Lab Document - University of Iowa Astronomy and Astrophysics
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
The Lifecycle of Stars
... to document the stages of a star’s lifecycle. Using the paper I provide, you will have to design and ...
... to document the stages of a star’s lifecycle. Using the paper I provide, you will have to design and ...
August Skies
... lopsided house or, if someone insisted that it represent a primate type figure, I’d make it a gnome with a big pointy hat and name him Gulcifer. Given the choices, how would you describe this stellar grouping? ...
... lopsided house or, if someone insisted that it represent a primate type figure, I’d make it a gnome with a big pointy hat and name him Gulcifer. Given the choices, how would you describe this stellar grouping? ...
20 Stars/Distances/Magnitudes
... 3. You see a star in the night sky, and you look up its distance to be 10 parsecs. What would you expect to observe for a parallax angle for this star? ...
... 3. You see a star in the night sky, and you look up its distance to be 10 parsecs. What would you expect to observe for a parallax angle for this star? ...
star brightness
... it would appear over 38 our in times fainter than uld be daytime sky! In fact, it wo in night sky, which is the ma the in n cyo Pro as t as fain g) Do all Canis minoris (The Sm star of the constellation ion of Orion. near the great constellat ary stars, like our Sun, but bin Many stars are not singl ...
... it would appear over 38 our in times fainter than uld be daytime sky! In fact, it wo in night sky, which is the ma the in n cyo Pro as t as fain g) Do all Canis minoris (The Sm star of the constellation ion of Orion. near the great constellat ary stars, like our Sun, but bin Many stars are not singl ...
Astronomy 120
... (b) Regulus and Capella have about the same luminosity. Which star is larger? (c) Vega and Sirius have about the same surface temperature. Which star is more luminous? (d) Which star would appear redder, Vega or Pollux? 5. Zeilik Study Exercise 13.6 What procedure does an astronomer follow to find o ...
... (b) Regulus and Capella have about the same luminosity. Which star is larger? (c) Vega and Sirius have about the same surface temperature. Which star is more luminous? (d) Which star would appear redder, Vega or Pollux? 5. Zeilik Study Exercise 13.6 What procedure does an astronomer follow to find o ...
P10263v1.2 Lab 5 Text
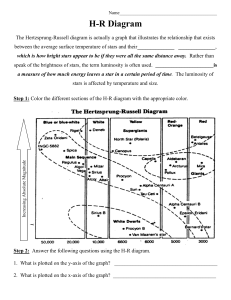
... Sun). This information about the sizes and temperatures of standard stars leads us to the graph on the next page, showing the relationship between color and absolute magnitude for standard stars (the so-called “Main Sequence” stars) like the stars in the Pleiades. Note that “color” in this exercise ...
... Sun). This information about the sizes and temperatures of standard stars leads us to the graph on the next page, showing the relationship between color and absolute magnitude for standard stars (the so-called “Main Sequence” stars) like the stars in the Pleiades. Note that “color” in this exercise ...
STARS- hot glowing sphere of gas that produces energy by
... B) Apparent brightness—brightness as seen from earth 3] Formation of stars A) Nebula (cloud of dust and gas) collapses under its own gravity B) Friction in core causes temperature to reach 10,000,000 c C) fusion begins and a star is born 4] How stars are found A) Loner-by itself (our sun) B) Binary ...
... B) Apparent brightness—brightness as seen from earth 3] Formation of stars A) Nebula (cloud of dust and gas) collapses under its own gravity B) Friction in core causes temperature to reach 10,000,000 c C) fusion begins and a star is born 4] How stars are found A) Loner-by itself (our sun) B) Binary ...
Spring Stargazing - Trimble County Schools
... cup to Capella. This star will help form a pentagon shape. This is Auriga, the Charioteer. Capella is 42 ly away and is 130 times brighter than our sun. • Just beneath Capella is Epsilon Aurigau. It is one of the brightest known stars in the galaxy. It 20,000 times brighter than our sun, but is 2,00 ...
... cup to Capella. This star will help form a pentagon shape. This is Auriga, the Charioteer. Capella is 42 ly away and is 130 times brighter than our sun. • Just beneath Capella is Epsilon Aurigau. It is one of the brightest known stars in the galaxy. It 20,000 times brighter than our sun, but is 2,00 ...
