SOLAR ECLIPSES
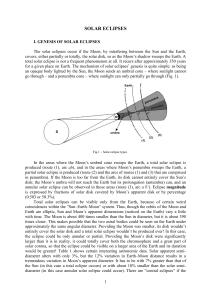
... is expressed by fractions of solar disk covered by Moon’s apparent disk or by percentage (0.503 or 50.3%). Total solar eclipses can be visible only from the Earth, because of certain weird coincidences within the ”Sun–Earth–Moon“ system. Thus, though the orbits of the Moon and Earth are elliptic, Su ...
... is expressed by fractions of solar disk covered by Moon’s apparent disk or by percentage (0.503 or 50.3%). Total solar eclipses can be visible only from the Earth, because of certain weird coincidences within the ”Sun–Earth–Moon“ system. Thus, though the orbits of the Moon and Earth are elliptic, Su ...
AY1 Homework for Quiz 2: Spring 2017
... 9. “Hydrostatic” models for the Sun or other stars are based on (check any that are correct): ____ A. Gas pressure compressing stars to the point just before they become liquid ____ B. Balancing the fo ...
... 9. “Hydrostatic” models for the Sun or other stars are based on (check any that are correct): ____ A. Gas pressure compressing stars to the point just before they become liquid ____ B. Balancing the fo ...
Comets, Asteroids, and Meteors
... Asteroids • Not all asteroids are located in the asteroids belt and can pass near Earth • Jupiter’s gravity kept the asteroids from forming a planet • Some asteroids orbit just before and after Jupiter • Largest asteroid, Ceres, is 580 mi across but most are less than a few miles across ...
... Asteroids • Not all asteroids are located in the asteroids belt and can pass near Earth • Jupiter’s gravity kept the asteroids from forming a planet • Some asteroids orbit just before and after Jupiter • Largest asteroid, Ceres, is 580 mi across but most are less than a few miles across ...
The celestial sphere, the coordinates system, seasons, phases of
... total of 7,000 km. An observer located inside this strip will see a total solar eclipse. Partial solar eclipse: If the observer is located in the penumbral part of the shadow, only part of the Sun will be covered and the observer will see a partial solar eclipse Annular solar eclipse: If the Moon is ...
... total of 7,000 km. An observer located inside this strip will see a total solar eclipse. Partial solar eclipse: If the observer is located in the penumbral part of the shadow, only part of the Sun will be covered and the observer will see a partial solar eclipse Annular solar eclipse: If the Moon is ...
Title of PAPER - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... absorbed by a planet may be re-emitted, from the night-side, as the body rotates. Satellites can be located at specific orbits, such as the L1 point where the satellite will be constantly between the planet and the Sun, or the L2 point whereby the satellite will be perpetually located behind the pla ...
... absorbed by a planet may be re-emitted, from the night-side, as the body rotates. Satellites can be located at specific orbits, such as the L1 point where the satellite will be constantly between the planet and the Sun, or the L2 point whereby the satellite will be perpetually located behind the pla ...
6.6 Relative Positions and Motion of the Earth, Moon and Sun
... The gravity of the Moon, the pull which it exerts on the Earth, causes two high tides on the Earth every day – one every 12 hours and 25 minutes. The Moon is much smaller than the Earth, with a diameter of 2159 miles, or 3476 kilometres. It is airless, waterless and lifeless. If the moon didn't spin ...
... The gravity of the Moon, the pull which it exerts on the Earth, causes two high tides on the Earth every day – one every 12 hours and 25 minutes. The Moon is much smaller than the Earth, with a diameter of 2159 miles, or 3476 kilometres. It is airless, waterless and lifeless. If the moon didn't spin ...
ASTR-100 - Jiri Brezina Teaching
... March), it marks the beginning of spring, and the autumnal equinox is the place where it crosses moving southward (about 21 Sep.), it marks the beginning of fall. The sun is farthest north at the point called the summer solstice about 21 June, (the longest day, beginning of summer on the North Hemis ...
