8hrdiagram1s
... If you know the luminosity and you measure the flux you can find the distance (F = L/4pd2) Called spectroscopic parallax ...
... If you know the luminosity and you measure the flux you can find the distance (F = L/4pd2) Called spectroscopic parallax ...
PH142 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... At the conclusion of the course, the students will be able to: 1. Describe the physical nature of the Sun. 2. Describe the physical processes on the Sun. 3. Explain the sequence of events during a solar eclipse--partial, annular, total. 4. Demonstrate an understanding of the methods of distance meas ...
... At the conclusion of the course, the students will be able to: 1. Describe the physical nature of the Sun. 2. Describe the physical processes on the Sun. 3. Explain the sequence of events during a solar eclipse--partial, annular, total. 4. Demonstrate an understanding of the methods of distance meas ...
Diapositiva 1
... starsknown as the Trapezium. Gathered within a region about 1.5 light-years in radius, they dominate the core of the dense Orion Nebula Star Cluster. Ultraviolet ionizing radiation from the Trapezium stars, mostly from the brightest star Theta-1 Orionis C powers the complex star forming region's ent ...
... starsknown as the Trapezium. Gathered within a region about 1.5 light-years in radius, they dominate the core of the dense Orion Nebula Star Cluster. Ultraviolet ionizing radiation from the Trapezium stars, mostly from the brightest star Theta-1 Orionis C powers the complex star forming region's ent ...
I : Internal structure of main sequence stars
... The luminosity L The efficiency of the fusion η The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
... The luminosity L The efficiency of the fusion η The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
PowerPoint Presentation - ASTR498E High energy
... A star leaves the main sequence once it exhausts its supply of hydrogen in the core This lifetime depends upon ...
... A star leaves the main sequence once it exhausts its supply of hydrogen in the core This lifetime depends upon ...
Supernova
... Explosions • Stars may explode cataclysmically. – Large energy release (103 – 106 L) – Short time period (few days) • These explosions used to be classified as novas or supernovas. – Based on absolute magnitude • They are now all called supernovas. ...
... Explosions • Stars may explode cataclysmically. – Large energy release (103 – 106 L) – Short time period (few days) • These explosions used to be classified as novas or supernovas. – Based on absolute magnitude • They are now all called supernovas. ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.