Test and answer key - Solar Physics and Space Weather
... The smaller the orbit, the longer it takes for the planet to complete one revolution. The smaller the radius of a planet, the more rapidly it rotates on its axis. *The larger the orbit, the longer it takes for the planet to complete one revolution. The time to complete one revolution of its orbit de ...
... The smaller the orbit, the longer it takes for the planet to complete one revolution. The smaller the radius of a planet, the more rapidly it rotates on its axis. *The larger the orbit, the longer it takes for the planet to complete one revolution. The time to complete one revolution of its orbit de ...
Maya .(English)
... Maya astronomy Maya were skilled observers of the sky: they calculated the complex motions of the Sun, the stars and planets and recorded this information in their codices (“Dresden Codex”). From this information, they developed calendars to Keep track of celestial movements: their solar calendar w ...
... Maya astronomy Maya were skilled observers of the sky: they calculated the complex motions of the Sun, the stars and planets and recorded this information in their codices (“Dresden Codex”). From this information, they developed calendars to Keep track of celestial movements: their solar calendar w ...
Earth Science Library wk 2 (WP)
... But if the planets are not connected to anything. What drives their motions? ...
... But if the planets are not connected to anything. What drives their motions? ...
March 2013 - Joliet Junior College
... Jupiter is the only major planet visible in the evening sky during March. Saturn is working its way into the evening sky, but the change of time pushes back Saturn’s rising time until 11 pm. By the end of March, Saturn will be rising at 9:30. Venus and Mars are too close to the sun to be observed. V ...
... Jupiter is the only major planet visible in the evening sky during March. Saturn is working its way into the evening sky, but the change of time pushes back Saturn’s rising time until 11 pm. By the end of March, Saturn will be rising at 9:30. Venus and Mars are too close to the sun to be observed. V ...
May 2009 Tz 2
... Observations of the night sky indicate that there are many regions of the universe that do not contain any stars. ...
... Observations of the night sky indicate that there are many regions of the universe that do not contain any stars. ...
Blue Marble in Empty Space
... diameter fits more than 100 times in the Sun’s, and more than 100 Suns fit in the distance Earth-Sun.) Astronomers call this distance an astronomical unit. In the distance to our neighbouring planets Venus and Mars fit respectively 3,300 and 6,100 Earths. And that is when the planets are closest to ...
... diameter fits more than 100 times in the Sun’s, and more than 100 Suns fit in the distance Earth-Sun.) Astronomers call this distance an astronomical unit. In the distance to our neighbouring planets Venus and Mars fit respectively 3,300 and 6,100 Earths. And that is when the planets are closest to ...
Contents
... The “missing solar neutrinos” problem was real Contributions from Canadian and Japanese scientists Efficiency of the proton-proton chain reactions ...
... The “missing solar neutrinos” problem was real Contributions from Canadian and Japanese scientists Efficiency of the proton-proton chain reactions ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... 44. What causes the phases of the moon, eclipses, and tides? As the moon revolves around the earth, we see different portions of the sunlight side causing moon phases. At certain times of the year, the sun, moon, and Earth align in the same plane during a new or full moon causing an eclipse. Tides a ...
... 44. What causes the phases of the moon, eclipses, and tides? As the moon revolves around the earth, we see different portions of the sunlight side causing moon phases. At certain times of the year, the sun, moon, and Earth align in the same plane during a new or full moon causing an eclipse. Tides a ...
Chapter 6 The Archean Eon of Precambrian Time I. Introduction
... ii. temporarily lost by being incorporated into hydrous clay minerals that settle to the ocean floors, but returned water to the surface in the course of volcanic eruptions VI. When the World was Young - The Hadean The Hadean marks an interval of time when the Earth was constantly bombarded by large ...
... ii. temporarily lost by being incorporated into hydrous clay minerals that settle to the ocean floors, but returned water to the surface in the course of volcanic eruptions VI. When the World was Young - The Hadean The Hadean marks an interval of time when the Earth was constantly bombarded by large ...
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 3 Review
... 3. Other bodies, such as the Earth, also experience impacts, but are somewhat more protected by their atmospheres. If these bodies are active as well, these craters can be resurfaced. 4. Unlike the Moon, however, Mercury has a rather large iron core and is much denser. • Why is Mercury’s orbit aroun ...
... 3. Other bodies, such as the Earth, also experience impacts, but are somewhat more protected by their atmospheres. If these bodies are active as well, these craters can be resurfaced. 4. Unlike the Moon, however, Mercury has a rather large iron core and is much denser. • Why is Mercury’s orbit aroun ...
