SDO | SOLAR DYNAMICS OBSERVATORY HTTP://WWW.NASA
... star, with the numerals from I down to VII. Why do we need to know these things? Well, temperature can tell you about a star’s mass, length of life, brightness and even how its life might end. How do we know what stars are made of or what their future holds? Sixty Symbols explains it best. ...
... star, with the numerals from I down to VII. Why do we need to know these things? Well, temperature can tell you about a star’s mass, length of life, brightness and even how its life might end. How do we know what stars are made of or what their future holds? Sixty Symbols explains it best. ...
Natural Climate Variability
... • These oscillations, from more elliptic to less elliptic, are of prime importance to glaciation • The oscillation alters the distance from the Earth to the Sun, thus changing the distance the Sun's short wave radiation must travel to reach Earth • This reduces or increases the amount of radiation r ...
... • These oscillations, from more elliptic to less elliptic, are of prime importance to glaciation • The oscillation alters the distance from the Earth to the Sun, thus changing the distance the Sun's short wave radiation must travel to reach Earth • This reduces or increases the amount of radiation r ...
Telling Time by the Sun - Cornell Astronomy
... 1. The Earth rotates on its axis once every ~24 hours (day). 2. The Earth revolves around the Sun once every ~365 days (year). 3. The Moon revolves around the Earth once every ~28 days (month). 4. The orbital planes of objects in the Solar System lie (almost) in the equatorial planes of the major bo ...
... 1. The Earth rotates on its axis once every ~24 hours (day). 2. The Earth revolves around the Sun once every ~365 days (year). 3. The Moon revolves around the Earth once every ~28 days (month). 4. The orbital planes of objects in the Solar System lie (almost) in the equatorial planes of the major bo ...
Document
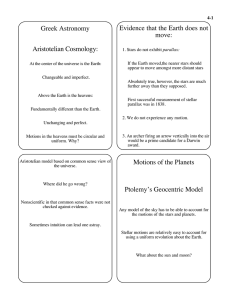
... Plato (c. 350 B.C.) suggested the need for a framework (e.g. stars revolve around the Earth which is fixed) “Geocentric Universe”: fixed relationship between stars Ptolemy (c. 100 A.D.) refined the system introduced (most notably) by Hipparchus to explain the observed motions of the stars and planet ...
... Plato (c. 350 B.C.) suggested the need for a framework (e.g. stars revolve around the Earth which is fixed) “Geocentric Universe”: fixed relationship between stars Ptolemy (c. 100 A.D.) refined the system introduced (most notably) by Hipparchus to explain the observed motions of the stars and planet ...
Solutions
... 17) Why does the atmosphere of Saturn have a much lower amount of Helium than we expect it to have because of solar abundances? a) Saturn is not big enough to collect and hold onto Helium b) Saturn’s Helium rains into the core c) the Helium has been changed into other elements d) TRICK! Saturn has ...
... 17) Why does the atmosphere of Saturn have a much lower amount of Helium than we expect it to have because of solar abundances? a) Saturn is not big enough to collect and hold onto Helium b) Saturn’s Helium rains into the core c) the Helium has been changed into other elements d) TRICK! Saturn has ...
Doppler Effect - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... The experimenters had to take into account the relative movement of the Earth and Moon when tuning the receiver. The maximum difference between the frequency of the detected and transmitted waves was 300 Hz. What is the name of this effect? ...
... The experimenters had to take into account the relative movement of the Earth and Moon when tuning the receiver. The maximum difference between the frequency of the detected and transmitted waves was 300 Hz. What is the name of this effect? ...
Astr40 HWII - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... B. hot portions of gas rising to the surface, and cool ones falling. C. heat transfer by contact of molecules. 32. The reason for the low number of detections of which solar particle (at earth) was under dispute for a long time? A. gamma rays B. electrons C. neutrinos 33. The apparent brightness of ...
... B. hot portions of gas rising to the surface, and cool ones falling. C. heat transfer by contact of molecules. 32. The reason for the low number of detections of which solar particle (at earth) was under dispute for a long time? A. gamma rays B. electrons C. neutrinos 33. The apparent brightness of ...
05Sky1.ppt - NMSU Astronomy
... http://www.astrosociety.org/education/resources/pseudobib. html#1 ...
... http://www.astrosociety.org/education/resources/pseudobib. html#1 ...
Star Study Guide Chapter 21 Test
... Measuring distances to stars How to Measure PARALLAX: the ...
... Measuring distances to stars How to Measure PARALLAX: the ...
The Milky Way - Computer Science Technology
... They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. ...
... They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. ...
Chapter 2 User`s Guide to the Sky
... They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. ...
... They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. ...
Astronomy Review
... The phases of the Moon depend on the positions of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. Phases of the Moon – New Moon:the entire half/side of the Moon facing the Earth is dark – Quarter Moon:half of the side of the Moon facing Earth is lighted and the other half is dark; the Moon appears as a half-circle; there ...
