Astro 2 - Red Hook Central School District
... • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jjmjEDY qbCk • From 4:48 ...
... • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jjmjEDY qbCk • From 4:48 ...
Introduction to Stars: Their Properties
... 1 parsec (pc) = 3.26 light years 1 kiloparsec (1 kpc) = 1000 pc; 1 megaparsec (1 Mpc) = 1,000,000 pc ...
... 1 parsec (pc) = 3.26 light years 1 kiloparsec (1 kpc) = 1000 pc; 1 megaparsec (1 Mpc) = 1,000,000 pc ...
HW #5 Answers (Due 9/29)
... make Helium, the protons have to over come the repulsive force between them. This means that they have to be moving extremely fast or their average kinetic energy has to be very large. That means a high temperature. Also, collisions have to be head-on collisions. If not the particles will just scatt ...
... make Helium, the protons have to over come the repulsive force between them. This means that they have to be moving extremely fast or their average kinetic energy has to be very large. That means a high temperature. Also, collisions have to be head-on collisions. If not the particles will just scatt ...
+(J - cloudfront.net
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
No Slide Title
... The neutron star may continue to gain mass from nearby stars. At a critical moment, it becomes so dense it collapses in on itself, becoming a single point of zero size! Its gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape from inside a certain boundary - the EVENT HORIZON. The star is now a BLACK ...
... The neutron star may continue to gain mass from nearby stars. At a critical moment, it becomes so dense it collapses in on itself, becoming a single point of zero size! Its gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape from inside a certain boundary - the EVENT HORIZON. The star is now a BLACK ...
Telescopes (continued). Properties of Stars.
... Measuring the Apparent Brightness Stars emit radiation of all wavelengths. No detector is sensitive to the entire spectrum. Usually we measure apparent brightness in a small range of the complete spectrum. Eyes are sensitive to visible light. When we measure the apparent brightness in the visible r ...
... Measuring the Apparent Brightness Stars emit radiation of all wavelengths. No detector is sensitive to the entire spectrum. Usually we measure apparent brightness in a small range of the complete spectrum. Eyes are sensitive to visible light. When we measure the apparent brightness in the visible r ...
mass per nucleon
... main sequence star (core Hydrogen burning) core Hydrogen exhausted (sub-giant) shell Hydrogen burning (red giant) core Helium burning (Helium Flash) shell Helium burning (double-shell burning red giant) planetary nebula white dwarf ...
... main sequence star (core Hydrogen burning) core Hydrogen exhausted (sub-giant) shell Hydrogen burning (red giant) core Helium burning (Helium Flash) shell Helium burning (double-shell burning red giant) planetary nebula white dwarf ...
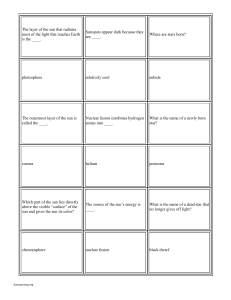
Chapter 21 Study Guide
... 12. A building that contains one or more telescopes is called an _____________________________. 13. Name one reason why astronomers have built large telescopes on the tops of mountains. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 14. The Hubble Space Telesco ...
... 12. A building that contains one or more telescopes is called an _____________________________. 13. Name one reason why astronomers have built large telescopes on the tops of mountains. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 14. The Hubble Space Telesco ...
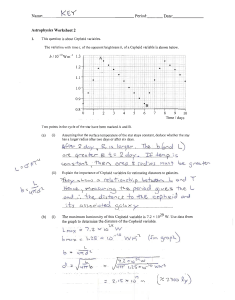
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram March 16 −
... Emitted energy per unit surface area è ...
... Emitted energy per unit surface area è ...
Name: Period : ______ The Universe – Life and Death of a Star How
... 2. “The Pillars of Creation are a stellar ____________________. New stars are in the process of being ______________ in the central regions.” 3. The Pillars are towering clouds of _________________ _________________________. 4. What element is the key component in stars? 5. What is the force that pu ...
... 2. “The Pillars of Creation are a stellar ____________________. New stars are in the process of being ______________ in the central regions.” 3. The Pillars are towering clouds of _________________ _________________________. 4. What element is the key component in stars? 5. What is the force that pu ...