AST 207 Test 2 Answers 20 October 2010
... Newton showed that Kepler’s Laws apply for the case of an object orbiting an object with a much larger mass. Therefore Kepler’s1st law applies. A star orbits the black body in an ellipse with the black hole at one focus. b. (3 pts.) A star has been observed to orbit at a distance of 100AU. How long ...
... Newton showed that Kepler’s Laws apply for the case of an object orbiting an object with a much larger mass. Therefore Kepler’s1st law applies. A star orbits the black body in an ellipse with the black hole at one focus. b. (3 pts.) A star has been observed to orbit at a distance of 100AU. How long ...
PPT
... 3. The Square of a Planet’s Period (P in Years) Equals the Cube of the Semi-Major Axis of its Orbit (A in AU) ...
... 3. The Square of a Planet’s Period (P in Years) Equals the Cube of the Semi-Major Axis of its Orbit (A in AU) ...
Black Holes and General Relativity
... GPS satellites use atomic clocks. Position determined by timing radio signals. In orbit Fg = ¼ Fg at Earth surface. Clock on satellite runs fast by 45 msec per day. D=vt D=ct DD = cDt DD = 3 x 105 km/s * 45 x 10-6 s/day DD = 13.5 km/day ...
... GPS satellites use atomic clocks. Position determined by timing radio signals. In orbit Fg = ¼ Fg at Earth surface. Clock on satellite runs fast by 45 msec per day. D=vt D=ct DD = cDt DD = 3 x 105 km/s * 45 x 10-6 s/day DD = 13.5 km/day ...
Galileo`s Motion, Newton`s Gravity
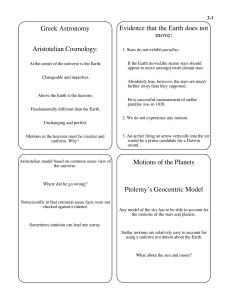
... about why planets orbited stars • Philosophical arguments only • Newton’s Realization – To understand the motion of the planets, it is first necessary to understand motion! ...
... about why planets orbited stars • Philosophical arguments only • Newton’s Realization – To understand the motion of the planets, it is first necessary to understand motion! ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy - University of Texas Astronomy
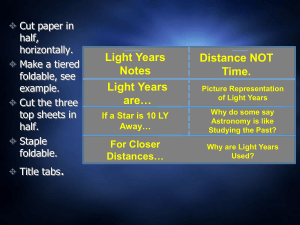
... You judge the distance to objects (depth perception) from the fact that your two eyes view an object from two different locations, so have to look in different directions to look at an object. The different direction to an object from different positions is called parallax. Astronomers use the chang ...
... You judge the distance to objects (depth perception) from the fact that your two eyes view an object from two different locations, so have to look in different directions to look at an object. The different direction to an object from different positions is called parallax. Astronomers use the chang ...
Chapter 4 Chapter 4 - The Solar System The Solar System
... Chapter 4 - The Solar System • 1 star • 9 8 planets • 63 moons • asteroids, comets, meteoroids ...
... Chapter 4 - The Solar System • 1 star • 9 8 planets • 63 moons • asteroids, comets, meteoroids ...
WhatsInSolarSystem - School
... Planets and Dwarf Planets Planets According to the International Astronomical Union a planet is an object which: 1. Is in orbit around the Sun 2. Has a mass big enough so that its gravity pulls it into a nearly round shape 3. Has "cleared the neighbourhood" around its orbit. Dwarf Planets As telesco ...
... Planets and Dwarf Planets Planets According to the International Astronomical Union a planet is an object which: 1. Is in orbit around the Sun 2. Has a mass big enough so that its gravity pulls it into a nearly round shape 3. Has "cleared the neighbourhood" around its orbit. Dwarf Planets As telesco ...
Celestial Motions - Georgia State University
... about planetary motion in our sky? • Planets usually move slightly eastward from night to night relative to the stars. • But sometimes they go westward relative to the stars for a few weeks: apparent retrograde motion ...
... about planetary motion in our sky? • Planets usually move slightly eastward from night to night relative to the stars. • But sometimes they go westward relative to the stars for a few weeks: apparent retrograde motion ...
mean solar day
... •The position of the extended Earth rotation axis into the sky •The North direction can be found by drawing a line straight down to the horizon ...
... •The position of the extended Earth rotation axis into the sky •The North direction can be found by drawing a line straight down to the horizon ...