... March), it marks the beginning of spring, and the autumnal equinox is the place where it crosses moving southward (about 21 Sep.), it marks the beginning of fall. The sun is farthest north at the point called the summer solstice about 21 June, (the longest day, beginning of summer on the North Hemis ...
Astronomy 1400: Homework 5
... the diffraction limit from the book in Math Insight 6.2 that already did the unit conversions for you to give the answer in arcseconds (the constant is 2.5 × 105′′ instead of 1.22 in the formula above), but then you would have had to calculate the answer to part a) in arcseconds. The important part ...
... the diffraction limit from the book in Math Insight 6.2 that already did the unit conversions for you to give the answer in arcseconds (the constant is 2.5 × 105′′ instead of 1.22 in the formula above), but then you would have had to calculate the answer to part a) in arcseconds. The important part ...
physics class 11 chapter 2 ncert
... The air inside this room contains a large number of molecules as compared to that present in a geometry box. A proton is more massive than an electron. Speed of sound is less than the speed of light. Question 2.5: A new unit of length is chosen such that the speed of light in vacuum is unity. What i ...
... The air inside this room contains a large number of molecules as compared to that present in a geometry box. A proton is more massive than an electron. Speed of sound is less than the speed of light. Question 2.5: A new unit of length is chosen such that the speed of light in vacuum is unity. What i ...
Student Activity DOC - TI Education
... distance from the Sun. Orbital radius can be measured in units of kilometers or AU (Astronomical Units). Earth has an orbital radius of 1 AU. This means that Earth, is approximately 1 AU, or 150 million kilometers, away from the Sun on average. Other characteristics of celestial bodies include the d ...
... distance from the Sun. Orbital radius can be measured in units of kilometers or AU (Astronomical Units). Earth has an orbital radius of 1 AU. This means that Earth, is approximately 1 AU, or 150 million kilometers, away from the Sun on average. Other characteristics of celestial bodies include the d ...
Student Activity PDF - TI Education
... distance from the Sun. Orbital radius can be measured in units of kilometers or AU (Astronomical Units). Earth has an orbital radius of 1 AU. This means that Earth, is approximately 1 AU, or 150 million kilometers, away from the Sun on average. Other characteristics of celestial bodies include the d ...
... distance from the Sun. Orbital radius can be measured in units of kilometers or AU (Astronomical Units). Earth has an orbital radius of 1 AU. This means that Earth, is approximately 1 AU, or 150 million kilometers, away from the Sun on average. Other characteristics of celestial bodies include the d ...
Planet Hunters
... of several hundred worlds, but astronomers have never given up the combined efforts of many hard-working scientists and brilliant young dream of seeing such worlds directly. Such observations would let planet hunters. Maybe they’ll even be answered by some of you! i us find new planets with a single ...
... of several hundred worlds, but astronomers have never given up the combined efforts of many hard-working scientists and brilliant young dream of seeing such worlds directly. Such observations would let planet hunters. Maybe they’ll even be answered by some of you! i us find new planets with a single ...
13 The Family of Stars
... angle in Alexandria. By measuring the angle θ and the distance b between the cities he calculated the radius r = b/θ. ...
... angle in Alexandria. By measuring the angle θ and the distance b between the cities he calculated the radius r = b/θ. ...
EXERCISES: Set 2 of 4 Q1: The absolute magnitude of the Sun in
... (a) At what distances would: (i) a star like the Sun, (ii) a globular cluster, (iii) a galaxy like the Milky Way be as bright as the background sky? You can assume that in all three cases the distances involved are sufficiently large that the astronomical sources in question can be safely considered ...
... (a) At what distances would: (i) a star like the Sun, (ii) a globular cluster, (iii) a galaxy like the Milky Way be as bright as the background sky? You can assume that in all three cases the distances involved are sufficiently large that the astronomical sources in question can be safely considered ...
