Distances to the Stars in Leo
... If the distance to the star is known via its measured parallax (as it was discussed in class), it is a somewhat easyl matter for astronomers, or anyone else for that matter, to determine the absolute magnitude of the star using the distance-magnitude relation. However, most stars are too far away to ...
... If the distance to the star is known via its measured parallax (as it was discussed in class), it is a somewhat easyl matter for astronomers, or anyone else for that matter, to determine the absolute magnitude of the star using the distance-magnitude relation. However, most stars are too far away to ...
Lucas - WordPress.com
... Hercules Hercules is named for the famous hero of Greek mythology by the same name. It’s one of the larger constellations, but its stars are of only moderate brightness. The Keystone is a well known trapezoidshaped asterism (association of stars that are not an official constellation) within Hercu ...
... Hercules Hercules is named for the famous hero of Greek mythology by the same name. It’s one of the larger constellations, but its stars are of only moderate brightness. The Keystone is a well known trapezoidshaped asterism (association of stars that are not an official constellation) within Hercu ...
Life Cycle of Stars - Faulkes Telescope Project
... Massive Stars Massive stars burn their fuel very quickly and remain on the main sequence for only a few hundred thousand years, when their fuel runs out they expand into Red Supergiants. If the star is massive enough, the collapse will trigger a violent explosion known as a Supernova (plural Superno ...
... Massive Stars Massive stars burn their fuel very quickly and remain on the main sequence for only a few hundred thousand years, when their fuel runs out they expand into Red Supergiants. If the star is massive enough, the collapse will trigger a violent explosion known as a Supernova (plural Superno ...
Society News - Bristol Astronomical Society
... small telescopes, the primary is a magnitude +2.2 K-class yellow-orange giant, it’s companion is a magnitude +2.5 yellow G-class star. The two stars are separated by 4.4 arcseconds. The rear and tail of the lion is formed by a trio of stars consisting of beta (β) (Denebola), delta (δ) (Zosma) and th ...
... small telescopes, the primary is a magnitude +2.2 K-class yellow-orange giant, it’s companion is a magnitude +2.5 yellow G-class star. The two stars are separated by 4.4 arcseconds. The rear and tail of the lion is formed by a trio of stars consisting of beta (β) (Denebola), delta (δ) (Zosma) and th ...
A Star is a ball of matter that is pulled together by gravity, and that
... •_____________________Magnitude: the amount of ____________ that is actually given off by a star. 4. Measuring the Distance to Stars: we measure the distance between objects in space using ___________. –Parallax is the apparent change in _______________of a star in the sky when viewed from two diffe ...
... •_____________________Magnitude: the amount of ____________ that is actually given off by a star. 4. Measuring the Distance to Stars: we measure the distance between objects in space using ___________. –Parallax is the apparent change in _______________of a star in the sky when viewed from two diffe ...
Great Migrations & other natural history tales
... On the similarities of chemical composition of most pop. I stars Observations show that many stars are surrounded by dust and sometimes detectable gas, in the form of the so-called debris disks or replenished dust disks, originally called Vega-type disks. The Sun has a zodiacal light disk, which is ...
... On the similarities of chemical composition of most pop. I stars Observations show that many stars are surrounded by dust and sometimes detectable gas, in the form of the so-called debris disks or replenished dust disks, originally called Vega-type disks. The Sun has a zodiacal light disk, which is ...
Branches of Earth Science
... White ______________ (size of Earth) Medium Size (the sun) *MOST ______________ * ______________ (10-1000 x’s the sun) o Largest ______________ Giant (1000 x the diameter of the sun) o Belelgeus o Rigel o Antares Composition (______________ Makeup) o Most stars have the ______________ general ...
... White ______________ (size of Earth) Medium Size (the sun) *MOST ______________ * ______________ (10-1000 x’s the sun) o Largest ______________ Giant (1000 x the diameter of the sun) o Belelgeus o Rigel o Antares Composition (______________ Makeup) o Most stars have the ______________ general ...
lecture12
... temperatures of stars on a scale defined by spectral types, called O B A F G K M, ranging from the hottest (type O) to the coolest (type M) stars. ...
... temperatures of stars on a scale defined by spectral types, called O B A F G K M, ranging from the hottest (type O) to the coolest (type M) stars. ...
Lifetimes of stars
... • So based on the extra fuel, you expect this star to live longer than the Sun, but this is more than counteracted by the high rate of using the fuel. This is the general trend. Massive stars are like gas-guzzling SUVs Low-mass stars are Toyota Prius. ...
