Properties of Stars in general
... Blue stars – very hot ~ 20,000K White stars - hot ~ 10,000k Sun-like stars – yellow ~ 6,000K Orange stars ~ 4500k Red stars ~ 3000K Temperature has a major effect on the spectral lines seen in the atmosphere of a star ...
... Blue stars – very hot ~ 20,000K White stars - hot ~ 10,000k Sun-like stars – yellow ~ 6,000K Orange stars ~ 4500k Red stars ~ 3000K Temperature has a major effect on the spectral lines seen in the atmosphere of a star ...
Stellar Classification Worksheet 2
... Explain how each of the 5 characteristics in the boxes below is used to classify stars. In each box, give 2 examples of stars and their specific characteristics. Use pages 127-129 in the textbook and the examples below to complete the worksheet. ...
... Explain how each of the 5 characteristics in the boxes below is used to classify stars. In each box, give 2 examples of stars and their specific characteristics. Use pages 127-129 in the textbook and the examples below to complete the worksheet. ...
Observational Astronomy Star Charts
... – The rising and setting of the stars is caused by the Earth’s rotation about its axis. ...
... – The rising and setting of the stars is caused by the Earth’s rotation about its axis. ...
First Exam - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... 26. You look up in the night sky and see the planet Jupiter, the planet Mars, and the Moon very close together. You know that they are located in or close to one of the following. Which is it? (a) the ecliptic ∗ (b) the celestial equator (c) the zenith (d) the north celestial pole (e) the constellat ...
... 26. You look up in the night sky and see the planet Jupiter, the planet Mars, and the Moon very close together. You know that they are located in or close to one of the following. Which is it? (a) the ecliptic ∗ (b) the celestial equator (c) the zenith (d) the north celestial pole (e) the constellat ...
Star names and magnitudes
... Many stars are variable, which complicates labelling based on brightness! If they have a Bayer designation (eg dCep), they keep these. Otherwise, their constellation name is prefixed by one or two letters, depending on the time of discovery. 334 combinations of letters are available – after that the ...
... Many stars are variable, which complicates labelling based on brightness! If they have a Bayer designation (eg dCep), they keep these. Otherwise, their constellation name is prefixed by one or two letters, depending on the time of discovery. 334 combinations of letters are available – after that the ...
If you wish to a copy of this months Night Sky News
... The Planets Mercury is not well placed low in the east at sunrise, and is best observed in the first days of the month. As it closes in on the Sun over the next month, it will become impossible to observe. Venus is catching up with us on its orbit inside the Earth’s orbit, so its angular size is inc ...
... The Planets Mercury is not well placed low in the east at sunrise, and is best observed in the first days of the month. As it closes in on the Sun over the next month, it will become impossible to observe. Venus is catching up with us on its orbit inside the Earth’s orbit, so its angular size is inc ...
What are yellow stars?
... Yellow stars are stars that have reached a temperature of 5,000 to 6,000 degrees Fahrenheit, and around 6,000 Kelvin. Yellow Stars have an average temperature and that makes them yellow. Blue stars are the hottest, red are the coldest. Arcturus and Antares are some of the biggest Yellow Stars that w ...
... Yellow stars are stars that have reached a temperature of 5,000 to 6,000 degrees Fahrenheit, and around 6,000 Kelvin. Yellow Stars have an average temperature and that makes them yellow. Blue stars are the hottest, red are the coldest. Arcturus and Antares are some of the biggest Yellow Stars that w ...
Folie 1 - univie.ac.at
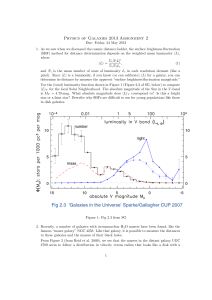
... variations in stars brighter than visual magnitude 4.0 (and with less accuracy also down to a visual magnitude of 7.0). There are 534 stars brighter than V = 4.0 mag in the sky and observable at the proposed precision level with BRITE-Constellation. Considering the typical time scales for their vari ...
... variations in stars brighter than visual magnitude 4.0 (and with less accuracy also down to a visual magnitude of 7.0). There are 534 stars brighter than V = 4.0 mag in the sky and observable at the proposed precision level with BRITE-Constellation. Considering the typical time scales for their vari ...
Spectra of stars
... The continuous spectrum originates from the surface of the star and the absorption lines are produced when light passes upwards and outwards through the tenuous upper layers of the star. By looking at the spectrum of a star astronomers can determine: (a) the temperature of the star (b) the velocity ...
