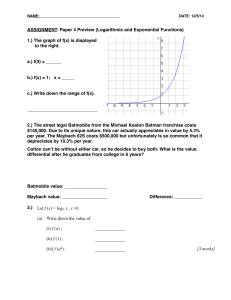
Let f (x) = log x , Let f (x) = loga x , x>0 . (a) Write down the value of (i
... 7.) As we learned in class, our Twinkle Twinkle little stars have apparent magnitude (brightness visible from Earth) and absolute magnitude (actual brightness exuded from the star). The equation is: m – M = log (d/10)5 where “m” is the apparent magnitude, “M” is the absolute magnitude, and “d” is th ...
... 7.) As we learned in class, our Twinkle Twinkle little stars have apparent magnitude (brightness visible from Earth) and absolute magnitude (actual brightness exuded from the star). The equation is: m – M = log (d/10)5 where “m” is the apparent magnitude, “M” is the absolute magnitude, and “d” is th ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Lecture 10 February 13
... spectra of two stars of different type Spectroscopic Binary Doppler shift shows orbital motion Eclipsing Binary light varies Half of all stars are in binaries…. Binary stars are formed at birth. Both components will have same age and composition. Can vary in mass Can be very distant (0.1pc) or touch ...
... spectra of two stars of different type Spectroscopic Binary Doppler shift shows orbital motion Eclipsing Binary light varies Half of all stars are in binaries…. Binary stars are formed at birth. Both components will have same age and composition. Can vary in mass Can be very distant (0.1pc) or touch ...
Monday, December 8 - Otterbein University
... b. Aries would be in the South because the stars shift by one constellation. c. Pisces would be in the South because the stars shift a constellation per ...
... b. Aries would be in the South because the stars shift by one constellation. c. Pisces would be in the South because the stars shift a constellation per ...
stars
... • Are a group of stars that are connected together to make a picture (like connect the dots) • They were used but early explorers to navigate the sea at night • All together there are 88 constellations in the night sky. ...
... • Are a group of stars that are connected together to make a picture (like connect the dots) • They were used but early explorers to navigate the sea at night • All together there are 88 constellations in the night sky. ...
From the Everett and Seattle Astronomical Societies, this is IT
... the sun, because the heat and pressure from such big stars' cores forces matter away from the surface. Eikenberry said one possibility is that the big star was formed in a process called shock-induced star formation, which occurs when a supernova blows up and slams the gaseous material in a molecula ...
... the sun, because the heat and pressure from such big stars' cores forces matter away from the surface. Eikenberry said one possibility is that the big star was formed in a process called shock-induced star formation, which occurs when a supernova blows up and slams the gaseous material in a molecula ...
Stars: Other Suns
... • Apply Kepler’s 3rd law to get sum of masses from orbital period, separation (need distance!) ...
... • Apply Kepler’s 3rd law to get sum of masses from orbital period, separation (need distance!) ...
Bellringer - Madison County Schools
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its SIZE and TEMPERATURE. ...
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its SIZE and TEMPERATURE. ...
MAUI STARGAZING MAY OBSERVING LIST DEEP SPACE
... Scorpius rising (Scorpion) Southern Cross rising (Centaurus) Taurus (The Bull) Ursa Major (Big Bear) Ursa Minor (Little Bear) Virgo (Maiden) FIRST MAGNITUDE STARS - First magnitude stars are the 20 brightest stars visible in the night sky from Planet Earth. Hipparchos, introduced the magnitude scale ...
... Scorpius rising (Scorpion) Southern Cross rising (Centaurus) Taurus (The Bull) Ursa Major (Big Bear) Ursa Minor (Little Bear) Virgo (Maiden) FIRST MAGNITUDE STARS - First magnitude stars are the 20 brightest stars visible in the night sky from Planet Earth. Hipparchos, introduced the magnitude scale ...
Chapter 26.4
... Constellations Zodiac – “Birthday” Constellations “Move” on the ecliptic line – and can only be seen during certain months. The month of your birthday, you cannot see your zodiac constellation because it is BEHIND the sun. ...
... Constellations Zodiac – “Birthday” Constellations “Move” on the ecliptic line – and can only be seen during certain months. The month of your birthday, you cannot see your zodiac constellation because it is BEHIND the sun. ...
No Slide Title
... Chapter 10: Measuring the Stars Distances to the Stars Parallax: the apparent shift in the position of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one a ...
... Chapter 10: Measuring the Stars Distances to the Stars Parallax: the apparent shift in the position of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one a ...
HR Diagram
... Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram provides a way to group similar stars. The H-R diagram is a gra ...
... Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram provides a way to group similar stars. The H-R diagram is a gra ...
Problem set 2
... As experiments show, on Oct. 1 the sun subtends an angular diameter of 32 arcmin. (a) Calculate the solid angle Ω⊙ subtended by the sun, in steradians. (b) Show that the flux (in W m−2 s−1 or its cgs equivalent) of solar radiation on earth is F = I(T⊙ ) · Ω⊙ with T⊙ = 5777 K, and calculate this valu ...