6 Minute English
... Neil So the main gas is hydrogen, which accounts for 90% of the sun’s matter. Now, 'matter' means what something is made of. Rob And hydrogen creates all the sun’s energy. Heat and light energy is created all the time in the sun’s core as a result of gas explosions or nuclear reactions. And this bit ...
... Neil So the main gas is hydrogen, which accounts for 90% of the sun’s matter. Now, 'matter' means what something is made of. Rob And hydrogen creates all the sun’s energy. Heat and light energy is created all the time in the sun’s core as a result of gas explosions or nuclear reactions. And this bit ...
Your Place in Space and Time
... 100 billion stars — so many stars that it would take thousands of years just to count them out loud. ...
... 100 billion stars — so many stars that it would take thousands of years just to count them out loud. ...
Sample
... Arcminutes and arcseconds are subdivisions of degrees. There are 60 arcminutes in 1 degree, and there are 60 arcseconds in 1 arcminute. Circumpolar stars are stars that never appear to rise or set from a given location, but are always visible on any clear night. From the North Pole, every visible st ...
... Arcminutes and arcseconds are subdivisions of degrees. There are 60 arcminutes in 1 degree, and there are 60 arcseconds in 1 arcminute. Circumpolar stars are stars that never appear to rise or set from a given location, but are always visible on any clear night. From the North Pole, every visible st ...
File - We All Love Science
... – Uranus tilts almost to orbital plane – Venus tilts so much it spins “backwards” • Retrograde, but orbits with other planets ...
... – Uranus tilts almost to orbital plane – Venus tilts so much it spins “backwards” • Retrograde, but orbits with other planets ...
Electromagnetic Waves - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... particular “medium”—a kind of matter. The so-called “speed of light” is the speed of any electromagnetic wave in a vacuum, without interference with matter. That speed is very fast, about 300,000 kilometers per second. This constant speed allows scientists to use light to measure distance. See Tutor ...
... particular “medium”—a kind of matter. The so-called “speed of light” is the speed of any electromagnetic wave in a vacuum, without interference with matter. That speed is very fast, about 300,000 kilometers per second. This constant speed allows scientists to use light to measure distance. See Tutor ...
Lecture 14+15 - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... (Period P in years)2 = (Semi-major aixs a in AU) 3 planet moves slower when it is farther from Sun can use observed Period P infer a, and hence mean orbital speed in km/s ...
... (Period P in years)2 = (Semi-major aixs a in AU) 3 planet moves slower when it is farther from Sun can use observed Period P infer a, and hence mean orbital speed in km/s ...
Astronomy
... orbits of stars. One example of this was found at Building J at Monte Alban, it was constructed in an arrow shape, so that the five brightest stars of that time would set at the point of the arrow. A line drawn perpendicular to the front steps on the building showed that it would point directly to t ...
... orbits of stars. One example of this was found at Building J at Monte Alban, it was constructed in an arrow shape, so that the five brightest stars of that time would set at the point of the arrow. A line drawn perpendicular to the front steps on the building showed that it would point directly to t ...
ppt
... Analysing spectra gave rise to the subject of Astrophysics. Previously astronomy was just about categorising objects based on their appearance (morphology). But by studying their spectra, we can use physical models to understand their nature. Many of these astronomical objects just appear as dots in ...
... Analysing spectra gave rise to the subject of Astrophysics. Previously astronomy was just about categorising objects based on their appearance (morphology). But by studying their spectra, we can use physical models to understand their nature. Many of these astronomical objects just appear as dots in ...
Semester 2 Course Review
... How has the model of our Solar System changed over time? Why? How does this change in Solar System models demonstrate the scientific process? How are planetary systems formed? Why are planets closer to the sun made of different substances than planets farther from the sun? Why do some planets appear ...
... How has the model of our Solar System changed over time? Why? How does this change in Solar System models demonstrate the scientific process? How are planetary systems formed? Why are planets closer to the sun made of different substances than planets farther from the sun? Why do some planets appear ...