Compare the following sets of stars using the words: BRIGHTER or
... 3. Sirius B (brighter and hotter) and Procyon B (dimmer and cooler) 4. Sun (dimmer and cooler) and Vega (brighter and hotter) 5. Alpha Centauri A (dimmer and cooler) and Canopus (brighter and hotter) 6. Describe the sun’s location on the HR diagram: Along the Main Sequence about average brightness a ...
... 3. Sirius B (brighter and hotter) and Procyon B (dimmer and cooler) 4. Sun (dimmer and cooler) and Vega (brighter and hotter) 5. Alpha Centauri A (dimmer and cooler) and Canopus (brighter and hotter) 6. Describe the sun’s location on the HR diagram: Along the Main Sequence about average brightness a ...
Review 2
... Solar system formation. What is a nebula? What evidence do we have that stars form within dark interstellar clouds? What triggers the collapse of interstellar clouds to form stars? What is a protostar and how does it form? What stops a protostar from growing even more? What are the various types of ...
... Solar system formation. What is a nebula? What evidence do we have that stars form within dark interstellar clouds? What triggers the collapse of interstellar clouds to form stars? What is a protostar and how does it form? What stops a protostar from growing even more? What are the various types of ...
the lab handout here
... A Main Sequence star that is 10,000 times more luminous than the sun, most likely has a temperature of _________________________________________________________________ ...
... A Main Sequence star that is 10,000 times more luminous than the sun, most likely has a temperature of _________________________________________________________________ ...
Stars and Galaxies – Notes
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are doublestar systems in which two stars revolve around each ...
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are doublestar systems in which two stars revolve around each ...
Stars - Madison County Schools
... • Begin their lives as clouds of dust and gas called nebula • Gravity may cause the nebula to contract • Matter in the gas cloud will begin to condense into a dense region called a protostar • The protostar continues to condense, it heats up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and ...
... • Begin their lives as clouds of dust and gas called nebula • Gravity may cause the nebula to contract • Matter in the gas cloud will begin to condense into a dense region called a protostar • The protostar continues to condense, it heats up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and ...
Friday, Oct. 10
... times less light than the Sun does. A star with an absolute magnitude of 0 (that’s 5 magnitudes smaller than the Sun) emits about 2.5x2.5x2.5x2.5x2.5 (or 100) times as much light as the Sun. Remember: smaller magnitudes mean more light. ...
... times less light than the Sun does. A star with an absolute magnitude of 0 (that’s 5 magnitudes smaller than the Sun) emits about 2.5x2.5x2.5x2.5x2.5 (or 100) times as much light as the Sun. Remember: smaller magnitudes mean more light. ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... the size of the star whether it is smaller then our sun, the same size or larger then our sun ...
... the size of the star whether it is smaller then our sun, the same size or larger then our sun ...
Merak
... How Far Away: 62 light years away How Bright: About 50 times brighter than the Sun Where to View: In the constellation Ursa Major. When to View:All year round in the Northern Hemisphere ...
... How Far Away: 62 light years away How Bright: About 50 times brighter than the Sun Where to View: In the constellation Ursa Major. When to View:All year round in the Northern Hemisphere ...
SOLUTIONS ASTROPHYSICS – OPTION D 2015-17
... The question is meaningless within the big bang model since by definition time started with the big bang. It is as meaningless as to ask for a place 1 km north of the north pole. However, recent developments within string theory suggest that the question may not be as meaningless as it appears. See ...
... The question is meaningless within the big bang model since by definition time started with the big bang. It is as meaningless as to ask for a place 1 km north of the north pole. However, recent developments within string theory suggest that the question may not be as meaningless as it appears. See ...
STARS Chapter 8 Section 1
... The inner layers are very dense and hot. But the outer layers are made up of cool gases. Elements in a star’s atmosphere absorb some of the light that radiates from the star. Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, astronomers can tell what elements a star is made of from t ...
... The inner layers are very dense and hot. But the outer layers are made up of cool gases. Elements in a star’s atmosphere absorb some of the light that radiates from the star. Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, astronomers can tell what elements a star is made of from t ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while, WHY? Realize that once our Sun starts to run out of hydrogen fuel and has exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size t ...
... mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while, WHY? Realize that once our Sun starts to run out of hydrogen fuel and has exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size t ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.