... As experiments show, on Oct. 1 the sun subtends an angular diameter of 32 arcmin. (a) Calculate the solid angle Ω⊙ subtended by the sun, in steradians. (b) Show that the flux (in W m−2 s−1 or its cgs equivalent) of solar radiation on earth is F = I(T⊙ ) · Ω⊙ with T⊙ = 5777 K, and calculate this valu ...
An introduction to the HR diagram File
... • At the top left of the main sequence the stars have very large radius and high surface temperatures. This is what makes them highly luminous. • They are using up their hydrogen fuel tremendously quickly. So they are extremely short lived (c10 000 000 years) • These high mass stars finish their liv ...
... • At the top left of the main sequence the stars have very large radius and high surface temperatures. This is what makes them highly luminous. • They are using up their hydrogen fuel tremendously quickly. So they are extremely short lived (c10 000 000 years) • These high mass stars finish their liv ...
Chapter 1 Vocabulary – The Puzzled of Matter
... Pulsar – a spinning neutron star that appears to give off strong pulses of radio waves Black Hole – an object whose surface gravity is so great that no even electromagnetic waves can escape from it Constellation – a group of stars that appears to from a pattern as seen from Earth Star System – a gro ...
... Pulsar – a spinning neutron star that appears to give off strong pulses of radio waves Black Hole – an object whose surface gravity is so great that no even electromagnetic waves can escape from it Constellation – a group of stars that appears to from a pattern as seen from Earth Star System – a gro ...
AP Physics - Universal Gravitation
... 106 m, what is the magnitude of the free-fall acceleration on the surface of Roton? A) 31 m/s2 B) 27 m/s2 C) 34 m/s2 D) 40 m/s2 E) 19 m/s2 2. What is the magnitude of the free-fall acceleration at a point that is a distance 2R above the surface of the Earth, where R is the radius of the Earth? A) 4. ...
... 106 m, what is the magnitude of the free-fall acceleration on the surface of Roton? A) 31 m/s2 B) 27 m/s2 C) 34 m/s2 D) 40 m/s2 E) 19 m/s2 2. What is the magnitude of the free-fall acceleration at a point that is a distance 2R above the surface of the Earth, where R is the radius of the Earth? A) 4. ...
PHYSICS 015
... it’s big, yes, but hardly dominant. (Moreover, there are globular star clusters of comparable mass, located here and there in the galaxy.) So our SMBH doesn’t ‘control’ the Milky Way the way the Sun ‘controls’ the planets! There are galaxies in which we find evidence for billionsolar-mass black hole ...
... it’s big, yes, but hardly dominant. (Moreover, there are globular star clusters of comparable mass, located here and there in the galaxy.) So our SMBH doesn’t ‘control’ the Milky Way the way the Sun ‘controls’ the planets! There are galaxies in which we find evidence for billionsolar-mass black hole ...
Red Dwarfs and Barnard`s star. Their origin and significance to
... Barnard’s star. An ancient Red Dwarf. Barnard's Star is a very low-mass red dwarf star about six light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Ophiuchus. Barnard's Star is the fourth-closest known individual star to the Sun, after the three components of the Alpha Centauri system. Despite its ...
... Barnard’s star. An ancient Red Dwarf. Barnard's Star is a very low-mass red dwarf star about six light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Ophiuchus. Barnard's Star is the fourth-closest known individual star to the Sun, after the three components of the Alpha Centauri system. Despite its ...
An Assessment: Think Pair Share
... How does the size of a star near the top left of the H-R diagram compare with a star of the same luminosity near the top right of the H-R diagram? ...
... How does the size of a star near the top left of the H-R diagram compare with a star of the same luminosity near the top right of the H-R diagram? ...
Distances farther out
... Earlier CN break was used to get absolute mag. But now known , some stars (giants by all other criterion) - wrongly called dwarfs on basis on CN alone . (4215 A break was too weak to classify them as giants) . Coz of carbon & Nitrogen abundances, well below solar metal deficient pop II stars in ga ...
... Earlier CN break was used to get absolute mag. But now known , some stars (giants by all other criterion) - wrongly called dwarfs on basis on CN alone . (4215 A break was too weak to classify them as giants) . Coz of carbon & Nitrogen abundances, well below solar metal deficient pop II stars in ga ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... For stars tens of times more massive than the sun, the outer layers of the star explode outwards (supernova: a stellar explosion that occurs at the end of a massive star’s life) After the explosion, the core left behind becomes a neutron star (the gravity of a neutron star is 300000times that of Ear ...
... For stars tens of times more massive than the sun, the outer layers of the star explode outwards (supernova: a stellar explosion that occurs at the end of a massive star’s life) After the explosion, the core left behind becomes a neutron star (the gravity of a neutron star is 300000times that of Ear ...
Unit 10 H-R Diagram Worksheet
... _______________________________________________________________ 9. About how many times brighter than the Sun is Betelgeuse? _________________________________ 10. If Betelgeuse is so bright, why does the Sun appear brighter to us? _____________________________________________________________ 11. Whi ...
... _______________________________________________________________ 9. About how many times brighter than the Sun is Betelgeuse? _________________________________ 10. If Betelgeuse is so bright, why does the Sun appear brighter to us? _____________________________________________________________ 11. Whi ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.