... The phases of the Moon depend on the positions of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. Phases of the Moon – New Moon:the entire half/side of the Moon facing the Earth is dark – Quarter Moon:half of the side of the Moon facing Earth is lighted and the other half is dark; the Moon appears as a half-circle; there ...
hubble amazing universe worksheet
... 9. Hubble even showed a star about to die! As a star runs out of ______________, it expands, and it is released into space. 10. Someday, our own star will expand and engulf the earth. Luckily, this will happen in ________________billion years. 11. Some stars are 100 times more massive that our sun. ...
... 9. Hubble even showed a star about to die! As a star runs out of ______________, it expands, and it is released into space. 10. Someday, our own star will expand and engulf the earth. Luckily, this will happen in ________________billion years. 11. Some stars are 100 times more massive that our sun. ...
Unit 5: Space Exploration Topic 1: Our Eyes Only • Define FRAME
... objective lens. • How does a REFRACTING TELESCOPE differ from a REFLECTING TELESCOPE? Which provides a better image? Refracting telescopes have a lens for their objectives and reflecting telescopes have objective mirrors. Refractors five better images than equal-size reflectors, but reflectors can b ...
... objective lens. • How does a REFRACTING TELESCOPE differ from a REFLECTING TELESCOPE? Which provides a better image? Refracting telescopes have a lens for their objectives and reflecting telescopes have objective mirrors. Refractors five better images than equal-size reflectors, but reflectors can b ...
History of astronomy
... The accuracy of Tycho's best positional measurements was +/- 1 arc minute. This was an improvement of a factor of 10 over previous observations. If the stars were closer than 3438 Astronomical Units, Tycho should have been able to measure their trigonometric parallaxes. But he found no parallax for ...
... The accuracy of Tycho's best positional measurements was +/- 1 arc minute. This was an improvement of a factor of 10 over previous observations. If the stars were closer than 3438 Astronomical Units, Tycho should have been able to measure their trigonometric parallaxes. But he found no parallax for ...
Space ppt
... scientific models (geocentric, heliocentric) as they describe our solar system, and the Big Bang as it describes the formation of the universe. b. Describe the position of the solar system in the Milky Way galaxy and the universe ...
... scientific models (geocentric, heliocentric) as they describe our solar system, and the Big Bang as it describes the formation of the universe. b. Describe the position of the solar system in the Milky Way galaxy and the universe ...
UCSB CLAS
... A planet (P) is moving around the Sun (S) in an elliptical orbit. As the planet moves from aphelion to perihelion, the Sun’s gravitational force A. does positive work on the planet. B. does negative work on the planet. C. does positive work on the planet during part of the motion and negative work d ...
... A planet (P) is moving around the Sun (S) in an elliptical orbit. As the planet moves from aphelion to perihelion, the Sun’s gravitational force A. does positive work on the planet. B. does negative work on the planet. C. does positive work on the planet during part of the motion and negative work d ...
Units And Measurements
... A system of units is the complete set, of units, both fundamental and derived, for all kinds of physical quantities. Each system is named in terms of fundamental units on which it is based. The common systems, of units used in mechanics are given below: (a) The FPS system is the British Engineering ...
... A system of units is the complete set, of units, both fundamental and derived, for all kinds of physical quantities. Each system is named in terms of fundamental units on which it is based. The common systems, of units used in mechanics are given below: (a) The FPS system is the British Engineering ...
Goal: To understand how Saturn formed and what its core is like
... • Some objects were tossed into enormously large orbits by the gas giants (cough – Jupiter – cough). • These orbits can go out as far as a light year. • This is the source of long period comets. ...
... • Some objects were tossed into enormously large orbits by the gas giants (cough – Jupiter – cough). • These orbits can go out as far as a light year. • This is the source of long period comets. ...
Astronomy Library wk 4 .cwk (WP)
... But what about the Sun, Venus, and Mercury which all move together and orbit in one year? ...
... But what about the Sun, Venus, and Mercury which all move together and orbit in one year? ...
Boy Scout Astronomy Merit Badge Workbook
... 5. Do the following: a. List the names of the five most visible planets. Explain which ones can appear in phases similar to lunar phases and which ones cannot, and explain why. b. Find out when each of the five most visible planets that you identified in requirement 5a will be observable in the even ...
... 5. Do the following: a. List the names of the five most visible planets. Explain which ones can appear in phases similar to lunar phases and which ones cannot, and explain why. b. Find out when each of the five most visible planets that you identified in requirement 5a will be observable in the even ...
Western Civilizations Chapter 17
... ◦ Thought universe could be divided into 2 parts: the mind and the body ◦ This is called Cartesian Dualism ◦ Believed rigorous reasoning by an individual could discover the truth about nature and then use these truths to help satisfy human needs ◦ Descartes found himself in dispute with medieval tho ...
... ◦ Thought universe could be divided into 2 parts: the mind and the body ◦ This is called Cartesian Dualism ◦ Believed rigorous reasoning by an individual could discover the truth about nature and then use these truths to help satisfy human needs ◦ Descartes found himself in dispute with medieval tho ...