... The continuous spectrum originates from the surface of the star and the absorption lines are produced when light passes upwards and outwards through the tenuous upper layers of the star. By looking at the spectrum of a star astronomers can determine: (a) the temperature of the star (b) the velocity ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... galaxies. Black holes are thought to do this by heating up and blasting away the gas that fuels star formation. • The blue color here represents radiation pouring out from material very close to the black hole. The grayish structure surrounding the black hole, called a torus, is made up of gas and d ...
... galaxies. Black holes are thought to do this by heating up and blasting away the gas that fuels star formation. • The blue color here represents radiation pouring out from material very close to the black hole. The grayish structure surrounding the black hole, called a torus, is made up of gas and d ...
Exploring Space
... When the core of the Protostar reaches 10 million K, pressure is so great that nuclear fusion occurs- a star is born Heat from fusion of hydrogen is released When balance is maintained from inward pressure (gravity) and outward pressure (heat) the Main-Sequence stage is ...
... When the core of the Protostar reaches 10 million K, pressure is so great that nuclear fusion occurs- a star is born Heat from fusion of hydrogen is released When balance is maintained from inward pressure (gravity) and outward pressure (heat) the Main-Sequence stage is ...
Chapter 16 Lesson 2: What is a Star
... Some galaxies are called irregular because they are not spiral or elliptical and do not have a definite shape. 1. Irregular galaxies are probably young galaxies with their stars are still forming. Constellations a. Ursa Major is a constellation, an area of the sky and all the stars seen in that area ...
... Some galaxies are called irregular because they are not spiral or elliptical and do not have a definite shape. 1. Irregular galaxies are probably young galaxies with their stars are still forming. Constellations a. Ursa Major is a constellation, an area of the sky and all the stars seen in that area ...
Messier Galaxies of #202541
... overabundance of confusing dim stars. Plot all the stars, compare them with the star map, and then add the Messier galaxies when you find them. Two areas will stand out: 4 dim stars around Rho Virginis and 4 dim stars near 6 Coma Berenicis. Rho and 6 Coma will be important guide stars. These stars h ...
... overabundance of confusing dim stars. Plot all the stars, compare them with the star map, and then add the Messier galaxies when you find them. Two areas will stand out: 4 dim stars around Rho Virginis and 4 dim stars near 6 Coma Berenicis. Rho and 6 Coma will be important guide stars. These stars h ...
Everything Under and Over The Stars
... mass-radius relationship. This is that The higher the mass, the smaller the radius, thus no stable white dwarf can exist. White dwarfs evolve from other stars with three, four, sometimes higher solar masses. It then swells to a red giant, and expels its outer layer in an incredibly catastrophic even ...
... mass-radius relationship. This is that The higher the mass, the smaller the radius, thus no stable white dwarf can exist. White dwarfs evolve from other stars with three, four, sometimes higher solar masses. It then swells to a red giant, and expels its outer layer in an incredibly catastrophic even ...
Galactic Address/Stars/Constellations
... What is a star? • A star is an object in space that produces its own light and heat through nuclear ...
... What is a star? • A star is an object in space that produces its own light and heat through nuclear ...
Chapter 28.3 Topic questions
... 11. Red Super Giant stars have surface temperatures that are cooler than our earth, so why do they have greater luminosity than the sun? 12. The H-R diagram also includes which stars that are near the end of their life, what are these stars called? 13. A star begins it life in a cloud of gas and dus ...
... 11. Red Super Giant stars have surface temperatures that are cooler than our earth, so why do they have greater luminosity than the sun? 12. The H-R diagram also includes which stars that are near the end of their life, what are these stars called? 13. A star begins it life in a cloud of gas and dus ...
Stars - Trimble County Schools
... • Location changes throughout the year due to Earth’s orbit – Classified by season ...
... • Location changes throughout the year due to Earth’s orbit – Classified by season ...
Amie Bickert - ColonialAcademyScience
... Protostar- earliest stage of a stars life White dwarf: blue-white core of the star that is left behind cools forms this. Supernovas: an explosion of a suergiant Neutron star: the remains of high-mass stars. Black holes- an object with gravity so strong that nothing, not even light, can esc ...
... Protostar- earliest stage of a stars life White dwarf: blue-white core of the star that is left behind cools forms this. Supernovas: an explosion of a suergiant Neutron star: the remains of high-mass stars. Black holes- an object with gravity so strong that nothing, not even light, can esc ...
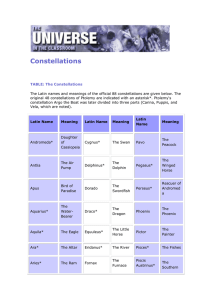
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.