* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download galaxies and stars - Valhalla High School
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
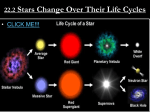
• The Universe Big Bang Theory • According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe formed in an enormous explosion about 10 to 15 billion years ago. • The universe has been expanding ever since. Galaxies • The Milky Way is the galaxy in which our solar system is located. • A galaxy is a giant structure that contains billions of stars. • The farther away a galaxy is from us, the faster it is moving. • It takes 2 million years for light from the Andromeda galaxy to reach earth. • Astronomers have classified most galaxies into three main categories: spiral, elliptical and irregular. Spiral Galaxies Elliptical Galaxies: only old stars Irregular Galaxies Nebula • About five billion years ago a giant cloud of gas and dust, or nebula, collapsed to form the solar system. • Slowly the nebula shrank to form a spinning disk. Star Systems • More than half of all stars are members of groups of two or more stars • Binary systems have two stars • A system where one star blocks the other is an eclipsing binary • A system with three stars is a triple star system Stars • The Milky Way contains hundreds of billions of stars • Distances to stars are measured in light years. • A light year is the distance light travels in one year—9.5 million million kilometers Classifying Stars ¤ All stars are huge spheres of glowing gas ¤ They are made up mostly of hydrogen ¤ They all engage in nuclear fusion ¤ The sun appears brightest because it is closest to Earth ¤ The main characteristics used to classify stars are size, temperature and brightness. Sizes of stars • The sun is a medium size star • Some stars are very large—giants and supergiants • Some stars are smaller than the sun— white dwarf stars, neutron stars • White dwarf stars are the size of Earth and neutron stars are smaller Color and Temperature of Stars • A star’s color reveals its temperature • The coolest stars appear reddish, about 3,200 degrees Celsius • The hottest stars appear bluer than the sun, over 10,000 degrees Celsius • The sun has a surface temperature of about 5,000 degrees Celsius Brightness of Stars • Stars give off different amounts of light. • How bright a star looks from Earth depends on both how far it is and how bright the star actually is. • Brightness is described in two ways: – Apparent magnitude – Absolute magnitude Magnitude • A star’s apparent magnitude is its brightness as seen from Earth • A star looks brighter the closer it is to Earth • A star’s absolute magnitude is the brightness a star would have if it were at a standard distance from Earth. Hertzsprung-Russell diagram The temperatures of stars are on the x axis and the brightness is on the y axis. Most stars are on a diagonal line called the Main Sequence, where surface temperature increases as brightness increases. Giants and supergiants are higher and farther to the right. White dwarfs are hot but not very bright so they are at the bottom center. Life and Death of Stars