The HR Diagram and Stars Worksheet
... 2. Use your book to add the following information to the H-R diagram. a. Page 622 – Add the Spectral Class below the temperatures. b. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to add and label the band that represents Main Sequence stars. c. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to label the following areas: Blue Gia ...
... 2. Use your book to add the following information to the H-R diagram. a. Page 622 – Add the Spectral Class below the temperatures. b. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to add and label the band that represents Main Sequence stars. c. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to label the following areas: Blue Gia ...
Main Sequence Star What is happening in the core? How does the
... Main Sequence Star What is happening in the core? How does the star support itself? ...
... Main Sequence Star What is happening in the core? How does the star support itself? ...
New Braunfels Astronomy Club
... Look for it just west, then southwest of Vega in the first week of May. As May progresses 41P moves into eastern Hercules, about 4-5° east-southeast of omicron (ο) Herculis (in his left hand). If we’re lucky, it will make magnitude 6 or even 5. Either way it should be a nice binocular and telescope ...
... Look for it just west, then southwest of Vega in the first week of May. As May progresses 41P moves into eastern Hercules, about 4-5° east-southeast of omicron (ο) Herculis (in his left hand). If we’re lucky, it will make magnitude 6 or even 5. Either way it should be a nice binocular and telescope ...
stars - allenscience
... The brightness of a star as we see it from Earth is dependent on two things: 1. How big/hot the star is. 2. How far away the star is. ...
... The brightness of a star as we see it from Earth is dependent on two things: 1. How big/hot the star is. 2. How far away the star is. ...
Document
... b. Which star looks most red? GL 725A Most blue? Achernar c. Which star is the most luminous? Canopus Least luminous? GL 725A d. Which star appears the brightest? Canopus Faintest? GL 725A e. Which star’s spectrum shows the strongest Balmer lines of Hydrogen? Vega f. Which star’s spectrum most resem ...
... b. Which star looks most red? GL 725A Most blue? Achernar c. Which star is the most luminous? Canopus Least luminous? GL 725A d. Which star appears the brightest? Canopus Faintest? GL 725A e. Which star’s spectrum shows the strongest Balmer lines of Hydrogen? Vega f. Which star’s spectrum most resem ...
Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics
... KEY: Chemical Composition •Scientists study the star’s _black_ _line _ _spectrum__ to determine what it is made of. Stars vary in their composition, but most are made of _hydrogen___, _helium___, and a small amount of _other_ _elements__. ...
... KEY: Chemical Composition •Scientists study the star’s _black_ _line _ _spectrum__ to determine what it is made of. Stars vary in their composition, but most are made of _hydrogen___, _helium___, and a small amount of _other_ _elements__. ...
Chapter 20 The Universe
... North Star (POLARIS) doesn’t move! TRUE NORTH Others move around it depending on time of day and year. Brightness Apparent magnitude- brightness as it appears from Earth. Depends on 1. how much light is emitted. 2. Distance from Earth Absolute magnitude= luminosity How much light is really emitted. ...
... North Star (POLARIS) doesn’t move! TRUE NORTH Others move around it depending on time of day and year. Brightness Apparent magnitude- brightness as it appears from Earth. Depends on 1. how much light is emitted. 2. Distance from Earth Absolute magnitude= luminosity How much light is really emitted. ...
Can We Make A Star?
... Who Would Make It? • Scientists in many different parts of the world are trying to learn everything they can about stars • They may build a team of scientists who have been studying stars for their entire career • This would take years of training even for them ...
... Who Would Make It? • Scientists in many different parts of the world are trying to learn everything they can about stars • They may build a team of scientists who have been studying stars for their entire career • This would take years of training even for them ...
SAMPLE TEST: Stars and Galaxies Multiple Choice Identify the letter
... 47. The most basic way to measure the distance to a star is ____________________. 48. A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. 49. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ____________________ as it appears from ____________________. 50. Some stars, called _________________ ...
... 47. The most basic way to measure the distance to a star is ____________________. 48. A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. 49. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ____________________ as it appears from ____________________. 50. Some stars, called _________________ ...
Constellations Test Review
... 12. Explain why the stars appear to be moving at night, but in reality they are not. ...
... 12. Explain why the stars appear to be moving at night, but in reality they are not. ...