Astronomy 2 Relativity and Gravitation
... Vega is an AOV star, of effective temperature T = 9520 K, and absolute bolometric magnitude Mbol = 0.3. Given that the Sun has effective temperature 5800 K and Mbol = 4.72, estimate the radius of Vega in units of the solar radius, stating ...
... Vega is an AOV star, of effective temperature T = 9520 K, and absolute bolometric magnitude Mbol = 0.3. Given that the Sun has effective temperature 5800 K and Mbol = 4.72, estimate the radius of Vega in units of the solar radius, stating ...
Astronomy 1 Study Guide Key 16
... 7. A galaxy is a collection of stars. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way. 8. It has many solar systems with in its arms. At the center of our spiral galaxy is a black hole, so our galaxy is also called a quasar. Stars Be able to read an H-R diagram. ...
... 7. A galaxy is a collection of stars. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way. 8. It has many solar systems with in its arms. At the center of our spiral galaxy is a black hole, so our galaxy is also called a quasar. Stars Be able to read an H-R diagram. ...
Stars Unit
... Many stars orbit each other= Binary Stars BINARY STARS We can find the mass of these stars by the size their orbits, also the small star blocks light from the big star, that tells us their size as well. ...
... Many stars orbit each other= Binary Stars BINARY STARS We can find the mass of these stars by the size their orbits, also the small star blocks light from the big star, that tells us their size as well. ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
The Life of a Star
... • Begin as a ball of gas and dust. • Go from there to mainsequence, red-giant or supergiant, then to white dwarf. • Or be a massive star that goes from main-sequence to supernova to neutron star (perhaps pulsar) and perhaps becomes a black hole. ...
... • Begin as a ball of gas and dust. • Go from there to mainsequence, red-giant or supergiant, then to white dwarf. • Or be a massive star that goes from main-sequence to supernova to neutron star (perhaps pulsar) and perhaps becomes a black hole. ...
Name: ____________ Period: ______ STAR BIOGRAPHY Name of
... *May include diagram *Talk about the birth of your star, include its age if known, what life cycle it is in, and predict what will happen in the future with your star. (Include each Life Cycle Stage) ...
... *May include diagram *Talk about the birth of your star, include its age if known, what life cycle it is in, and predict what will happen in the future with your star. (Include each Life Cycle Stage) ...
Summer 2001 Day 07: Intro to Solar System
... 4) What does the brightness of a star depend on? A) Define brightness as the watts/m2 received from a star. B) Brightness follows an inverse square relation B=L/(4πR2). Draw the picture (see figure 54.2 C) Calculate the brightness of the Sun as seen from Earth B=1,355 W/m2 i) Typical stellar brightn ...
... 4) What does the brightness of a star depend on? A) Define brightness as the watts/m2 received from a star. B) Brightness follows an inverse square relation B=L/(4πR2). Draw the picture (see figure 54.2 C) Calculate the brightness of the Sun as seen from Earth B=1,355 W/m2 i) Typical stellar brightn ...
Photometry
... Slide the plastic overlay up and down until the main sequence on the overlay best aligns with the main sequence on your paper graph. Keep the y axes precisely parallel and over top one another. Seek a best fit for the central portion of the combined patterns. (The cool red stars in the lower right o ...
... Slide the plastic overlay up and down until the main sequence on the overlay best aligns with the main sequence on your paper graph. Keep the y axes precisely parallel and over top one another. Seek a best fit for the central portion of the combined patterns. (The cool red stars in the lower right o ...
December 1, 2011 - Perry Local Schools
... 1. Place the small flashlight on a desk or table near the front of the room. 2. Place the large flashlight on a desk or table near the back of the room. 3. Gather at the front of the room so they can all see both flashlights easily. 4. Turn on both flashlights. 5. Darken the room. 6. Observe and co ...
... 1. Place the small flashlight on a desk or table near the front of the room. 2. Place the large flashlight on a desk or table near the back of the room. 3. Gather at the front of the room so they can all see both flashlights easily. 4. Turn on both flashlights. 5. Darken the room. 6. Observe and co ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.