... • So based on the extra fuel, you expect this star to live longer than the Sun, but this is more than counteracted by the high rate of using the fuel. This is the general trend. Massive stars are like gas-guzzling SUVs Low-mass stars are Toyota Prius. ...
Stellar Evolution: After the Main Sequence
... As a cluster ages, the main sequence is “eaten away” from the upper left as stars of progressively smaller mass evolve into red giants ...
... As a cluster ages, the main sequence is “eaten away” from the upper left as stars of progressively smaller mass evolve into red giants ...
Stars - Mc Guckin Science
... faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Friday, August 28 - Otterbein University
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
The Mass-Luminosity Relationship and Stellar Lifetimes
... • Larger stars will live (1 / Mstar)3 x 1010 years • This equation is good for all stars 0.43 Msun and above. ...
... • Larger stars will live (1 / Mstar)3 x 1010 years • This equation is good for all stars 0.43 Msun and above. ...
The Stars - University of Redlands
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
How to Find the North Star ppt
... Dipper as shown, toward the Little Dipper. The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
... Dipper as shown, toward the Little Dipper. The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
6. 1 Star Distances 6. 2 Apparent Brightness, Intrinsic Brightness
... surface area on stellar luminosity and is commonly plotted as absolute magnitude versus spectral type but also as luminosity versus surface temperature or color. ...
... surface area on stellar luminosity and is commonly plotted as absolute magnitude versus spectral type but also as luminosity versus surface temperature or color. ...
1705 chart front
... The Big Dipper is not officially a constellation; it’s what astronomers sometimes call an asterism. The Big Dipper is a familiar name for this pattern of stars, especially known to observers in the United States, but it’s not one of the 88 constellations recognized by astronomers worldwide. Ursa Maj ...
... The Big Dipper is not officially a constellation; it’s what astronomers sometimes call an asterism. The Big Dipper is a familiar name for this pattern of stars, especially known to observers in the United States, but it’s not one of the 88 constellations recognized by astronomers worldwide. Ursa Maj ...
The Family of Stars
... more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 100 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. Both stars are equally luminous, but the flux received from star A is 5 times less than from star B, so star A ...
... more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 100 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. Both stars are equally luminous, but the flux received from star A is 5 times less than from star B, so star A ...
Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies
... 2. Stellar mass is expressed as multiples of the sun’s mass Betelgeuse’s mass – 20 solar masses F. Temperature and Color 1. Blue stars are hot 2. Red stars are cool G. Luminosity 1. The actual brightness of the star is luminosity 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star w ...
... 2. Stellar mass is expressed as multiples of the sun’s mass Betelgeuse’s mass – 20 solar masses F. Temperature and Color 1. Blue stars are hot 2. Red stars are cool G. Luminosity 1. The actual brightness of the star is luminosity 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star w ...
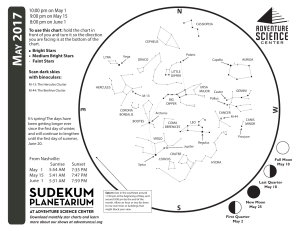
Night Sky Checklist October–November
... Square is high in the south, Alpheratz is the upper left star. Its name comes from an Arabic phrase meaning “navel of the horse,” and reflects a time when Alpheratz was considered as part of Pegasus. Markab is the brightest star in Pegasus and the second brightest star of the Great Square. When the ...
... Square is high in the south, Alpheratz is the upper left star. Its name comes from an Arabic phrase meaning “navel of the horse,” and reflects a time when Alpheratz was considered as part of Pegasus. Markab is the brightest star in Pegasus and the second brightest star of the Great Square. When the ...
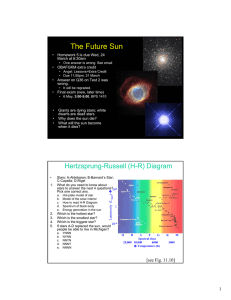
The Future Sun • Homework 5 is due Wed, 24 March at 6:30am
... O star: 30M~; 200,000L~ Lifetime=amount of fuel/consumption rate ...
... O star: 30M~; 200,000L~ Lifetime=amount of fuel/consumption rate ...
www.aavso.org
... The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons falling on is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure many stars at once, as compared to photomultiplier tubes which only measure one star at a time. ...
... The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons falling on is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure many stars at once, as compared to photomultiplier tubes which only measure one star at a time. ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.