J tieutifit meti(au.
... est to the earth on October 19th and farthest from it on the governing factor in traction systems for city n�p, North of Andromeda the eye is caught by a zigzag October 7th. but suddenly it was found electricity was destined to rowof stars resembling the letter" W;"these mark the ...
... est to the earth on October 19th and farthest from it on the governing factor in traction systems for city n�p, North of Andromeda the eye is caught by a zigzag October 7th. but suddenly it was found electricity was destined to rowof stars resembling the letter" W;"these mark the ...
The Life Cycle of a Star Webquest:
... 15. What is the scientific name for the twinkling of stars? ___________________________ 16. Why do stars twinkle? ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Why don’t planets twinkle? ________ ...
... 15. What is the scientific name for the twinkling of stars? ___________________________ 16. Why do stars twinkle? ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Why don’t planets twinkle? ________ ...
The Night Sky 12-07
... The bright winter stars are visible setting in the west as total darkness falls about two hours after sunset. Sirius, the well-known brightest star, puts on a show by scintillating rapidly in the heavier air near the horizon. Up in the southwest above Sirius is Procyon, another bright white star. Hi ...
... The bright winter stars are visible setting in the west as total darkness falls about two hours after sunset. Sirius, the well-known brightest star, puts on a show by scintillating rapidly in the heavier air near the horizon. Up in the southwest above Sirius is Procyon, another bright white star. Hi ...
22 October: The Formation of Stars
... • When we see massive main sequence stars (spectral class O), we know they are young. • With fairly simple observations, we can find groups of O and B stars (OB associations) ...
... • When we see massive main sequence stars (spectral class O), we know they are young. • With fairly simple observations, we can find groups of O and B stars (OB associations) ...
Astronomy 360 - indstate.edu
... This is the preferred coordinate system (Equatorial Coordinates) to pinpoint objects on the celestial sphere. Unlike the horizontal coordinate system, equatorial coordinates are independent of the observer's location and the time of the observation. This means that only one set of coordinates is re ...
... This is the preferred coordinate system (Equatorial Coordinates) to pinpoint objects on the celestial sphere. Unlike the horizontal coordinate system, equatorial coordinates are independent of the observer's location and the time of the observation. This means that only one set of coordinates is re ...
Worksheet: Stars and the HR Diagram
... Background: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the br ...
... Background: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the br ...
answers - Salem State University
... larger. In instellar medium (ISM) where there is not sufficient gravity to force the materials of the ISM to contract, the pressure will be lower than in a star or on most planets. 10. There is larger nuclear fusion (more energy and emission) in a high mass due to gravity increasing the pressure and ...
... larger. In instellar medium (ISM) where there is not sufficient gravity to force the materials of the ISM to contract, the pressure will be lower than in a star or on most planets. 10. There is larger nuclear fusion (more energy and emission) in a high mass due to gravity increasing the pressure and ...
PHYS299B_Final_HudsonJustin
... Background Information • An eclipsing binary star is a star that orbits another star, that when one begins to move in front of the other, it blocks the light which is visible from Earth. • 78 Tau is in the Taurus constellation with a brightness magnitude of 3.35-3.41 and a period of 0.07564 days (1. ...
... Background Information • An eclipsing binary star is a star that orbits another star, that when one begins to move in front of the other, it blocks the light which is visible from Earth. • 78 Tau is in the Taurus constellation with a brightness magnitude of 3.35-3.41 and a period of 0.07564 days (1. ...
Homework #2
... 4) Given below is a HR-diagram prepared from data taken by the Hipparcos satellite using 4477 stars whose parallax distance is accurately determined. Consider a main sequence star with color index B-V = 0.65. What would be its absolute magnitude (as accurately as you can read the graph)? If another ...
... 4) Given below is a HR-diagram prepared from data taken by the Hipparcos satellite using 4477 stars whose parallax distance is accurately determined. Consider a main sequence star with color index B-V = 0.65. What would be its absolute magnitude (as accurately as you can read the graph)? If another ...
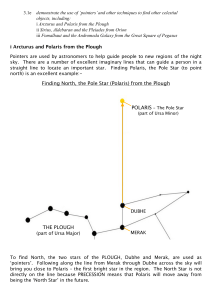
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.